Python API Reference¶
- Release
13.2.2
Classes:
|
Exception class thrown by the Artelys Kalis library. |
|
Utility class for text console managment |
A contradiction is a c++ exception thrown whenever kalis deduce that the problem is inconsistent (i.e it has no solution) |
|
|
This class implements a generic class for propagation of any binary constraint by local 2-consistency (arc consistency) Two algorithms (AC3 and AC2001) are available for propagation of the constraint. |
|
This class implements a generic class for propagation of any binary constraint by local 2-consistency (arc consistency). |
|
This class creates a X = abs(Y) constraint |
An OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with any type of KNumVar objective, which use an absolute difference criteria. |
|
|
This class creates a X1 <> X2 <> . |
|
Assign And Forbid branching scheme |
|
AssignVar Branching scheme |
|
This class represents an auxiliary variable to use in relaxations. |
|
Value selector that selects the value of a variable that implies the best bound for the objective. |
|
This class represent an expression of the form X (+ , -) Y + cste where X and Y are variables and cste an integer constant. |
|
Abstract class defining branching schemes. |
This class implements an array of KBranchingScheme |
|
|
A branching scheme group represents a list of branching schemes to use nested branching schemes. |
List of brancing scheme group. |
|
Selection object to choose among a list of branching scheme group. |
|
A nested branching scheme. |
|
|
Linear relaxation solver for Clp |
|
This linear relaxation solver relies on CoinMP to solve the LP/MIP problem. |
|
Conditionnal numeric linear combination constraint. |
|
This class creates a Binary conjunction on two constraints C1 and C2. |
|
This class is an abstract interface for all constraints in Artelys Kalis |
|
This class implements an array of KConstraint |
This constraint states that some tasks requiring a resource do not exceed the resource capacity. |
|
A time-dependant resource usage constraint. |
|
|
The cycle constraint ensures that the graph implicitly represented by a set of variables and their domain contains no sub-tours (tour visiting a partial number of nodes). |
|
Discrete resource |
|
This class creates a Binary disjunction on two constraints C1 or C2 |
This class implements an array of KDisjunction |
|
|
This class implements a disjunction selector that selects the disjunction in the input order. |
|
This class implements a disjunction selector that selects first the disjunction ith the highest priority |
|
Abstract interface class for disjunction selection heuristic Since: 2016.1 |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) == C constraint |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) >= C constraint |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) <= C constraint |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) != C constraint |
This class implements an array of doubles |
|
|
This class creates a x == tab[i + cste] constraint |
|
This class creates a X == Tab[I + cste1][J + cste2] constraint |
|
This class represent an expression of type Tab[I] where Tab is an array of integer value and I is the indexing variable |
|
This class represent an expression of type Tab[I+a][J+b] where Tab is an array of integer value; I,J are the indexing variable and a and b indexing offsets |
|
This class creates a X == C constraint. |
|
This class creates a X == Y + C constraint. |
|
This class creates an Equivalence on two constraints C1 <==> C2. |
|
This class implements a variable with continuous real valued domain. |
|
This branching scheme is suited for branching on KFloatVar objects. |
|
Float variable selector |
This class implements a generic class for propagation of any nary constraint by forward checking/arc consistency or generalized arc consistency |
|
This class implements a generic class for propagation of any n-ary constraint by generalized arc consistency |
|
|
This class implements a Global Cardinality Constraint. |
|
This class creates a X >= C constraint. |
|
This class creates a X >= Y + C constraint |
|
This class creates an implication on two constraints C1 ==> C2 |
|
This class represents a solution of a relaxation solver, that is, a mapping from variables (KNumVar and/or KAuxVar) to their value. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable in the input order. |
|
This class implements an array of integers |
|
This class implements an matrix of integers |
|
This class implements an integer variable with enumerated (finite) domain. |
|
This class implements an array of KIntVar with enumerated (finite) domains |
|
Abstract class for Branching scheme. |
|
This class implements an matrix of KIntVar |
|
An OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with integer objective only. |
|
Branching scheme for splitting float variables into a set of intervals. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the smallest domain. |
|
Largest domain duration task selection heuristic |
Largest Earliest Completion time task selection heuristic |
|
|
Largest Earliest Start time task selection heuristic |
|
Largest Latest Completion time task selection heuristic |
|
Largest Latest Start time task selection heuristic |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the largest upperbound in its domain. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the largest lower bound. |
|
This variable selector selects the variable with biggest reduced cost in current LP solution of the provided linear relaxation solver. |
|
This class creates a X <= C constraint. |
|
This class creates a Sum(ai.Xi) { <= , != , == } C constraint |
|
This class represents a linear relation (equality or inequality) between variables. |
|
This class represent a linear term of the form Sum(coeffs[i].lvars[i]) + cst |
|
This class represents a linear relaxation of a domain. |
|
This class is intended as a superclass for linear relaxation solvers. |
|
This class creates a vMax = max(X1,X2,…,Xn) constraint |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable involved in the maximum number of constraints. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with maximum regret on its lowerbound. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with maximum regret on its upperbound. |
|
This class implements a value selector that returns values in decreasing order. |
|
This class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from the middle value in the domain of the variable. |
|
This class creates a vMin = min(X1,X2,…,Xn) constraint |
|
Value selector that selects the value of a variable that implies the best problem size reduction when instantiated. |
|
This class implements a value selector that returns values in increasing order. |
|
This variable selector selects the variable with biggest fractional part in the current solution held by the provided linear relaxation solver. |
|
A nearest neighboor branching scheme based on a distance matrix. |
|
This value selector chooses the value closest to the relaxed solution contained in the provided solver. |
|
This class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from target in the domain of the variable. |
|
This class represent a non linear term. |
|
This class creates a X != C constraint |
|
This class creates a X <> Y + C constraint |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) == C constraint |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) >= C constraint |
|
This class creates a abs(X-Y) <= C constraint |
|
This class creates a X == Y + Z constraint |
|
This class creates a X == Y + C constraint |
|
This class creates a X == C constraint |
|
This class creates a X >= C constraint |
|
This class creates a X >= Y + C constraint |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable in the input order. |
|
This variable selector selects the variable with biggest reduced cost in current LP solution of the provided linear relaxation solver. |
|
This class creates a X <= C constraint |
|
This class creates a Sum(ai.Xi) { <= , != , == } C constraint |
|
This class creates a X <= Y + C constraint |
|
This class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from the middle value in the domain of the variable. |
|
This value selector chooses the value closest to the relaxed solution contained in the provided solver. |
|
This class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from target in the domain of the variable . |
|
This class represents a constraint to propagate any non linear constraint of the form KNonLinearTerm COMPARATOR KNonLinearTerm. |
|
An OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with any type of KNumVar objective, which use both a relative and absolute difference criteria. |
|
Smallest domain variable selector |
|
Abstract interface class for value selection heuristic See also: KMaxToMin KMinToMax KMiddle KRandomValue KNearestValue |
|
Superclass of decision variables |
This class implements an array of KNumVar. |
|
|
Abstract interface class for variable selection heuristic. |
|
This class creates a X = |Y| constraint |
|
This class creates a X = atan2(Y, Z) constraint. Atan2(Y, Z) is defined as follow : - atan(Y/Z) if Z > 0 - atan(Y/Z) + PI if Z < 0 and Y >= 0 - atan(Y/Z) - PI if Z < 0 and Y < 0 - (+ PI / 2) if Z = 0 and Y > 0 - (- PI / 2) if Z = 0 and Y < 0 - undefined if Z = 0 and Y = 0. |
|
This class creates a X = ln(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X = Y ^ C constraint |
|
This class creates a X = Y^2 constraint |
|
This class creates a X = Y * C constraint |
|
This class creates a X == Y * Z constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} acos(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} asin(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} atan(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} cos(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} exp(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} ln(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} sin(Y) constraint |
|
This class creates a X {==,<=,>=} tan(Y) constraint |
|
This class represent an expression of type occur(target,lvars) where target is the value for wich we want to restrict the number of occurence(s) in the lVars array of variables. |
|
This class creates an occurence constraint of a value in a list of variables |
|
This interface sets a framework for objects providing method to check if the current solution is close enough to the optimum, and, if not, to give a new bound to set on the objective variable. |
|
|
|
|
|
Parallel branching scheme |
|
|
|
A variable selector based on a path order. |
|
Probe branching scheme |
|
ProbeDisjunction branching scheme |
|
Constraint satisfaction and optimization problems include variables, constraints ( modeling entities ) and might have solutions after search. |
|
This class implements a value selector that selects a value at random in the domain of the variable. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects an uninstantiated variable at random. |
|
A relation term between an expression and constants. |
An OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with any type of KNumVar objective, which use a relative difference criteria. |
|
|
This class is intended as a superclass for linear relaxation solvers. |
|
Resources (machines, raw material etc) can be of two different types : |
|
This class implements an array of KResource |
|
Resource selection heuristic |
|
A KResourceUsage object can be used to describe the a specific usage of a given resource. |
Utility container for storing a list of KResourceUsage |
|
|
Scheduling and planning problems are concerned with determining a plan for the execution of a given set of tasks. |
|
Nothing can be done in Artelys Kalis outside a KSession object. |
|
KSettleDisjunction branching scheme |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the smallest ratio domain size / degree in the constraint graph. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the smallest domain. |
Smallest Earliest Completion time task selection heuristic |
|
|
Smallest Earliest Start time task selection heuristic |
Smallest Latest Completion time task selection heuristic |
|
|
Smallest Latest Start time task selection heuristic |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the smallest upperbound. |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the smallest value in its domain. |
|
Smallest Target Start time task selection heuristic |
|
This class represents a solution of a KProblem. |
|
An array of KSolution objects |
|
This class represent a pool of solution of a KProblem. |
|
KSolver is the main class for solving problems defined in a KProblem instance. |
|
Callbacks for a KSolver events. |
|
SplitDomain Branching scheme |
|
SplitDomain Branching scheme |
|
Tasks (processing operations, activities) are represented by the class KTask. This object contains three variables : |
|
This class implements an array of KTask |
|
Tasks input order selection heuristic |
|
Tasks random order selection heuristic |
|
Abstract interface class for task selection heuristic A custom scheduling optimization strategy can be specified by using the KTaskSerializer branching scheme to select the task to be scheduled and value choice heuristics for its start and duration variables. |
|
Task-based branching strategy |
|
Constraint linking tasks and rank variables for unary scheduling. |
|
Superclass of KUnTerm and KBinTerm |
|
Timetable object for time-dependant resource usage constraint. |
This class implements an array of tuples of fixed arity |
|
|
This class represent an expression of the form X + cste where X is a variable |
|
Unary Resource |
|
This constraint states that some tasks are not overlapping chronologically. |
|
Abstract interface class for definition of user constraints |
|
The KUserNumConstraint is the generic counterpart to the KUserConstraint for implementing user constraints when using numeric variables. |
|
Abstract interface class for value selection heuristic |
|
Abstract interface class for variable selection heuristic |
|
This class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the widest domain. |
|
This class creates a X == Y - Z constraint |
|
This linear relaxation solver relies on XPress Optimizer to solve the LP/MIP problem. |
|
A Matrix template |
- class kalis.ArtelysException(*args)¶
Bases:
objectException class thrown by the Artelys Kalis library.
Example :
try { new KSession(); // Model and solve here } catch (ArtelysException &artelysException) { std::cerr << "An exception occured : " << artelysException.getMessage() << std::endl; }
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.Console¶
Bases:
objectUtility class for text console managment
Methods:
Clear the screen
return the default console text attributes
getX()return current X cursor position
getY()return current Y cursor position
gotoxy(x, y)position the cursor to (x,y) coordinates
restore the default console text attributes
setBackgroundColor(col)set the Background color of printed text
setColor(col)set the color of the printed text (background and foreground)
setForegroundColor(col)set the Foreground color of printed text
- clearScreen() → void¶
Clear the screen
- getConsoleTextAttributes() → unsigned int¶
return the default console text attributes
- getX() → int¶
return current X cursor position
- getY() → int¶
return current Y cursor position
- gotoxy(x: int, y: int) → void¶
position the cursor to (x,y) coordinates
- restoreDefaultConsoleTextAttributes() → void¶
restore the default console text attributes
- setBackgroundColor(col: char) → void¶
set the Background color of printed text
- setColor(col: unsigned int) → void¶
set the color of the printed text (background and foreground)
- setForegroundColor(col: char) → void¶
set the Foreground color of printed text
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.Contradiction¶
Bases:
objectA contradiction is a c++ exception thrown whenever kalis deduce that the problem is inconsistent (i.e it has no solution)
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KACBinConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class implements a generic class for propagation of any binary constraint by local 2-consistency (arc consistency) Two algorithms (AC3 and AC2001) are available for propagation of the constraint.
Example : X == Y + C
class XEqualYC : public KACBinConstraint { int _C; public: XEqualYC(const char* name, KIntVar& v1, KIntVar& v2, int cst) : KACBinConstraint(v1, v2, KACBinConstraint::ALGORITHM_AC2001, "XEqualYC") { _C = cst; } virtual bool testIfSatisfied(int valX, int valY) { return (valX == valY + _C); // the constraint is true if only iff valX == valY + C } };
See also: KACBinTableConstraint KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getInstanceCopyPtr(problem)Virtual copy method.
testIfSatisfied(val1, val2)Abstract interface for generic propagation of any binary constraint
- getInstanceCopyPtr(problem: KProblem) → KACBinConstraint *¶
Virtual copy method. Each modeling elements stored (and used) in the binary constraint must be copied using the KProblem::getCopyPtr() method.
- testIfSatisfied(val1: int, val2: int) → bool¶
Abstract interface for generic propagation of any binary constraint
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true if and only if the constraint is satisfied when v1 == val1 & v2 == val2
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KACBinTableConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class implements a generic class for propagation of any binary constraint by local 2-consistency (arc consistency). Two algorithms (AC3 and AC2001) are available for propagation of the constraint.
// Example : X == Y + 1 KProblem p(...); KIntVar X(p,"X",0,4); KIntVar Y(p,"Y",0,4); // truth table of constraint X == Y + 1 for X in [0..4] and Y in [0..4] // |0|1|2|3|4| // ------------- // 0 |0|1|0|0|0| // 1 |0|0|1|0|0| // 2 |0|0|0|1|0| // 3 |0|0|0|0|1| // 4 |0|0|0|0|0| // ------------- bool ** truthTable; truthTable = new bool*[X.getSup()]; for (int i=0; i < 5; ++i) { truthTable[i] = new bool[Y.getSup()]; std::memset(truthTable[i],false,Y.getSup() * sizeof(bool)); } truthTable[1][0] = true; // if X = 1 and Y = 0 then X == Y + 1 is satisfied truthTable[2][1] = true; // if X = 2 and Y = 1 then X == Y + 1 is satisfied truthTable[3][2] = true; // if X = 3 and Y = 2 then X == Y + 1 is satisfied truthTable[4][3] = true; // if X = 4 and Y = 3 then X == Y + 1 is satisfied p.post(KACBinTableConstraint(X,Y,truthTable,KACBinTableConstraint::ALGORITHM_AC2001,"X == Y + 1"))
See also: KACBinConstraint KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KAbs(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = abs(Y) constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); ... problem.post(KAbs("X=|Y|",X,Y)); ...
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KAbsoluteToleranceOptimalityChecker(maximize: bool, tolerance: double)¶
Bases:
kalis.KOptimalityToleranceCheckerAn OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with any type of KNumVar objective, which use an absolute difference criteria.
Methods:
isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj, bestBound)Check for the optimality tolearance
nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj)Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution.
- isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj: double, bestBound: double) → bool¶
Check for the optimality tolearance
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) –
bestBound (float) –
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true is the best solution is close enough - for some criteria - to the optimum
- nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj: double) → double¶
Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution. This prevent from storing too many solutions which are very similar.
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) – the best objective value of already found solutions.
- Return type
float
- Returns
a bound to set on the objective.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KAllDifferent(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X1 <> X2 <> … <> Xn constraint
Example :
KIntVarArray X(...); // ... // Strong propagation problem.post(KAllDifferent("allDiff(X)",X,KAllDifferent::GENERALIZED_ARC_CONSISTENCY)); // Weak propagation problem.post(KAllDifferent("allDiff(X)",X,KAllDifferent::FORWARD_CHECKING));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KAssignAndForbid(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeAssign And Forbid branching scheme
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignAndForbid(KSmallestDomain(),KMaxToMin());
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KAssignVar(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeAssignVar Branching scheme
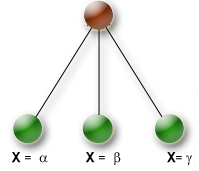
Example:
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(), KMaxToMin());
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KAuxVar(*args)¶
Bases:
objectThis class represents an auxiliary variable to use in relaxations.
KAuxVar objects represent auxiliary variables, consisting of a name, lower and upper bounds, and a type that is either “global” or “continuous”. They are intended to be used in relaxations, as new variables that are not needed in the CP problem but that can be necessary in the LP/MIP formulation.
Example (creation of a boolean auxiliary variable) :
KAuxVar auxVar(0, 1, true, "bool aux var");
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getInf()get the lower bound
set both bounds
getName()Get the name of this auxiliary variable
getSup()get the upper bound
isGlobal()check variable type
setInf(inf[, chain])set the lower bound.
setSup(sup[, chain])set the upper bound.
- getInf() → double¶
get the lower bound
- getInternalObject() → KAuxVar_I *¶
- set both bounds
- param inf
new value
- param chain
if this flag is set, Kalis attempts to chain the change in the auxiliary variable to the “real” variables (KIntVar and KFloatVar). Useful only for KAuxVar automatically generated by Kalis, such as indicator auxiliary variables.
- rtype
KAuxVar_I
- return
true iff the variable was not already instantiated to val
- getName() → char const *¶
Get the name of this auxiliary variable
- getSup() → double¶
get the upper bound
- isGlobal() → bool¶
check variable type
- setInf(inf: double, chain: bool = True) → bool¶
- set the lower bound.
- type inf
float
- param inf
new lower bound
- type chain
boolean, optional
- param chain
if this flag is set, Kalis attempts to chain the change in the lower bound of the auxiliary variable to the “real” variables (KIntVar and KFloatVar). Useful only for KAuxVar automatically generated by Kalis, such as indicator auxiliary variables.
- rtype
boolean
- return
a flag indicating if the domain was reduced
- setSup(sup: double, chain: bool = True) → bool¶
- set the upper bound.
- param inf
new upper bound
- type chain
boolean, optional
- param chain
if this flag is set, Kalis attempts to chain the change in the upper bound of the auxiliary variable to the “real” variables (KIntVar and KFloatVar). Useful only for KAuxVar automatically generated by Kalis, such as indicator auxiliary variables.
- rtype
boolean
- return
a flag indicating if the domain was reduced
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBestBoundValue(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorValue selector that selects the value of a variable that implies the best bound for the objective.
For each possible value in the domain of a given variable, the variable is instantiated on this value and the propagation is launched. The selected value will be the value that impacted the objective in the best way.
If the lower bound is used, the best value will be the value that induces the minimal lower bound on the objective. If the upper bound is used, the best value will be the value that induces the maximal upper bound on the objective.
Methods:
Return an allocated copy of the selector
selectNextValue(intVar)Selects the next objective best bound value for the given variable.
- getCopyPtr() → KValueSelector *¶
Return an allocated copy of the selector
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Selects the next objective best bound value for the given variable.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBinTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTermThis class represent an expression of the form X (+ , -) Y + cste where X and Y are variables and cste an integer constant.
See also: KUnTerm KLinTerm
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getSign1()return true if the sign of the first variable is positive
getSign2()return true if the sign of the second variable is positive
getV1()return a pointer to the first variable
getV2()return a pointer to the second variable
- getSign1() → bool¶
return true if the sign of the first variable is positive
- getSign2() → bool¶
return true if the sign of the second variable is positive
- getV1() → KNumVar *¶
return a pointer to the first variable
- getV2() → KNumVar *¶
return a pointer to the second variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBranchingScheme(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract class defining branching schemes. Search is made thanks to a tree search algorithm. At each node, propagation is made and if no solution exists, Artelys Kalis needs to split your problem in smaller subproblems covering (or not) all the initial problem. This partition is made following a branching scheme.
Different types of branching schemes exist. For example, a classical way is to choose a variable which has not been instantiated so far and to build a sub-problem for each remaining value in the variable’s domains, this sub-problem being the original problem where the variable has been instantiated to this value. And then, you can continue the search with these new nodes.
Choosing the right branching schemes to be used with your particular problem could greatly improve the performance of the tree search. Artelys Kalis allows you to choose between many classical branching schemes provided with the library and to easily program yourself the more specialized branching schemes that you suppose to be useful for your own problems.
See also: KAssignAndForbid KSplitDomain KSettleDisjunction KProbe
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getName()Return the name of the branching scheme
Return the current problem
Pretty printing of the branching scheme
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of the branching scheme
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
Return the current problem
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing of the branching scheme
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBranchingSchemeArray¶
Bases:
kalis.branchingschemearrayThis class implements an array of KBranchingScheme
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myStrategy; // First solve all the disjunctions in the problem myStrategy += KSettleDisjunction(); // then assign each remaining non bound variable by assigning values in // decreasing order to variables ordered by increasing size of domain myStrategy += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(),KMaxToMin());
See also: KBranchingScheme KValueSelector KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBranchingSchemeGroup(*args)¶
Bases:
objectA branching scheme group represents a list of branching schemes to use nested branching schemes.
See also: KBranchingSchemeGroupSerializer KBranchingSchemeGroupArray
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBranchingSchemeGroupArray¶
Bases:
kalis.bsgrouplistList of brancing scheme group.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBranchingSchemeGroupSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectSelection object to choose among a list of branching scheme group.
See also: KBranchingSchemeGroup KBranchingSchemeGroupSerializer KBranchingSchemeGroupArray
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KBranchingSchemeGroupSerializer(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeA nested branching scheme.
From a list of branching scheme groups, this brancing scheme apply iteratively each group.
The default group selector uses input order.
See also: KTaskSerializer KBranchingSchemeGroup KBranchingSchemeGroupSelector
Methods:
Get a copy pointer
- getCopyPtr() → KBranchingScheme *¶
Get a copy pointer
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KClpLinearRelaxationSolver(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KLinearRelaxationSolverLinear relaxation solver for Clp
Methods:
display()Print the internal state of the solver.
generateCuts(arg2)Cut generation
Get the best bound in a branch and bound tree.
getBound()Get the (lower for minimization, upper for maximization) bound computed by solve().
getLPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
getMIPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
Get the number of global variables.
Get a pointer to the solution contained in the solver.
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
Print variables name and their rank.
setObjective(var)Set objective variable.
setPresolve(arg2)Activate or deactivate presolve.
solve()Call the solver.
updateSolution(MIPflag)Update the KHybridSolution object with the current MIP (MIPflag=true) or LP (MIPflag=false) solution.
writeLP(filename)Write the current problem to a file in lp format.
- display() → void¶
Print the internal state of the solver. Use is discouraged, use method writeLP to output the content of the solver.
- generateCuts(arg2: KLinearRelaxation) → void¶
Cut generation
- getBestBound() → double¶
- Get the best bound in a branch and bound tree.
Useful if search terminated before optimality.
- getBound() → double¶
Get the (lower for minimization, upper for maximization) bound computed by solve().
- Note that :
solve() method must be called before the getBound() method
moreover, the return code provided by solve() must be checked before using the value returned by getBound().
- getLPSolution(*args) → double¶
- Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose value is checked
Overload 2:
Get the current LP solution for a KAuxVar variable. :type var:
KAuxVar:param var: variable whose value is checked
- getMIPSolution(*args) → double¶
Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose value is checked
- Overload 2:
Get the current MIP solution for a KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose value is checked
- getNumberGlobals() → int¶
Get the number of global variables.
- getSolutionPtr() → KHybridSolution *¶
Get a pointer to the solution contained in the solver. Method updateSolution must be used before the call.
- instantiateNumVarToCurrentSol(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- instantiateNumVarsToCurrentSol() → void¶
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- printVariables() → void¶
Print variables name and their rank.
This is useful to recover the meaning of the columns in the LP file produced by writeLP.
- setObjective(var: KNumVar) → void¶
- Set objective variable.
- type var
- param var
the new objective variable
- setPresolve(arg2: bool) → void¶
Activate or deactivate presolve.
- solve() → int¶
- Call the solver.
Call (Clp solver) and return an error code (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver for its meaning).
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- updateSolution(MIPflag: bool) → void¶
Update the KHybridSolution object with the current MIP (MIPflag=true) or LP (MIPflag=false) solution.
- Parameters
MIPflag (boolean) – true to get the current MIP solution, false for LP.
- writeLP(filename: char const *) → int¶
Write the current problem to a file in lp format.
- class kalis.KCoinLinearRelaxationSolver(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KLinearRelaxationSolverThis linear relaxation solver relies on CoinMP to solve the LP/MIP problem.
Example:
KProblem myProblem(mySession,""); // ... KLinearRelaxation * relax = myProblem.getLinearRelaxation(); KCoinLinearRelaxationSolver mySolver(*relax, objectiveVar, KProblem::Minimize);
You must have the coinMP.lib and coinMP.dll to use this.
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
display()Print the internal state of the solver.
generateCuts(relaxation)Generate cuts.
Get the best bound in a branch and bound tree.
getBound()Get the bound computed by the solver (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver).
getLPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
getMIPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
Get the number of global variables.
getReducedCost(*args)Overload 1:
Get a pointer to the solution contained in the solver.
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
printSolution(MIPflag)Print the current solution.
Print variables name and their rank.
setMipRelStop(arg2)Set MIPRELSTOP double control.
setObjective(var)Set objective variable.
setPresolve(arg2)Activate or deactivate presolve.
solve()Call the solver.
updateSolution(MIPflag)Update the KHybridSolution object with the current MIP (MIPflag=true) or LP (MIPflag=false) solution.
writeLP(filename)Write the current problem to a file in lp format.
- display() → void¶
Print the internal state of the solver.
Use is discouraged, use method writeLP to output the content of the solver.
- generateCuts(relaxation: KLinearRelaxation) → void¶
Generate cuts.
If possible, cuts are added to the matrix of constraints to make the relaxation tighter and improve the bound.
- getBestBound() → double¶
Get the best bound in a branch and bound tree.
Useful if search terminated before optimality.
- getBound() → double¶
Get the bound computed by the solver (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver).
- getLPSolution(*args) → double¶
Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose value is checked
Overload 2:
Get the current LP solution for a KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose value is checked
- getMIPSolution(*args) → double¶
- Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose value is checked
- Overload 2:
Get the current MIP solution for a KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose value is checked
- getNumberGlobals() → int¶
Get the number of global variables.
- getReducedCost(*args) → double¶
Overload 1:
Get reduced costs. Note that LP solve is must be complete.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the variable whose reduced cost in the current LP solution is retrieved- Return type
float
- Returns
reduced cost value
Overload 2:
Get reduced costs. Note that LP solve must be complete.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – the variable whose reduced cost in the current LP solution is retrieved- Return type
float
- Returns
reduced cost value
- getSolutionPtr() → KHybridSolution *¶
Get a pointer to the solution contained in the solver.
Method updateSolution() must be used before the call.
- instantiateNumVarToCurrentSol(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- instantiateNumVarsToCurrentSol() → void¶
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- printSolution(MIPflag: bool) → void¶
Print the current solution.
- Parameters
MIPflag (boolean) – to choose whether to print the current MIP solution or the current LP solution
- printVariables() → void¶
Print variables name and their rank.
This is useful to recover the meaning of the columns in the LP file produced by writeLP().
- setMipRelStop(arg2: double) → void¶
Set MIPRELSTOP double control.
- setObjective(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Set objective variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the new objective variable
- setPresolve(arg2: bool) → void¶
Activate or deactivate presolve.
- solve() → int¶
Call the solver.
Call (CoinMP) and return an error code (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver for its meaning).
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- updateSolution(MIPflag: bool) → void¶
Update the KHybridSolution object with the current MIP (MIPflag=true) or LP (MIPflag=false) solution.
- Parameters
MIPflag (boolean) – true to get the current MIP solution, false for LP.
- writeLP(filename: char const *) → int¶
Write the current problem to a file in lp format.
- class kalis.KConditionNumLinComb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintConditionnal numeric linear combination constraint.
This constraint can be represented as a linear combination Sum(a_i * X_i * f(X_i)) { <= , != , == } C where the function f(X_i) is an indicator (1 or 0) function to specify.
Methods:
conditionTest(varIndex)Method to overload for indicator function
- conditionTest(varIndex: int) → int¶
Method to overload for indicator function
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KConjunction(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a Binary conjunction on two constraints C1 and C2.
Example :
// C1 C2 C1 /\ C2 // ------------------------ // false false false // false true false // true false false // true true true KIntVar START0(...); KIntVar START1(...); // ... problem.post(START0 + 10 < 4 && START1 + 10 > 10); // or problem.post(KConjunction(START0 + 10 < 4,START1 + 10 > 10));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
objectThis class is an abstract interface for all constraints in Artelys Kalis
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KConstraintArray(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.constraintlistThis class implements an array of KConstraint
Example :
KIntVarArray TAB(...) KIntVar X(...) KIntVar Y(...) KIntVar Z(...) KConstraintArray constraintArray; constraintArray += KAllDifferent("alldiff(TAB)",TAB); constraintArray += X == Y + 2: constraintArray += (Y < 6) || (Z + 4 == X)s
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KCumulativeResourceConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
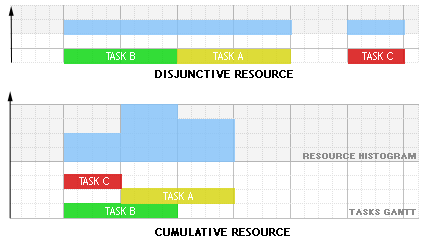
kalis.KConstraintThis constraint states that some tasks requiring a resource do not exceed the resource capacity. The primary use of this constraint is to express resource constraints.
- Resources (machines, raw material etc) can be of two different types:
Disjunctive when the resource can process only one task at a time (represented by the class KUnaryResource).
Cumulative when the resource can process several tasks at the same time (represented by the class KDiscreteResource).
Traditional examples of disjunctive resources are Jobshop problems, cumulative resources are heavily used for the Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP). Note that a disjunctive resource is semantically equivalent to a cumulative resource with maximal capacity one and unit resource usage for each task using this resource but this equivalence does not hold in terms of constraint propagation. The size of a task is its duration by its usage: use_i * dur_i = size_i.
The following schema shows an example with three tasks A,B and C executing on a disjunctive resource and on a cumulative resource with resource usage 3 for task A, 1 for task B and 1 for task C :
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KCumulativeResourceConstraintResourceUsage(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintA time-dependant resource usage constraint.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KCycle(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThe cycle constraint ensures that the graph implicitly represented by a set of variables and their domain contains no sub-tours (tour visiting a partial number of nodes). The constraint can take a second set of variables Preds, representing the inverse relation of the Succ function and ensure the following equivalences : succ(i) = j <==> pred(j) = i for all i and j. The third parameter of the cycle constraint allow to take into account an accumulated quantity along the tour such as distance, time or weight. More formally it ensure the following constraint : quantity = sum(i,j) M(i,j) for all edges i->j belonging to the tour.
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDiscreteResource(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KResourceDiscrete resource
A discrete resource can process several tasks at the same time.
The following schema shows an example with three tasks A,B and C executing on a disjunctive resource and on a cumulative resource with resource usage 3 for task A, 1 for task B and 1 for task C :

- Tasks may require, provide, consume and produce resources :
A task requires a resource if some amount of the resource capacity must be made available for the execution of the activity. The capacity is renewable which means that the required capacity is available after the end of the task.
A task provides a resource if some amount of the resource capacity is made available through the execution of the task. The capacity is renewable which means that the provided capacity is available only during the execution of the task.
A task consumes a resource if some amount of the resource capacity must be made available for the execution of the task and the capacity is non-renewable which means that the consumed capacity if no longer available at the end of the task.
A task produces a resource if some amount of the resource capacity is made available through the execution of the task and the capacity is non-renewable which means that the produced capacity is definitively available after the starting of the task.
- ArcConsistency = 32¶
TimeTabling Arc Consistency
- BoundConsistency = 16¶
TimeTabling Bound consistency
- EdgeFinding = 4¶
Tasks Intervals + EdgeFinding propagation scheme
- MaxAvailMinUsage = 8¶
Constrain and keep track of max availability,and minimum usage of the resource
- TasksIntervals = 2¶
Tasks Intervals propagation scheme
- TimeTabling = 1¶
TimeTabling propagation scheme
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDisjunction(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a Binary disjunction on two constraints C1 or C2
Example :
// C1 C2 C1 \/ C2 // ------------------------ // false false false // false true true // true false true // true true true KIntVar START(...); ... problem.post(START + 10 < 4 || START + 10 >= 4); // or problem.post(KDisjunction(START + 10 < 4,START + 10 >= 4));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return the known status
setStatus(branchNumber, status)Fix status of one part of the disjunction
- knownStatus() → bool¶
Return the known status
Known status is true if status of disjunction is proven at current point of the branch and bound, false if unknown.
- setStatus(branchNumber: int, status: bool) → void¶
Fix status of one part of the disjunction
- Parameters
branchNumber (int) – 0 for c1, 1 for c2
status (boolean) – true if corresponding constraint must be true
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDisjunctionArray¶
Bases:
kalis.disjunctionlistThis class implements an array of KDisjunction
Example :
KIntVar TASK0(...) KIntVar TASK1(...) KIntVar TASK2(...) KDisjunctionArray disjunctionArray; disjunctionArray += (TASK0 + 10 < TASK1) || (TASK1 + 4 < TASK0); disjunctionArray += (TASK1 + 4 < TASK2) || (TASK2 + 7 < TASK1); disjunctionArray += (TASK2 + 7 < TASK0) || (TASK0 + 10 < TASK2); KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSettleDisjunction(disjunctionArray);
See also: ArtelysList KDisjunction KBranchingScheme KSettleDisjunction
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDisjunctionInputOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KDisjunctionSelectorThis class implements a disjunction selector that selects the disjunction in the input order.
Example : KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSettleDisjunction(new KDisjunctionInputOrder());
See also: KDisjunctionSelector Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return a copy of this object
selectNextDisjunction(disjunctionArray)Virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own disjunction selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- getCopyPtr() → KDisjunctionSelector *¶
Return a copy of this object
- selectNextDisjunction(disjunctionArray: KDisjunctionArray) → KDisjunction *¶
Virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own disjunction selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDisjunctionPriorityOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KDisjunctionSelectorThis class implements a disjunction selector that selects first the disjunction ith the highest priority
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSettleDisjunction(new KDisjunctionPriorityOrder());
See also: KDisjunctionSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return a copy of this object
selectNextDisjunction(disjunctionArray)Virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own disjunction selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- getCopyPtr() → KDisjunctionSelector *¶
Return a copy of this object
- selectNextDisjunction(disjunctionArray: KDisjunctionArray) → KDisjunction *¶
Virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own disjunction selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDisjunctionSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract interface class for disjunction selection heuristic Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return a copy of this object
getName()Return the name of this disjunction selector
Print the name of this disjunction selector
selectNextDisjunction(disjunctionArray)Virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own disjunction selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- getCopyPtr() → KDisjunctionSelector *¶
Return a copy of this object
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this disjunction selector
- printName() → void¶
Print the name of this disjunction selector
- selectNextDisjunction(disjunctionArray: KDisjunctionArray) → KDisjunction *¶
Virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own disjunction selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDistanceEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) == C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KDistanceEqualXyc(X,Y,3)); // |X-Y| == 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDistanceGreaterThanXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) >= C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KDistanceGreaterThanXyc(X,Y,3)); // |X-Y| >= 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDistanceLowerThanXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) <= C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KDistanceLowerThanXyc(X,Y,3)); // |X-Y| <= 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDistanceNotEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) != C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KDistanceNotEqualXyc(X,Y,3)); // |X-Y| != 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KDoubleArray¶
Bases:
kalis.doublelistThis class implements an array of doubles
Example :
KDoubleArray doubleArray; doubleArray += 3.0; doubleArray += 5.0; // doubleArray = { 3.0 ,5.0 } doubleArray[0] = 2.2; // doubleArray = { 2.2 ,5.0 }
See also: KIntArray Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KElement(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a x == tab[i + cste] constraint
Example :
KIntArray tab(...); KIntVar x(...); KIntVar i(...); // ... problem.post(KElement(tab,i,x,4,"x == tab[i + 4]"));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KElement2D(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == Tab[I + cste1][J + cste2] constraint
Example :
KIntArray Tab(...); KIntVar X(...); KIntVar I(...); KIntVar J(...); // ... problem.post(KElement2D(Tab, I, J, X, 4, 8, "X == Tab[I + 4][J+8]"));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getValueForIndex(index1, index2)Get the value for I = index1 and J = index2
setUseValueFunction(useValueFunction)Choose value method between Table and method ‘getValueForIndex’
- getValueForIndex(index1: int, index2: int) → int¶
Get the value for I = index1 and J = index2
- setUseValueFunction(useValueFunction: bool) → void¶
Choose value method between Table and method ‘getValueForIndex’
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KEltTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTermThis class represent an expression of type Tab[I] where Tab is an array of integer value and I is the indexing variable
Example :
KProblem p(...); KIntVar X(...); KIntVar I(...); KIntArray valuesArray(...); KEltTerm eltTerm(valuesArray, I); // posting the constraint X can take its values indexed by the I variable in the valuesArray p.post(X == eltTerm); // equivalent to p.post(X == valuesArray[I]);
See also: KConstraint KElement
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
return the index variable
return the array of values indexed by the index variable
return the user pointer
- getIndexVar() → KIntVar *¶
return the index variable
- getLValues() → KIntArray *¶
return the array of values indexed by the index variable
- getUserPointer() → void *¶
return the user pointer
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KEltTerm2D(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTermThis class represent an expression of type Tab[I+a][J+b] where Tab is an array of integer value; I,J are the indexing variable and a and b indexing offsets
Example :
KProblem p(...); KIntVar X(...); KIntVar I(...); KIntVar J(...); KIntArray valuesArray(...); KEltTerm2D eltTerm(valuesArray,I,J); // posting the constraint X can take its values indexed by the I variable in the valuesArray p.post(X == eltTerm); // equivalent to p.post(X == valuesArray[I]);
See also: KConstraint KElement
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
return the index variable in dimension one
return the array of values indexed by the index variable
return the index variable in dimension two
- getFirstIndexVar() → KIntVar *¶
return the index variable in dimension one
- getLValues() → KIntMatrix *¶
return the array of values indexed by the index variable
- getSecondIndexVar() → KIntVar *¶
return the index variable in dimension two
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == C constraint.
Example :
KIntVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X == 5); // or problem.post(KEqualXc(X,5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == Y + C constraint.
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(X == Y + 5); // or problem.post(KEqualXyc(X,Y,5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KEquiv(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates an Equivalence on two constraints C1 <==> C2.
Example :
// C1 C2 C1 <==> C2 // -------------------------- // false false true // false true false // true false false // true true true KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); KIntVar Z(...); problem.post( KEquiv( X <= Y + 3 , Z > 4 ) );
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KFloatVar(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumVarThis class implements a variable with continuous real valued domain. Conceptually the continuous variables can be represented the following way :
Example:
KProblem p(...); // X is a continuous variable that can take real value between interval [0..10] KFloatVar X(p,"X",0,10);
See also: KNumVarArray KFloatVarArray Since: 2016.1
Methods:
canBeInstantiatedTo(value)check if value is in the domain
display(*args)Overload 1: pretty printing of the variable
Return a copy of this object
returns the number of constraints where this variable appears
returns current domain size of the variable
getInf()returns lower bound of this variable
returns true if the variable has been assigned a value, false otherwhise
returns value in variable’s domain and close to the middle
get a random value in the domain of the variable
getSup()returns upper bound of this variable
get target value
getValue()returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
Return the type of this variable :param KNumVar::IsKNumVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKIntVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKFloatVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar
instantiate(value)Instantiate the variable to value
isEqualTo(x)check if equal to x
optimize the internal representation of the domain
setInf(value)set the lower bound to value
setName(name)Set the name of the variable
setPrecisionRelativity(relativity)Set the precision relativity (true for relative precision and false for absolute precision
setSup(value)set the upper bound to value
setTarget(value)set the target value
shave lower bound of variable
shave upper bound of variable
shaveOnValue(val)shave the value ‘val’
useShaving(use)activate shaving Y/N
- canBeInstantiatedTo(value: int) → bool¶
check if value is in the domain
- display(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: pretty printing of the variable
Overload 2: pretty printing of the variable
- getCopyPtr() → KFloatVar *¶
Return a copy of this object
- getDegree() → int¶
returns the number of constraints where this variable appears
- getDomainSize() → int¶
returns current domain size of the variable
- getInf() → double¶
returns lower bound of this variable
- getIsInstantiated() → bool¶
returns true if the variable has been assigned a value, false otherwhise
- getMiddle() → double¶
returns value in variable’s domain and close to the middle
- getRandomValue() → double¶
get a random value in the domain of the variable
- getSup() → double¶
returns upper bound of this variable
- getTarget() → double¶
get target value
- getValue() → double¶
returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
- instanceof() → int¶
Return the type of this variable :param KNumVar::IsKNumVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKIntVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKFloatVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar
- instantiate(value: double const) → void¶
Instantiate the variable to value
- isEqualTo(x: kalis.KFloatVar) → bool¶
check if equal to x
- optimizeDomainRepresentation() → void¶
optimize the internal representation of the domain
- setInf(value: double) → void¶
set the lower bound to value
- setName(name: char const *) → void¶
Set the name of the variable
- setPrecisionRelativity(relativity: bool) → void¶
Set the precision relativity (true for relative precision and false for absolute precision
- setSup(value: double) → void¶
set the upper bound to value
- setTarget(value: double) → void¶
set the target value
- shaveFromLeft() → bool¶
shave lower bound of variable
- shaveFromRight() → bool¶
shave upper bound of variable
- shaveOnValue(val: int) → bool¶
shave the value ‘val’
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- useShaving(use: bool) → void¶
activate shaving Y/N
- class kalis.KFloatVarBranchingScheme(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeThis branching scheme is suited for branching on KFloatVar objects.
See also: KBranchingScheme KIntVarBranchingScheme KAssignAndForbidd KSplitDomain KSettleDisjunction KProbe
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
finishedBranching(branchingObject, …)Return true IFF branching is completed on one specific branch of the branch and bound
This method is called upon finishing branching for the current node and allows freeing objects created at the current node
getNextBranch(branchingObject, …)Return the next branch
Problem getter
goDownBranch(branchingObject, …)This method is called once a branch has been selected and a decision must be taken
goUpBranch(branchingObject, …)This method is called upon backtrack on a specific branch
Select the next KNumVar to branch on when one branch has been explored
- finishedBranching(branchingObject: KNumVar, branchingInformation: double *, currentBranchNumber: int) → bool¶
Return true IFF branching is completed on one specific branch of the branch and bound
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KNumVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (float) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- freeAllocatedObjectsForBranching(branchingObject: KNumVar, branchingInformation: double *) → void¶
This method is called upon finishing branching for the current node and allows freeing objects created at the current node
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KNumVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (float) – the branching information
- getNextBranch(branchingObject: KNumVar, branchingInformation: double *, currentBranchNumber: int) → double *¶
Return the next branch
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KNumVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (float) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
Problem getter
- goDownBranch(branchingObject: KNumVar, branchingInformation: double *, currentBranchNumber: int) → void¶
This method is called once a branch has been selected and a decision must be taken
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KNumVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (float) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- goUpBranch(branchingObject: KNumVar, branchingInformation: double *, currentBranchNumber: int) → void¶
This method is called upon backtrack on a specific branch
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KNumVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (float) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- selectNextBranchingVar() → KNumVar *¶
Select the next KNumVar to branch on when one branch has been explored
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KFloatVarSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorFloat variable selector
See also: KVariableSelector
Methods:
selectNextVariable(floatVarArray, gap)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics :type intVarArray:
KIntVarArray:param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable- selectNextVariable(floatVarArray: KNumVarArray, gap: double) → KFloatVar *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics :type intVarArray:
KIntVarArray:param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KGeneralizedArcConsistencyConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class implements a generic class for propagation of any nary constraint by forward checking/arc consistency or generalized arc consistency
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
testIfSatisfied(tuple)Abstract Interface for generic propagation of any binary constraint.
- testIfSatisfied(tuple: kalis.intvector) → bool¶
Abstract Interface for generic propagation of any binary constraint.
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true if and only if the constraint is satisfied when v1 == val1 & v2 == val2
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KGeneralizedArcConsistencyTableConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class implements a generic class for propagation of any n-ary constraint by generalized arc consistency
See also: KGeneralizedArcConsistencyConstraint KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KGlobalCardinalityConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class implements a Global Cardinality Constraint.
A GCC (Global Cardinality Constraint) over a set of variables is defined by three arrays called values, lowerBound, and upperBound. The constraint is satisfied if and only if the number of variables of the given set which are assigned to values[i] is greater or equal to lowerBound[i], and lower or equal to upperBound[i] for all i, and if no variable of the given set is assigned to a value which does not belong to values.
Posting a KGlobalCardinalityConstraint to a problem is equivalent, from a modelisation point of view, to posting two instances of {KOccurence} for each value. But this is absolutely not equivalent from a propagation point of view : GCC acquires a far better propagation, using the Regin algorithm.
Example. A group of tourists have to be transported from a point to another one, using a fleet of buses. The objective is to find the assignment which maximize a satisfaction of tourists, depending of their affinities. The bus capacity constraint can me modelized by the following code :
Bus [] fleet = // something ; Tourist [] tourists = // something ; KIntVarArray assignment = new KIntVarArray (problem, tourists.length, 0, fleet.length-1, "TouristBusesAssignment"); int [] capacity = new int [fleet.length]; // Capacities of the buses for (int i=0; i < fleet.length; i++) capacity[i] = fleet[i].capacity; KGlobalCardinalityConstraint gcc = new KGlobalCardinalityConstraint ("Buses Capacity constraint", assignment.getVars(), capacity);
See also: KCompleteAllDifferent KOccurence
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KGreaterOrEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X >= C constraint.
Example :
KIntVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X >= 3); // or problem.post(KGreaterOrEqualXc(X,3));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KGreaterOrEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X >= Y + C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(X >= Y + 3); // or problem.post(KGreaterOrEqualXyc(X,Y,3));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KGuard(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates an implication on two constraints C1 ==> C2
Example :
// C1 C2 C1 ==> C2 // ------------------------- // false false true // false true true // true false false // true true true KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); KIntVar Z(...); problem.post( KGuard( X <= Y + 3 , Z > 4 ) );
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KHybridSolution(*args)¶
Bases:
objectThis class represents a solution of a relaxation solver, that is, a mapping from variables (KNumVar and/or KAuxVar) to their value.
Example :
KXPRSLinearRelaxationSolver mySolver(...); mySolver.solve(); solverMIP.updateSolution(); KHybridSolution * mySol = solverMIP.getSolutionPtr(); mySol->print();
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
display()Print solution.
getVal(*args)Overload 1: Get the value of a KNumVar.
setVal(*args)Overload 1:
- display() → void¶
Print solution.
- getVal(*args) → double¶
Overload 1: Get the value of a KNumVar.
Overload 2: Get the value of a KAuxVar.
- setVal(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Set the value of a KNumVar.
- Parameters
variable – whose value is modified
new – value
Overload 2:
Set the value of a KAuxVar.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – varaible to modifynew – value
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KInputOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable in the input order.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KInputOrder(),KMaxToMin());
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextVariable(intVarArray)return the first uninstantiated variable in the order of creation
- selectNextVariable(intVarArray: KIntVarArray) → KIntVar *¶
return the first uninstantiated variable in the order of creation
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntArray(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.intlistThis class implements an array of integers
Example :
KIntArray intArray; intArray += 3; intArray += 5; // intArray = { 3,5 } intArray[0] = 2; // intArray = { 2,5 }
See also: KDoubleArray Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntMatrix(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.intmatrixThis class implements an matrix of integers
KProblem p(...); // mat is a matrix of integer // mat[0][0] mat[1][0] // mat[0][1] mat[1][1] // mat[0][2] mat[1][2] // with domain [0..10] KIntMatrix mat(p,2,3,0,10,"mat");
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
display()Pretty printing of the matrix
Get a pointer to a copy of this object
- display() → void¶
Pretty printing of the matrix
- getCopyPtr() → ArtelysMatrix< int > *¶
Get a pointer to a copy of this object
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntVar(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumVarThis class implements an integer variable with enumerated (finite) domain. Decision variables are the variable quantities that we are trying to instantiate in order to satisfy the constraints of our problem. In this version, Artelys Kalis works with integer variables : decision variables which are constrained to take only integer values. These integer variables are represented by instances of the class KIntVar.
Example :
KProblem p(...); // X is an integer variable that can take value 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 KIntVar X(p, "X", 0, 10); // Y is an integer variable that can take value 7,8,10 (3 different values) KIntVar Y(p, "Y", KIntArray(3, 7, 8, 10)); // Z is an integer variable that can take value 3,4,5 KIntVar Z; Z = KIntVar(p,3,5);
See also: KIntArray KIntVarArray
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
canBeInstantiatedTo(value)Check if value is in the domain
display(*args)Overload 1: Pretty printing
Return a copy of this KIntVar object
Returns the number of constraints where this variable appears
Returns current domain size of the variable
getInf()Returns lower bound of this variable
Returns integer lower bound of this variable
Returns integer upper bound of this variable
Returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
Returns true if the variable has been assigned a value, false otherwise
Returns value in variable’s domain and close to the middle
getName()Return the name of the variable
getNextDomainValue(next)Get value immediatly after “next” in the domain of the variable and put it into next
getPrevDomainValue(prev)Get value immediatly before “prev” in the domain of the variable and put it into prev
Get a random value in the domain of the variable
getSup()Returns upper bound of this variable
Get target value
getValue()Returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
Return the type of this variable :param KNumVar::IsKNumVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKIntVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKFloatVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar
instantiate(value)Instantiate the variable to a value
isEqualTo(x)Check if equal to x
Optimize the internal representation of the domain
remVal(value)Remove value from the variable’s domain
setInf(value)Set the lower bound to value
setName(name)Set the name of the variable
setSup(value)Set the upper bound to value
setTarget(value)Set the target value
Shave lower bound of variable
Shave upper bound of variable
shaveOnValue(val)Shave the value ‘val’
- canBeInstantiatedTo(value: int) → bool¶
Check if value is in the domain
- display(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: Pretty printing
Overload 2: Pretty printing
- getCopyPtr() → KIntVar *¶
Return a copy of this KIntVar object
- getDegree() → int¶
Returns the number of constraints where this variable appears
- getDomainSize() → int¶
Returns current domain size of the variable
- getInf() → double¶
Returns lower bound of this variable
- getIntInf() → int¶
Returns integer lower bound of this variable
- getIntSup() → int¶
Returns integer upper bound of this variable
- getIntValue() → int¶
Returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
- getIsInstantiated() → bool¶
Returns true if the variable has been assigned a value, false otherwise
- getMiddle() → double¶
Returns value in variable’s domain and close to the middle
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of the variable
- getNextDomainValue(next: int &) → void¶
Get value immediatly after “next” in the domain of the variable and put it into next
- getPrevDomainValue(prev: int &) → void¶
Get value immediatly before “prev” in the domain of the variable and put it into prev
- getRandomValue() → int¶
Get a random value in the domain of the variable
- getSup() → double¶
Returns upper bound of this variable
- getTarget() → double¶
Get target value
- getValue() → double¶
Returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
- instanceof() → int¶
Return the type of this variable :param KNumVar::IsKNumVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKIntVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKFloatVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar
- instantiate(value: int const) → void¶
Instantiate the variable to a value
- isEqualTo(x: kalis.KIntVar) → bool¶
Check if equal to x
- optimizeDomainRepresentation() → void¶
Optimize the internal representation of the domain
- remVal(value: int const) → void¶
Remove value from the variable’s domain
- setInf(value: int) → void¶
Set the lower bound to value
- setName(name: char const *) → void¶
Set the name of the variable
- setSup(value: int) → void¶
Set the upper bound to value
- setTarget(value: int) → void¶
Set the target value
- shaveFromLeft() → bool¶
Shave lower bound of variable
- shaveFromRight() → bool¶
Shave upper bound of variable
- shaveOnValue(val: int) → bool¶
Shave the value ‘val’
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntVarArray(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.intvarlistThis class implements an array of KIntVar with enumerated (finite) domains
Example :
KProblem p(...); // T is an array of KIntVar T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 with domain [0..10] KIntVarArray T(p,5,0,10,"T");
See also: KIntVar
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntVarBranchingScheme(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeAbstract class for Branching scheme. Search is made thanks to a tree search algorithm. At each node, propagation is made and if no solution exists, Artelys Kalis needs to split your problem in smaller subproblems covering (or not) all the initial problem. This partition is made following a branching scheme.
Different types of branching schemes exist. For example, a classical way is to choose a variable which has not been instantiated so far and to build a sub-problem for each remaining value in the variable’s domains, this sub-problem being the original problem where the variable has been instantiated to this value. And then, you can continue the search with these new nodes. Choosing the right branching schemes to be used with your particular problem could greatly improve the performance of the tree search. Artelys Kalis allows you to choose between many classical branching schemes provided with the library and to easily program yourself the more specialized branching schemes that you suppose to be useful for your own problems. This branching scheme is suited for branching on KIntVar objects only.
See also: KBranchingScheme KFloatVarBranchingScheme KAssignAndForbidd KSplitDomain KSettleDisjunction KProbe
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
finishedBranching(branchingObject, …)Return true IFF branching is completed on one specific branch of the branch and bound
This method is called upon finishing branching for the current node and allows freeing objects created at the current node.
getNextBranch(branchingObject, …)Return the next branch
Return the current problem
goDownBranch(branchingObject, …)This method is called once a branch has been selected and a decision must be taken
goUpBranch(branchingObject, …)This method is called upon backtrack on a specific branch
Select the next KIntVar to branch on when one branch has been explored
- finishedBranching(branchingObject: KIntVar, branchingInformation: int *, currentBranchNumber: int) → bool¶
Return true IFF branching is completed on one specific branch of the branch and bound
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KIntVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (int) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- freeAllocatedObjectsForBranching(branchingObject: KIntVar, branchingInformation: int *) → void¶
This method is called upon finishing branching for the current node and allows freeing objects created at the current node.
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KIntVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (int) – the branching information
- getNextBranch(branchingObject: KIntVar, branchingInformation: int *, currentBranchNumber: int) → int *¶
Return the next branch
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KIntVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (int) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
Return the current problem
- goDownBranch(branchingObject: KIntVar, branchingInformation: int *, currentBranchNumber: int) → void¶
This method is called once a branch has been selected and a decision must be taken
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KIntVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (int) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- goUpBranch(branchingObject: KIntVar, branchingInformation: int *, currentBranchNumber: int) → void¶
This method is called upon backtrack on a specific branch
- Parameters
branchingObject (
KIntVar) – the branching objectbranchingInformation (int) – the branching information
currentBranchNumber (int) – the current branch number
- selectNextBranchingVar() → KIntVar *¶
Select the next KIntVar to branch on when one branch has been explored
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntVarMatrix(problem: KProblem, N: int, M: int, lowerBound: int, upperBound: int, name: char const * = None)¶
Bases:
objectThis class implements an matrix of KIntVar
Example :
KProblem p(...); // mat is a matrix of KIntVar of size (2, 3) with domain [0..10] KIntVarMatrix mat(p, 2, 3, 0, 10, "mat");
See also: KIntArray
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
display()pretty printing of the matrix
getAll(n, all)put all the variables in the matrix into the “all” KIntVarArray
getCol(n, col)put all the variables with column index m into the “col” KIntVarArray
getElt(n, m)return the KIntVar at position (n,m) in the matrix
getPtr(n, m)return a pointer to the KIntVar at position (n,m) in the matrix
getRow(m, row)put all the variables with row index m into the “row” KIntVarArray
- display() → void¶
pretty printing of the matrix
- getAll(n: int, all: KIntVarArray) → KIntVarArray &¶
put all the variables in the matrix into the “all” KIntVarArray
- getCol(n: int, col: KIntVarArray) → KIntVarArray &¶
put all the variables with column index m into the “col” KIntVarArray
- getElt(n: int, m: int) → KIntVar &¶
return the KIntVar at position (n,m) in the matrix
- getPtr(n: int, m: int) → KIntVar *¶
return a pointer to the KIntVar at position (n,m) in the matrix
- getRow(m: int, row: KIntVarArray) → KIntVarArray &¶
put all the variables with row index m into the “row” KIntVarArray
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntegerObjectiveOptimalityChecker(maximize: bool)¶
Bases:
kalis.KOptimalityToleranceCheckerAn OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with integer objective only.
Methods:
isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj, bestBound)Check for the optimality tolearance
nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj)Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution.
- isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj: double, bestBound: double) → bool¶
Check for the optimality tolearance
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) –
bestBound (float) –
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true is the best solution is close enough - for some criteria - to the optimum
- nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj: double) → double¶
Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution. This prevent from storing too many solutions which are very similar.
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) – the best objective value of already found solutions.
- Return type
float
- Returns
a bound to set on the objective.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KIntervalDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeBranching scheme for splitting float variables into a set of intervals.
This branching scheme split the domain of a float variable into interval of length gap. If the boolean order is false, then interval are created in ascending order (descending order otherwise).
- For an initial domain [l, u], the created sub-domains will be:
In ascending order: [l + (k-1) * gap, min(l + k * gap, u)] for k=1,…,ceil((u-l)/gap)
In descending order: [u - k * gap, max(u - (k-1) * gap, l)] for k=1,…,ceil((u-l)/gap)
See also: KBranchingScheme
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the smallest domain.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KLargestDomain(),KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestDurationDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorLargest domain duration task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestEarliestCompletionTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorLargest Earliest Completion time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestEarliestStartTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorLargest Earliest Start time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestLatestCompletionTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorLargest Latest Completion time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestLatestStartTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorLargest Latest Start time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestMax(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the largest upperbound in its domain.
Example:
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KLargestMax(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestMin(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the largest lower bound.
Example:
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KLargestMin(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLargestReducedCost(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis variable selector selects the variable with biggest reduced cost in current LP solution of the provided linear relaxation solver.
Note that it does NOT call the solve() method of the solver automatically. The current LP solution is simply read as it is.
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLessOrEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X <= C constraint.
Example : KIntVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X <= 3); // or problem.post(KLessOrEqualXc(X,3));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLinComb(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a Sum(ai.Xi) { <= , != , == } C constraint
Example :
KIntVarArray X(...); problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] == 3); // or problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] <= 3); // or problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] >= 3); // or problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] != 3);
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLinRel(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KRelationThis class represents a linear relation (equality or inequality) between variables.
Variables involved in the KLinRel object can be a mix of KNumVar and KAuxVar.
Methods:
add(*args)Overload 1:
isSatisfied(sol)Is the linear relation satisfied for this instantiation ?
Print statistics about the equation.
- add(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Add a term (variable “times” coefficient) to the relation.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the variable involvedcoeff (float, optional) – its coefficient
- Overload 2:
Add a term (variable “times” coefficient) to the relation.
- type var
- param var
the variable involved
- type coeff
float, optional
- param coeff
its coefficient
- Overload 3:
Add a term (variable “times” coefficient) to the relation.
- type var
- param var
the variable involved
- param coeff
its coefficient
- Overload 4:
Add all the terms of the given relation (no reduction).
- type relation
- param relation
the relation to add
- isSatisfied(sol: kalis.KHybridSolution) → bool¶
Is the linear relation satisfied for this instantiation ?
- type sol
- param sol
hybrid solution to check
- printStat() → void¶
Print statistics about the equation.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLinTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTermThis class represent a linear term of the form Sum(coeffs[i].lvars[i]) + cst
Example :
KProblem p(...); KIntVarArray X(...); KLinTerm linTerm; linTerm = 3 * X[0]; linTerm = linTerm + 5; linTerm = linTerm + 2 * X[1]; linTerm = linTerm - 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3]; linTerm = linTerm - 7; // these lines are equivalent to : // linTerm = 3 * X[0] + 2 * X[1] - 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] - 2 // posting the constraint 3 * X[0] + 2 * X[1] - 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] - 2 >= 5 // will be converted into -3 * X[0] - 2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] - 5 * X[3] + 7 <= 0 p.post(linTerm >= 5);
See also: KConstraint KLinComb
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLinearRelaxation(*args)¶
Bases:
objectThis class represents a linear relaxation of a domain.
- A linear relaxation consists of the following.
A set of involved variables
A type for each variable (either continuous or global). The type of a variable in a relaxation need not be the same as its “intrinsic” type. For instance, a KIntVar (which is a global variable) can be set continuous in a relaxation. On the contrary, making a KFloatVar global in a relaxation is forbidden since it would not make much sense to “relax” the domain of a variable by restricting it.
A set of linear relations (KLinRel) representing linear (in)equalities with these variables
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
addSOS(sos)Add a SOS of type 1 or 2.
bigM(*args)Overload 1: Big-M method.
convexHull(*args)Overload 1: Convex hull method.
getRank(*args)Overload 1: Get the rank of a KNumVar variable.
insertVar(var)Insert a KIntVar variable.
isExact(*args)Overload 1: Check whether the relaxation is exact or not.
Print statistics about the relaxation.
printViolated(arg2)Print KLinRel that are violated by an hybrid solution (if any).
setName(arg2)set object name
- addSOS(sos: KLinRel) → void¶
Add a SOS of type 1 or 2.
SOS are stored as KLinRel, the constant of the KLinRel being either 1 or 2 depending on the type of the SOS.
A SOS1 (special ordered set of type 1) is a set of variables with the constraint that at most one variable in the set may be non-zero. Note that the comparator and the coefficients of the KLinRel plays no role.
A SOS2 (special ordered set of type 2) is a set of variables with the constraint that at most two variables in the set may be non-zero, and if there are two non-zeros, they must be adjacent. Adjacency is defined by the weights (coefficients in the KLinRel), which must be unique. Note that the comparator of the KLinRel plays no role.
- type sos
- param sos
the sos to add
- static bigM(*args) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Overload 1: Big-M method.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the big-M disjunction of the two arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
Overload 2: Big-M method with any number of arguments.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the big-M disjunction of the arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
- static convexHull(*args) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Overload 1: Convex hull method.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the convex hull of the two arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
Overload 2: Convex hull method, with any number of arguments.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the convex hull of the arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
- getRank(*args) → unsigned int¶
Overload 1: Get the rank of a KNumVar variable.
Note that method close() must be called first, otherwise ranks are undefined. :type var:
KNumVar:param var: variable to rankOverload 2: Get the rank of a KAuxVar.
Note that method close() must be called first, otherwise ranks are undefined. :type var:
KAuxVar:param var: variable to rank
- insertVar(var: KIntVar) → void¶
Insert a KIntVar variable.
Inserting a variable “manually” to the list of variables involved in the relaxation is not necessary in most cases, since variables are added automatically when a constraint in which they are involved is added to the Relaxation.
Note: if the KIntVar has indicators, they are automatically inserted in the relaxation as well. :type var:
KIntVar:param var: variable to add (with its indicators, if any)
- isExact(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: Check whether the relaxation is exact or not.
A relaxation is said to be “exact” when it represents exactly the underlying set of constraints (constraints that were relaxed), so it is not an intrinsic property. This flag is meant to inform the user, not the solver ! (it is not used by the solver in any way).
Overload 2: Setter for isRelaxationExact.
Same remark as for the previous getter.
- printStat() → void¶
- Print statistics about the relaxation.
Print only the number of variables (with their type), KLinRel and SOS involved.
- printViolated(arg2: KHybridSolution) → void¶
Print KLinRel that are violated by an hybrid solution (if any).
Useful to check whether a solution contained in a KHybridSolution object is valid.
- setName(arg2: char const *) → void¶
set object name
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KLinearRelaxationSolver(*args, **kwargs)¶
Bases:
kalis.KRelaxationSolverThis class is intended as a superclass for linear relaxation solvers.
- Such a solver must be provided with
a linear relaxation (KLinearRelaxation)
an objective variable (KNumVar)
a sense for optimization (KProblem::Sense).
- It relies on a LP/MIP solver to provide the following information:
a value (a bound for the relaxed problem, cf method getBound())
a solution, possibly not feasible for the original problem, but which can be used to guide the search for a feasible solution
if the problem is LP, reduced costs (that can be used for instance in the “reduced cost fixing” procedure).
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
generateCuts(relaxation)Cut generation
writeLP(filename)Writes the current problem to a file (in lp format).
- ALG_BARRIER = 3¶
Newton barrier method
- ALG_DUAL = 1¶
Dual simplex algorithm
- ALG_NETWORK = 2¶
Network simplex algorithm
- ALG_PRIMAL = 0¶
Primal simplex algorithm
- generateCuts(relaxation: KLinearRelaxation) → void¶
Cut generation
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- writeLP(filename: char const *) → int¶
Writes the current problem to a file (in lp format).
- Parameters
filename (string) – the path of the file to write (existing file is overwrited, if any)
- Return type
int
- Returns
return code is reserved for future use (for now, errors are trapped by an exception)
- kalis.KLinearRelaxation_bigM(*args) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Overload 1: Big-M method.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the big-M disjunction of the two arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
Overload 2: Big-M method with any number of arguments.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the big-M disjunction of the arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
- kalis.KLinearRelaxation_convexHull(*args) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Overload 1: Convex hull method.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the convex hull of the two arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
Overload 2: Convex hull method, with any number of arguments.
Get a new linear relaxation which is the convex hull of the arguments. Note: deleting it is user’s responsibility.
- class kalis.KMax(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a vMax = max(X1,X2,…,Xn) constraint
Example :
KIntVarArray X(...); KIntVar maxOfX(...); // ... problem.post(KMax("maxOfX=max(X)", maxOfX, X));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMaxDegree(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable involved in the maximum number of constraints.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KMaxDegree(),KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMaxRegretOnLowerBound(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with maximum regret on its lowerbound.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KMaxRegretOnLowerBound(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMaxRegretOnUpperBound(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with maximum regret on its upperbound.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KMaxRegretOnUpperBound(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMaxToMin(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that returns values in decreasing order.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)get Next Value
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
get Next Value
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMiddle(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from the middle value in the domain of the variable.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(), KMiddle());
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- Parameters
intVar (
KIntVar) – the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMin(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a vMin = min(X1,X2,…,Xn) constraint
Example :
KIntVarArray X(...); KIntVar minOfX(...); problem.post(KMin("minOfX=max(X)",minOfX,X));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMinMaxConflict(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorValue selector that selects the value of a variable that implies the best problem size reduction when instantiated.
For each possible value of the domain of the variable, the variable is instantiated and the problem size reduction is evaluated.
Methods:
Return an allocated copy of the selector
selectNextValue(intVar)Selects the value of the given variable that induces the best problem size once instantiated to this value.
- getCopyPtr() → KValueSelector *¶
Return an allocated copy of the selector
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Selects the value of the given variable that induces the best problem size once instantiated to this value.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMinToMax(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that returns values in increasing order.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(),KMinToMax());
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)get Next Value
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
get Next Value
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KMostFractional(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis variable selector selects the variable with biggest fractional part in the current solution held by the provided linear relaxation solver.
Note that it does NOT call the “solve” method of the solver, so if you want the relaxation to be re-solved at each node, you must use method KSolver::setOtherNodesRelaxationSolver.
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNearestNeighbor(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorA nearest neighboor branching scheme based on a distance matrix.
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- Parameters
intVar (
KIntVar) – the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNearestRelaxedValue(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorThis value selector chooses the value closest to the relaxed solution contained in the provided solver.
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)get Next Value
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
get Next Value
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNearestValue(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from target in the domain of the variable.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(), KNearestValue());
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- Parameters
intVar (
KIntVar) – the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNonLinearTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTermThis class represent a non linear term.
Example :
X + 3 * Y ^ 3
See also: KConstraint KNumLinComb
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
returns the KProblem associated with this variable
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
returns the KProblem associated with this variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNotEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X != C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X != 5); // or problem.post(KNotEqualXc(X,5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNotEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X <> Y + C constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(X != Y + 5); // or problem.post(KNotEqualXyc(X, Y, 5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumDistanceEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) == C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumDistanceEqualXyc(X, Y, 3)); // |X-Y| == 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumDistanceGreaterThanXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) >= C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KDistanceGreaterThanXyc(X, Y, 3)); // |X-Y| >= 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumDistanceLowerThanXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a abs(X-Y) <= C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KDistanceLowerThanXyc(X, Y, 3)); // |X-Y| <= 3
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumEqualXYZ(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == Y + Z constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); KNumVar Z(...); // ... problem.post(KNumEqualXYZ(X, Y, Z));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumEqualXYc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == Y + C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(X == Y + 5); // or problem.post(KNumEqualXyc(X, Y, 5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X == 5); // or problem.post(KNumEqualXc(X,5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumGreaterOrEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X >= C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X >= 3); // or problem.post(KNumGreaterOrEqualXc(X, 3));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumGreaterOrEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X >= Y + C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(X >= Y + 5); // or problem.post(KNumGreaterOrEqualXyc(X, Y, 5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumInputOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable in the input order.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KNumInputOrder(), KMaxToMin());
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
return the first uninstantiated variable in the order of creation
- getCopyPtr() → KNumVariableSelector *¶
return the first uninstantiated variable in the order of creation
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumLargestReducedCost(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumVariableSelectorThis variable selector selects the variable with biggest reduced cost in current LP solution of the provided linear relaxation solver.
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumLessOrEqualXc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X <= C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); // ... problem.post(X <= 3); // or problem.post(KNumLessOrEqualXc(X, 3));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumLinComb(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a Sum(ai.Xi) { <= , != , == } C constraint
Example :
KNumVarArray X(...); //... problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] == 3); // or problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] <= 3); // or problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] >= 3); // or problem.post(2 * X[1] + 3 * X[2] + 5 * X[3] + ... + 7 * X[n] != 3);
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- Equal = 0¶
Equality relation
- GreaterOrEqual = 1¶
Greater or Equal relation
- LessOrEqual = 3¶
Lest or Equal relation
- NotEqual = 2¶
Not equal relation
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumLowerOrEqualXyc(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X <= Y + C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(X <= Y + 5); // or problem.post(KNumLowerOrEqualXyc(X, Y, 5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumMiddle(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from the middle value in the domain of the variable.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(),KNumMiddle());
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(numVar)virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic :type intVar:
KNumVar:param intVar: the variable to selects a value for- selectNextValue(numVar: KNumVar) → double¶
virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic :type intVar:
KNumVar:param intVar: the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumNearestRelaxedValue(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumValueSelectorThis value selector chooses the value closest to the relaxed solution contained in the provided solver.
If the relaxed value for a KFloatVar variable is within its bounds, the selected value is simply the relaxed value. Otherwise, it is the upper or lower bound of the KFloatVar.
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumNearestValue(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that selects the nearest value from target in the domain of the variable .
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSplitDomain(KWidestDomain(), KNumNearestValue());
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic :type intVar:
KNumVar:param intVar: the variable to selects a value for- selectNextValue(intVar: KNumVar) → double¶
virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic :type intVar:
KNumVar:param intVar: the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumNonLinearComb(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class represents a constraint to propagate any non linear constraint of the form KNonLinearTerm COMPARATOR KNonLinearTerm.
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumObjectiveOptimalityChecker(maximize: bool, absoluteTolerance: double, relativeTolerance: double)¶
Bases:
kalis.KOptimalityToleranceCheckerAn OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with any type of KNumVar objective, which use both a relative and absolute difference criteria.
Methods:
isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj, bestBound)Check for the optimality tolearance
nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj)Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution.
- isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj: double, bestBound: double) → bool¶
Check for the optimality tolearance
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) –
bestBound (float) –
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true is the best solution is close enough - for some criteria - to the optimum
- nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj: double) → double¶
Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution. This prevent from storing too many solutions which are very similar.
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) – the best objective value of already found solutions.
- Return type
float
- Returns
a bound to set on the objective.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumSmallestDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumVariableSelectorSmallest domain variable selector
Methods:
selectNextVariable(numVarArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- selectNextVariable(numVarArray: KNumVarArray) → KNumVar *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumValueSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract interface class for value selection heuristic See also: KMaxToMin KMinToMax KMiddle KRandomValue KNearestValue
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic
- selectNextValue(intVar: KNumVar) → double¶
- virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic
- type intVar
- param intVar
the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumVar(*args)¶
Bases:
objectSuperclass of decision variables
Methods:
canBeInstantiatedTo(value)Return true if this variable can be instantiated to ‘value’
display(*args)Overload 1: Pretty printing
Return a copy of this object
returns the number of constraints where this variable appears
getIndex()Return the index of the variable
getInf()returns lower bound of this variable
returns true if the variable has been assigned a value, false otherwhise
returns the KProblem associated with this variable
getSup()returns upper bound of this variable
get target value
getValue()returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
Return the type of this variable :param KNumVar::IsKNumVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKIntVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKFloatVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar
instantiate(value)Instantiate the variable to value
isHidden()Return true iff this variable is hidden
setHidden(hidden)Hidden variable Y/N
setInf(value)set the lower bound to value
setName(name)Set the name of the variable
setSup(value)set the upper bound to value
setTarget(value)set the target value
useShaving(use)activate shaving Y/N
- IsKFloatVar = 2¶
Integer variables
- IsKIntVar = 1¶
Floating-point (continuous) variables
- IsKNumVar = 0¶
Numeric variables
- canBeInstantiatedTo(value: double) → bool¶
Return true if this variable can be instantiated to ‘value’
- display(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: Pretty printing
Overload 2: Pretty printing
- getCopyPtr() → KNumVar *¶
Return a copy of this object
- getDegree() → int¶
returns the number of constraints where this variable appears
- getIndex() → int¶
Return the index of the variable
- getInf() → double¶
returns lower bound of this variable
- getIsInstantiated() → bool¶
returns true if the variable has been assigned a value, false otherwhise
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
returns the KProblem associated with this variable
- getSup() → double¶
returns upper bound of this variable
- getTarget() → double¶
get target value
- getValue() → double¶
returns current instantiation of the variable (when the variable is not instantiated the returned value is undefined)
- instanceof() → int¶
Return the type of this variable :param KNumVar::IsKNumVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKIntVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar :param KNumVar::IsKFloatVar: for an instance of the class KNumVar
- instantiate(value: double const) → void¶
Instantiate the variable to value
- isHidden() → bool¶
Return true iff this variable is hidden
- setHidden(hidden: bool) → void¶
Hidden variable Y/N
- setInf(value: double) → void¶
set the lower bound to value
- setName(name: char const *) → void¶
Set the name of the variable
- setSup(value: double) → void¶
set the upper bound to value
- setTarget(value: double) → void¶
set the target value
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- useShaving(use: bool) → void¶
activate shaving Y/N
- class kalis.KNumVarArray¶
Bases:
kalis.numvarlistThis class implements an array of KNumVar.
Example :
KProblem p(...); KNumVarArray T; T += KIntVar(p, "X");
See also: KIntVar
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumVariableSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract interface class for variable selection heuristic.
- See also: KSmallestDomain KMaxDegree KSmallestMin KSmallestMax KLargestMin
KLargestMax KRandomVariable KSmallestDomDegRatio KMaxRegretOnLowerBound KMaxRegretOnUpperBound
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextVariable(numVarArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics
- selectNextVariable(numVarArray: KNumVarArray) → KNumVar *¶
- virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics
- param intVarArray
Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsAbsY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = |Y| constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXEqualsAbsY(X, Y));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsAtan2YZ(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = atan2(Y, Z) constraint. Atan2(Y, Z) is defined as follow :
atan(Y/Z) if Z > 0
atan(Y/Z) + PI if Z < 0 and Y >= 0
atan(Y/Z) - PI if Z < 0 and Y < 0
(+ PI / 2) if Z = 0 and Y > 0
(- PI / 2) if Z = 0 and Y < 0
undefined if Z = 0 and Y = 0
Domain of X variable is at least (-PI, PI].
Example :
KFloatVar X(...); KFloatVar Y(...); KFloatVar Z(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXEqualsAtan2YZ(X, Y, Z));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2020.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsLnY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = ln(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXEqualsLnY(X, Y));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsYArithPowC(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = Y ^ C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXEqualsYArithPowC(X, Y, 5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsYSquared(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = Y^2 constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // .. problem.post(KNumXEqualsYSquared(X, Y));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsYTimesC(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X = Y * C constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXEqualsYTimesC(X, Y, 5));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXEqualsYTimesZ(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == Y * Z constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); KNumVar Z(...); // ... problem.post(X == Y * Z); // or problem.post(KNumXEqualsYTimesZ(X, Y, Z));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorACosY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} acos(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorACosY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorASinY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} asin(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorASinY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorATanY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} atan(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorATanY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorCosY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} cos(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorCosY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorExpY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} exp(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorExpY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorLnY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} ln(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorLnY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorSinY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} sin(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorSinY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KNumXOperatorTanY(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X {==,<=,>=} tan(Y) constraint
Example :
KNumVar X(...); KNumVar Y(...); // ... problem.post(KNumXOperatorTanY(X, Y, GEQ));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KOccurTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTermThis class represent an expression of type occur(target,lvars) where target is the value for wich we want to restrict the number of occurence(s) in the lVars array of variables.
Example :
KProblem p(...); KIntVar countVar(...); KIntVarArray X(...); KOccurTerm occurTerm(3,X); // posting the constraint "the number of occurences of the value 3 in the // X variable array must be less than the value of countVar p.post(occurTerm <= countVar); // or p.post(occurTerm <= 5);
See also: KConstraint KOccurrence
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getLvars()return the array of variables in wich we want to restrict the number of occurences of the target value
return the target value
- getLvars() → KIntVarArray *¶
return the array of variables in wich we want to restrict the number of occurences of the target value
- getTarget() → int¶
return the target value
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KOccurrence(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates an occurence constraint of a value in a list of variables
Example :
KIntVarArray Tab(...); KIntVar countVar(...); problem.post( KOccurTerm(0,Tab) <= 5 ); // No more than 5 occurence of 0 in Tab problem.post( KOccurTerm(1,Tab) < 5 ); // No more than 4 occurence of 1 in Tab problem.post( KOccurTerm(2,Tab) >= countVar ); // No Less than countVar occurence of 2 in Tab problem.post( KOccurTerm(3,Tab) > countVar ); // No Less than countVar occurence of 3 in Tab
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KOptimalityToleranceChecker(*args, **kwargs)¶
Bases:
objectThis interface sets a framework for objects providing method to check if the current solution is close enough to the optimum, and, if not, to give a new bound to set on the objective variable.
Methods:
isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj, bestBound)Check for the optimality tolearance
nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj)Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution.
- isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj: double, bestBound: double) → bool¶
Check for the optimality tolearance
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) –
bestBound (float) –
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true is the best solution is close enough - for some criteria - to the optimum
- nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj: double) → double¶
Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution. This prevent from storing too many solutions which are very similar.
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) – the best objective value of already found solutions.
- Return type
float
- Returns
a bound to set on the objective.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KOptimizeListener(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KParallelSolverEventListener- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KOptimizeWithISListener(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KParallelSolverEventListener- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KParallelBranchingScheme(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeParallel branching scheme
Example:
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KParallelBranchingScheme(KSplitDomain(KSmallestDomain(), KMaxToMin()));
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KParallelSolverEventListener(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KSolverEventListenerMethods:
branchGoDown(thread)Called after each branchGoDown event
branchGoUp(thread)Called after each branchGoUp event
nodeExplored(thread)Called after constraint propagation in each node
Ask user for termination at each node
- branchGoDown(thread: int) → void¶
Called after each branchGoDown event
- branchGoUp(thread: int) → void¶
Called after each branchGoUp event
- nodeExplored(thread: int) → void¶
Called after constraint propagation in each node
- stopComputations() → bool¶
Ask user for termination at each node
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KPathOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorA variable selector based on a path order.
The initial successor is chosen randomly. Then, the following chosen variable will the designated successor in the previous branching choice.
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
return the first uninstantiated variable in the order of creation
- getCopyPtr() → KVariableSelector *¶
return the first uninstantiated variable in the order of creation
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KProbe(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeProbe branching scheme
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KProbeDisjunction(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeProbeDisjunction branching scheme
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KProblem(*args)¶
Bases:
objectConstraint satisfaction and optimization problems include variables, constraints ( modeling entities ) and might have solutions after search. Such problems are represented in Artelys Kalis by objects of the class KProblem. These objects are holding the modeling entities objects, the solutions objects and the objective variable object and the sense of the optimization.
These elements are store in a KProblem object which is declared as follows :
KProblem myProblem(mySession,"myProblem");
This statement creates a KProblem object named myProblem and held by the KSession object mySession.
For using Kalis parallel search algorithms, it is necessary to create multiple instances of the problem to be solved. This can be done by using the following KProblem declaration :
KProblem myProblem(mySession,"myProblem", n);
This statement creates a KProblem object named myProblem, storing n problem instances and held by the KSession object mySession.
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Collects all solutions from subproblem instances
Return the minimal conflict set for this problem
Returns best solution found if problem has an objective, last solution found otherwise
getInstanceOf(*args)Overload 1:
getLinearRelaxation(*args)Overload 1:
return the number of constraints in the problem
Return the number of solutions already found for this problem
return the number of variables in the problem
Return the Objective variable.
Return a measure of the problem size
getSimpleLinearRelaxation(rtype)Get an automatic relaxation of all the constraints in the array provided as an argument.
getSolution(*args)Overload 1: Returns last solution found
Get solution container
Returns true is the problem has an objective
Do some internal optimization to solve faster the problem
pretty printing of the disjunctions involved in the problem
printMinimalConflictSet([ctx, pfp, verboseLebel])Print a minimal conflict set for this problem.
pretty printing of the variables of the problem
Returns true iff at least one solution was found for this problem
Propagate changes in the problem, returns true if the problem is proved inconsistent, false otherwise
setLogLevel(logLevel)Set the output log level
setObjective(*args)Overload 1: Set the objective function to the problem
setPrintFunctionPointer(ctx, pfp)Set the print function pointer
setSense(sense)Sets optimization sense
trace(logLevel, format)Trace ‘printf’ style function
- HIGH = 3¶
Display all information
- INTERNALDEBUG = 4¶
Display all information (including internal debug information)
- LOW = 1¶
Display errors and basic search information
- MEDIUM = 2¶
Display errors, warnings and detailed search information
- Maximize = 1¶
Maximize objective variable
- Minimize = 0¶
Minimize objective variable
- NONE = 0¶
Display no information, except requested by user (e.g. call to print() method)
- collectAllSolutions() → void¶
Collects all solutions from subproblem instances
- computeMinimalConflictSet() → kalis.KConstraintArray¶
Return the minimal conflict set for this problem
- getBestSolution() → KSolution &¶
Returns best solution found if problem has an objective, last solution found otherwise
- getInstanceOf(*args) → KBranchingSchemeGroupArray *¶
Overload 1:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KIntVar object. The copy is already managed.
Overload 2:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KFloatVar object. The copy is already managed.
Overload 3:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KIntVarArray object. The copy is already managed.
Overload 4:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KNumVarArray object. The copy is already managed.
Overload 5:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KTaskArray object. The copy is already managed.
Overload 6:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KDisjunctionArray object. The copy is already managed.
Overload 7:
Returns mono-instance copy of multi-instance KBranchingSchemeGroupArray object. The copy is already managed.
- getLinearRelaxation(*args) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Overload 1:
Get an automatic relaxation of all the posted constraints (if relaxation available).
See the reference manual page of a constraint to check the available options. All constraints for which a relaxation is available provide at least strategies 0 and 1 : “0” is supposed to be tighter and “1” lighter. Automatic relaxation 0 is LP by default and automatic relaxation 1 is MIP by default, but you can change the type (global / continuous) of the variables using setGlobal and setAllGlobal of KLinearRelaxation.
- Parameters
strategy (int, optional) – parameter to choose the relaxation you want to use.
Overload 2:
Get an automatic relaxation of all the constraints in the array provided as an argument.
- Parameters
constraintClassArray (int) – types of constraints you want to relax (must have nbElem elements)
strategyArray (int) – strategy for each constraint (must have nbElem elements)
nbElem (int) – number of elements in the arrays
- getNumberOfConstraints() → int¶
return the number of constraints in the problem
- getNumberOfSolutions() → int¶
Return the number of solutions already found for this problem
- getNumberOfVariables() → int¶
return the number of variables in the problem
- getObjective() → kalis.KNumVar¶
Return the Objective variable.
Throws an ArtelysException if the problem has no objective.
- getProblemSize() → double¶
Return a measure of the problem size
- getSimpleLinearRelaxation(rtype: int) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Get an automatic relaxation of all the constraints in the array provided as an argument.
- Parameters
constraintArray – constraints you want to relax (must have nbElem elements)
strategyArray – strategy for each constraint (must have nbElem elements)
nbElem – number of elements in the arrays
- getSolution(*args) → KSolution &¶
Overload 1: Returns last solution found
Overload 2: Returns the solution numbered ‘index’
- getSolutionContainer() → KSolutionContainer &¶
Get solution container
- hasObjective() → bool¶
Returns true is the problem has an objective
- optimizeInternalRepresentation() → void¶
Do some internal optimization to solve faster the problem
- printDisjunctionsStates() → void¶
pretty printing of the disjunctions involved in the problem
- printMinimalConflictSet(ctx: void * = None, pfp: PrintFunctionPtr * = None, verboseLebel: int = 1) → void¶
Print a minimal conflict set for this problem.
- Parameters
ctx (void, optional) – printing context
pfp (PrintFunctionPtr, optional) – pointer to a printing function
verboseLevel – verbosity level of the calculations
- printVariablesStates() → void¶
pretty printing of the variables of the problem
- problemIsSolved() → bool¶
Returns true iff at least one solution was found for this problem
- propagate() → bool¶
Propagate changes in the problem, returns true if the problem is proved inconsistent, false otherwise
- setLogLevel(logLevel: KProblem::LogLevel) → void¶
Set the output log level
- setObjective(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: Set the objective function to the problem
Overload 2: Set the objective function to the problem as an continuous variable
- setPrintFunctionPointer(ctx: void *, pfp: PrintFunctionPtr *) → void¶
Set the print function pointer
- setSense(sense: int) → void¶
Sets optimization sense
- Parameters
sense (int) – Maximization or Minimization
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- trace(logLevel: KProblem::LogLevel, format: char const *) → void¶
Trace ‘printf’ style function
- class kalis.KRandomValue(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KValueSelectorThis class implements a value selector that selects a value at random in the domain of the variable.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(),KRandomValue());
See also: KValueSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextValue(intVar)Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- Parameters
intVar (
KIntVar) – the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KRandomVariable(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects an uninstantiated variable at random.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KRandomVariable(),KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KRelation(*args, **kwargs)¶
Bases:
objectA relation term between an expression and constants.
Methods:
add(relation)Add all the terms of the given relation (no reduction).
isSatisfied(sol)Is the linear relation satisfied for this instantiation ?
setComparator(cmp)Set comparator based on argument and discards the bounds that are no longer relevant.
- add(relation: KRelation) → void¶
Add all the terms of the given relation (no reduction).
- type relation
- param relation
the relation to add
- isSatisfied(sol: kalis.KHybridSolution) → bool¶
Is the linear relation satisfied for this instantiation ?
- type sol
- param sol
hybrid solution to check
- setComparator(cmp: KRelation::Comparator) → void¶
Set comparator based on argument and discards the bounds that are no longer relevant.
- type cmp
int
- param cmp
comparator to be applied in the linar relation
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KRelativeToleranceOptimalityChecker(maximize: bool, tolerance: double)¶
Bases:
kalis.KOptimalityToleranceCheckerAn OptimalityToleranceChecker to use with any type of KNumVar objective, which use a relative difference criteria.
Methods:
isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj, bestBound)Check for the optimality tolearance
nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj)Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution.
- isGoodEnough(bestSolutionObj: double, bestBound: double) → bool¶
Check for the optimality tolearance
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) –
bestBound (float) –
- Return type
boolean
- Returns
true is the best solution is close enough - for some criteria - to the optimum
- nextBoundToTry(bestSolutionObj: double) → double¶
Returns a bound to set on the objective, in order to look for solution which are not too close from the current best known solution. This prevent from storing too many solutions which are very similar.
- Parameters
bestSolutionObj (float) – the best objective value of already found solutions.
- Return type
float
- Returns
a bound to set on the objective.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KRelaxationSolver(*args, **kwargs)¶
Bases:
objectThis class is intended as a superclass for linear relaxation solvers.
- Such a solver must be provided with
a linear relaxation (KLinearRelaxation)
an objective variable (KNumVar)
a sense for optimization (KProblem::Sense).
- It relies on a LP/MIP solver to provide the following information:
a value (a bound for the relaxed problem, cf method getBound())
a solution, possibly not feasible for the original problem, but which can be used to guide the search for a feasible solution
if the problem is LP, reduced costs (that can be used for instance in the “reduced cost fixing” procedure).
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
generateCuts(relaxation)Cut generation
Get the resolution algorithm
getBound()Get the (lower for minimization, upper for maximization) bound computed by solve().
Get the configurator of a KRelaxationSolver
getLPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
getMIPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
Get the total number of global variables.
Get the amount of time spent during the last call to solve().
Get the total amount of time spent in computations since the object was built.
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
isGlobal(*args)Overload 1: Return true if the given variable is set as global
setAlgorithm(alg)Set the resolution algorithm
setAllGlobal(isGlobal)(Un)set variables as global.
setConfigurator(configurator)Set the configurator of a KRelaxationSolver
setGlobal(*args)Overload 1:
setIndicatorsGlobal(isGlobal)Set all indicator auxiliary variables global.
setMaxMIPSol(arg2)Stop global search after maxMIPSol feasible solutions found.
setObjective(var)Set objective variable.
setSense(arg2)Set the sense of optimization (maximize, minimize).
setSolveAsMIP(flag)Set this flag to 0 if you want to solve as LP a linear relaxation containing global entities (1 is the default).
solve()Solve the relaxed optimization problem.
Return true if the flag “solveAsMIP” is set
- generateCuts(relaxation: KLinearRelaxation) → void¶
Cut generation
- getAlgorithm() → int¶
Get the resolution algorithm
- getBound() → double¶
Get the (lower for minimization, upper for maximization) bound computed by solve().
- Note that :
solve() method must be called before the getBound() method
moreover, the return code provided by solve() must be checked before using the value returned by getBound().
- getConfigurator() → KRelaxationSolverConfigurator *¶
Get the configurator of a KRelaxationSolver
- getLPSolution(*args) → double¶
Overload 1:
Get the current LP solution for a given KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose value is checked- Return type
float
- Returns
value of var in the current MIP solution
- Overload 2:
Get the current relaxed solution for a given KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose value is checked- Return type
float
- Returns
value of var in the current solution
- getMIPSolution(*args) → double¶
Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a given KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose solution is checked- Return type
float
- Returns
value of var in the current MIP solution
Overload 2:
Get the current MIP solution for a given KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose solution is checked- Return type
float
- Returns
value of var in the current MIP solution
- getNumberGlobals() → int¶
Get the total number of global variables.
- getTimeSpentInLastComputation() → double¶
Get the amount of time spent during the last call to solve().
- getTotalTimeSpentInComputation() → double¶
Get the total amount of time spent in computations since the object was built.
- instantiateNumVarToCurrentSol(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- instantiateNumVarsToCurrentSol() → void¶
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- isGlobal(*args) → bool¶
Overload 1: Return true if the given variable is set as global
Overload 2: Return true if the given variable is set as global
- setAlgorithm(alg: int) → void¶
Set the resolution algorithm
- setAllGlobal(isGlobal: bool) → void¶
(Un)set variables as global.
Set or unset as “global” all KIntVar and KAuxVar with global type (note that a KFloatVar variables are not modified, since it would make little sense to set them global.)
- Parameters
isGlobal (boolean) – new global status
- setConfigurator(configurator: KRelaxationSolverConfigurator) → void¶
Set the configurator of a KRelaxationSolver
- setGlobal(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Set (or unset) a KIntVar as global.
- Parameters
var (
KIntVar) – variable to modifyisGlobal (boolean) – new global status
Overload 2:
Set (or unset) a KAuxVar global.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable to checkisGlobal (boolean) – new global status
- setIndicatorsGlobal(isGlobal: bool) → void¶
Set all indicator auxiliary variables global.
- Parameters
isGlobal (boolean) – new global status
- setMaxMIPSol(arg2: int) → void¶
Stop global search after maxMIPSol feasible solutions found.
0 for no limit, this is the default. If the limit is low, this is likely to cause optimization to end before optimality.
- setObjective(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Set objective variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the new objective variable
- setSense(arg2: KProblem::Sense) → void¶
Set the sense of optimization (maximize, minimize).
- Parameters
sense – new sense for optimization
- setSolveAsMIP(flag: bool) → void¶
Set this flag to 0 if you want to solve as LP a linear relaxation containing global entities (1 is the default).
- Parameters
flag (boolean) – New flag value
Deprecated: The new way of doing this is to use a configurator
- solve() → int¶
Solve the relaxed optimization problem.
- This methods returns the following error codes :
0 : optimal
1 : infeasible
2 : search interrupted prematurely, a solution was found
3 : search interrupted prematurely, no solution was found
4 : other problem
- solveAsMIP() → bool¶
Return true if the flag “solveAsMIP” is set
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KResource(*args)¶
Bases:
object- Resources (machines, raw material etc) can be of two different types :
Disjunctive when the resource can process only one task at a time (represented by the class KUnaryResource).
Cumulative when the resource can process several tasks at the same time (represented by the class KDiscreteResource).
Traditional examples of disjunctive resources are Jobshop problems, cumulative resources are heavily used for the Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP). Note that a disjunctive resource is semantically equivalent to a cumulative resource with maximal capacity one and unit resource usage for each task using this resource but this equivalence does not hold in terms of constraint propagation.
The following schema shows an example with three tasks A,B and C executing on a disjunctive resource and on a cumulative resource with resource usage 3 for task A, 1 for task B and 1 for task C :

- Tasks may require, provide, consume and produce resources :
A task requires a resource if some amount of the resource capacity must be made available for the execution of the activity. The capacity is renewable which means that the required capacity is available after the end of the task.
A task provides a resource if some amount of the resource capacity is made available through the execution of the task. The capacity is renewable which means that the provided capacity is available only during the execution of the task.
A task consumes a resource if some amount of the resource capacity must be made available for the execution of the task and the capacity is non-renewable which means that the consumed capacity if no longer available at the end of the task.
A task produces a resource if some amount of the resource capacity is made available through the execution of the task and the capacity is non-renewable which means that the produced capacity is definitively available after the starting of the task.
Methods:
addIdleTimeSteps(idleTimeSteps)Add idle time steps to this resource.
close()Close this resource
display(*args)Overload 1: Pretty printing of this resource
Return a copy of this object
Return the KIntVar representing the difference between LST and EST variables
Return the KIntVar representing the earliest starting time of all the tasks executing on this resource
getIndex()Return the unique index of the resource
Return the capacity at timestep 0
Return the initial resource stock at time step t
Return true if all the tasks on this resource are fixed
Return the KIntVar representing the latest completion time of all the tasks executing on this resource
Return the initial resource storage at time step 0
Return the initial resource storage at time step t
Return the initial resource stock at time step t
Return the minimum tasks duration
getName()Return the name of this resource
Return the number of tasks using this resource
Return the KIntVar representing the slack for this resource
getStartBasedDuration(task, start)When declaring a task having a start based duration (through setStartBasedDuration or setDurationWithIdleTimes), this method will return the actual duration of task if it begins at start timestep.
getTask(index)Return task with index ‘index’ in this resource
isIdleTimeStep(timestep)Return true IFF timestep is an idle timestep for this resource
printResourceGantt(*args)Overload 1:
printTaskGantt(*args)Overload 1:
setDuration(task, duration)Set the duration of the task if the task is assigned to this resource.
setDurationWithIdleTimes(task, duration, …)Set a duration constraint conditional to some idle time windows and on the task assignment.
setInitialCapacityBetween(t0, t1, capa)Set the initial resource stock between time steps t0 and t1 to capa
setMaxAvailabilityBetween(t0, t1, capa)Set the initial resource stock between time steps t0 and t1 to capa
setMinUsageBetween(t0, t1, capa)Set the initial resource stock between time steps t0 and t1 to capa
setName(name)Set the name of this resource
setSetupTime(task1, task2, afterT1[, afterT2])Add a coupled setup time between two tasks for the current resource.
setStartBasedDuration(task, t1, t2, duration)Set a duration computed from the value taken by the start variable if the task is assigned to this resource.
updateDurationWithIdleTimes(task, t1, t2, …)Update the current start-based duration constraint with a new idle window.
- addIdleTimeSteps(idleTimeSteps: KIntArray) → void¶
Add idle time steps to this resource.
During “idle time steps”, the resource does nothing, i.e. its usage (consumption, production, …) for any task T is set to zero and delayed one time step after (if T is executed on this very time step).
- close() → void¶
Close this resource
- display(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: Pretty printing of this resource
Overload 2: Pretty printing of this resource with a print function pointer
- getCopyPtr() → KResource *¶
Return a copy of this object
- getDURVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return the KIntVar representing the difference between LST and EST variables
- getESTVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return the KIntVar representing the earliest starting time of all the tasks executing on this resource
- getIndex() → int¶
Return the unique index of the resource
- getInitialCapacity() → int¶
Return the capacity at timestep 0
- getInitialCapacityAt(t: int) → int¶
Return the initial resource stock at time step t
- getIsInstantiated() → bool¶
Return true if all the tasks on this resource are fixed
- getLCTVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return the KIntVar representing the latest completion time of all the tasks executing on this resource
- getMaxAvailability() → int¶
Return the initial resource storage at time step 0
- getMaxAvailabilityAt(t: int) → int¶
Return the initial resource storage at time step t
- getMinUsageAt(t: int) → int¶
Return the initial resource stock at time step t
- getMinimumTasksDuration() → int¶
Return the minimum tasks duration
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this resource
- getNumberOfTasks() → int¶
Return the number of tasks using this resource
- getSlackVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return the KIntVar representing the slack for this resource
- getStartBasedDuration(task: kalis.KTask, start: int) → int¶
When declaring a task having a start based duration (through setStartBasedDuration or setDurationWithIdleTimes), this method will return the actual duration of task if it begins at start timestep.
If the start value is not available in the start-based duration domain, -1 will be returned.
See also: setDurationWithIdleTimes setDurationWithIdleTimes setDuration
Since: 13.2.1
- getTask(index: int) → KTask *¶
Return task with index ‘index’ in this resource
- isIdleTimeStep(timestep: int) → bool¶
Return true IFF timestep is an idle timestep for this resource
- printResourceGantt(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Pretty printing the resource Gantt chart in the console
- Parameters
s (
KSolution) – Given scheduling solutionfactor (int) – distortion factor to print the Gantt in the console
- Overload 2:
Pretty printing the resource Gantt chart
- printTaskGantt(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Pretty printing the task Gantt chart in the console
- Parameters
s (
KSolution) – Given scheduling solutionfactor (int) – distortion factor to print the Gantt in the console
- Overload 2:
Pretty printing the task Gantt chart
- setDuration(task: KTask, duration: int) → void¶
Set the duration of the task if the task is assigned to this resource.
If the task is assigned to this resource, the duration variable will take the given duration value:
(task.assign(r) = 1) => task.duration = duration
Note that this is equivalent than setting start based duration with one possible value.
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – The concerned taskduration (int) – The actual duration taken if the task is allocated to the resource
See also: getStartBasedDuration setDurationWithIdleTimes
Since: 13.2.1
- setDurationWithIdleTimes(task: KTask, duration: int, idleStarts: KIntArray, idleEnds: KIntArray, allowStartInIdle: bool) → void¶
Set a duration constraint conditional to some idle time windows and on the task assignment.
If the task is assigned to this resource, the then the following statements will be enforced.
- From the given nominal duration, the duration variable will be constrained to take the following values:
duration if the task does not intersect any idle time window
duration increased by total length of the intersecting idle time windows
For example, if a resource is idle on two time windows [s1, e1) and [s2, e2), then this method declares that the tasks intersecting those idle times windows will be extended.
If a task T1 starts before s1 but its duration make it intersect [s1, e1), then its duration variable will be T1.duration = duration + e1 - s1
If a task T2 starts before s1 but its updated duration make it intersect [s1, e1) and [s2, e2), then its duration variable will be T2.duration = duration + (e1 - s1) + (e2 - s2)
If a task T3 starts in the idle interval [s1, e1), then its duration variable will be T3.duration = duration + (e1 - T3.start)
If a task T4 starts in the idle interval [s1, e1) and its updated duration make it intersect [s2, e2) then its duration variable will be T4.duration = duration + (e1 - T4.start) + (e2 - s2)
Note that if allowStartInIdle is false then T3 and T4 cases will be forbidden. The idle time windows can be given in any order and can be intersecting (union is made). Note that idle time windows are a strict end interval (end time step is not in the interval). If the nominal duration is dependent on the start time of the task, the updateDurationWithIdleTimes method can be used instead.
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – The concerned taskduration (int) – The expected nominal duration of the task without idle times
idleStarts (
KIntArray) – The idle time windows start (must be of same length as idleEnds)idleEnds (
KIntArray) – The idle time windows end (must be of same length as idleStarts)allowStartInIdle (boolean) – If true, the task will be able to start in an idle time window.
See also: setStartBasedDuration getStartBasedDuration setDuration
Since: 13.2.1
- setInitialCapacityBetween(t0: int, t1: int, capa: int) → void¶
Set the initial resource stock between time steps t0 and t1 to capa
- Parameters
t0 (int) – start of the interval
t1 (int) – end of the interval
capa (int) – initial resource stock
- setMaxAvailabilityBetween(t0: int, t1: int, capa: int) → void¶
Set the initial resource stock between time steps t0 and t1 to capa
- Parameters
t0 (int) – start of the interval
t1 (int) – end of the interval
capa (int) – initial resource stock
- setMinUsageBetween(t0: int, t1: int, capa: int) → void¶
Set the initial resource stock between time steps t0 and t1 to capa
- Parameters
t0 (int) – start of the interval
t1 (int) – end of the interval
capa (int) – initial resource storage
- setName(name: char const *) → void¶
Set the name of this resource
- setSetupTime(task1: KTask, task2: KTask, afterT1: int, afterT2: int = 0) → void¶
Add a coupled setup time between two tasks for the current resource. This means that if the two given tasks are assigned to the resource, then the start of the second task must be after the end of the first task plus the given duration :
r.assign(t1) and r.assign(t2) => t1.end + d <= t2.start
- setStartBasedDuration(task: KTask, t1: int, t2: int, duration: int) → void¶
Set a duration computed from the value taken by the start variable if the task is assigned to this resource.
If the task is assigned to this resource, the duration variable will take the given duration value if the start of the task is between the given interval:
(t1 <= task.start <= t2) and (task.assign(r) = 1) => task.duration = duration
This method can be called successively to specify different durations on different intervals. Calling successively with intersectings intervals will override existing values on the intersection. Also, propagation should not be called between sucessive calls. Note: All values not included in any of the given intervals will be forbidden for the start variable.
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – The concerned taskt1 (int) – The first interval extremity
t2 (int) – The second interval extremity
duration (int) – The actual duration taken if the start is in the given interval
See also: getStartBasedDuration setDurationWithIdleTimes setDuration
Since: 13.2.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- updateDurationWithIdleTimes(task: KTask, t1: int, t2: int, allowStartInIdle: bool) → void¶
Update the current start-based duration constraint with a new idle window.
When having previously set a start-based duration (through setDuration or setStartBasedDuration), this method will update the start-based durations to simulate idle times windows.
Warning: when adding several idle time windows, they must be added in increasing time order and time windows must be disjoints. If not done this way, durations might be inconsistent. Also, propagation should not be called between sucessive calls.

resource.setDuration(task, 13); // Adding a first idle time window resource.updateDurationWithIdleTimes(task, 10, 15); int d = resource.getStartBasedDuration(task, 7); // d = 18 // Adding the second idle time window resource.updateDurationWithIdleTimes(task, 23, 31); d = resource.getStartBasedDuration(task, 7); // d = 26
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – The concerned taskt1 (int) – The idle time window start
t2 (int) – The idle time window end
allowStartInIdle (boolean) – If true, the task will be able to start in the idle time window.
See also: getStartBasedDuration setDuration setStartBasedDuration setDurationWithIdleTimes
Since: 13.2.1
- class kalis.KResourceArray(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.resourcelistThis class implements an array of KResource
Example :
KSchedule s(...); // R is an array of KResource R0 R1 R2 R3 R4 KResourceArray R(s,5,0,10,"T");
See also: KResource
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KResourceSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectResource selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextResource(resArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KResourceSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextResource(resArray: KResourceArray) → KResource *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KResourceUsage(*args)¶
Bases:
objectA KResourceUsage object can be used to describe the a specific usage of a given resource.
Methods:
display(*args)Overload 1: Pretty printing
- display(*args) → void¶
Overload 1: Pretty printing
Overload 2: Pretty printing
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KResourceUsageArray¶
Bases:
kalis.resourceusagelistUtility container for storing a list of KResourceUsage
See also: KResourceUsage
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSchedule(p: KProblem, name: char const *, timeMin: int, timeMax: int)¶
Bases:
objectScheduling and planning problems are concerned with determining a plan for the execution of a given set of tasks.
The objective may be to generate a feasible schedule that satisfies the given constraints (such as sequence of tasks or limited resource availability) or to optimize a given criterion such as the makespan of the schedule.
Artelys-Kalis defines several aggregate modeling objects to simplify the formulation of standard scheduling problems like tasks,resources and schedule objects. by the types KUnaryResource and KDiscreteResource. When working with these scheduling objects it is often sufficient to state the objects and their properties, such as task duration or resource use; the necessary constraint relations are set up automatically by Artelys-Kalis (referred to as implicit constraints).
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
addRelaxationSolver(solver)Add a relaxation solver to be used during the resolution process
addResource(resource)Add a resource to this schedule
addTask(task)Add a task to this schedule
close()Close this schedule (no tasks or resources can be added after this
display(*args)Overload 1:
Find a initial heuristic solution for this schedule
Find the optimal solution for this schedule
getDblAttrib(attribute)Return the value of a double attribute
getDblControl(control)Return the value of a double control
Return a pointer to the durations array of all the tasks in this schedule
Return a pointer to the end dates array of all the tasks in this schedule
getIntAttrib(attribute)Return the value of an int attribute
getIntControl(control)Return the value of an int control
Return a reference to the objective variable representing the makespan of this schedule
Return the number of resources in this schedule
Return the number of tasks in this schedule
Return a reference to the objective variable of this schedule
Return the problem associated to this schedule
getResource(nbResource)Return a pointer to the resource number ‘nbResource’ in this schedule in the input order
Return a pointer to the list of resource of this schedule
Return the solver object used to optimize the schedule
Return a pointer to the start dates array of all the tasks in this schedule
getTask(nbTask)Return a pointer to the task number ‘nbTask” in the input order
Return a pointer to the list of tasks of this schedule
Return the maximal time horizon of this schedule
Return the minimal time horizon of this schedule
isClosed()Return true if the schedule is closed
Find suboptimal solutions for this schedule using a local search algorithm.
optimize()Launch the optimization phase
printRessourcesGantt(sol, factor)Pretty printing of the solution of this schedule
setDblAttrib(attribute, value)Set the value of a double attribute
setDblControl(control, value)Set the value of a double control
setFunctionPointers(asyncfunc, sol, nodes, …)Set the callback functions to call when the schedule is optimized
setIntAttrib(attribute, value)Set the value of an int attribute of the solver
setIntControl(control, value)Set the value of an int control of the solver
setObjective(*args)Overload 1:
setTimeMax(timemax)Setting the maxiaml horizon timestep
setTimeMin(timemin)Setting the minimal horizon timestep
- Inconsistent = 0¶
Schedule is inconsistent
- Optimal = 2¶
Schedule is feasible and optimal
- Suboptimal = 1¶
Schedule is feasible
- addRelaxationSolver(solver: KLinearRelaxationSolver) → void¶
Add a relaxation solver to be used during the resolution process
- addResource(resource: KResource) → void¶
Add a resource to this schedule
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resource to add to this schedule
- close() → void¶
Close this schedule (no tasks or resources can be added after this
- display(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Pretty printing of the schedule
Overload 2:
Pretty printing of the schedule
- findInitialSolution() → int¶
Find a initial heuristic solution for this schedule
Return Inconsistent if this schedule has no solution. Return Suboptimal if the heuristic solution is subobtimal. Return Optimal if the heuristic solution is optimal.
- findOptimalSolution() → int¶
Find the optimal solution for this schedule
Return Inconsistent if this schedule has no solution. Return Optimal if the heuristic solution is optimal
- getDblAttrib(attribute: KSolver::DblAttrib) → double¶
Return the value of a double attribute
- Parameters
attribute (int) – double attribute to retrieve
See also: DblAttrib
- getDblControl(control: KSolver::DblControl) → double¶
Return the value of a double control
- Parameters
control (int) – double control to retrieve
See also: DblControl
- getDurationsArray() → KIntVarArray *¶
Return a pointer to the durations array of all the tasks in this schedule
- getEndDatesArray() → KIntVarArray *¶
Return a pointer to the end dates array of all the tasks in this schedule
- getIntAttrib(attribute: KSolver::IntAttrib) → int¶
Return the value of an int attribute
- Parameters
attribute (int) – integer attribute to retrieve
See also: IntAttrib
- getIntControl(control: KSolver::IntControl) → int¶
Return the value of an int control
- Parameters
control (int) – integer control to retrieve
See also: IntControl
- getMakeSpan() → KIntVar &¶
Return a reference to the objective variable representing the makespan of this schedule
- getNumberOfResources() → int¶
Return the number of resources in this schedule
- getNumberOfTasks() → int¶
Return the number of tasks in this schedule
- getObjective() → KNumVar &¶
Return a reference to the objective variable of this schedule
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
Return the problem associated to this schedule
- getResource(nbResource: int) → KResource *¶
Return a pointer to the resource number ‘nbResource’ in this schedule in the input order
- getResourceArray() → KResourceArray *¶
Return a pointer to the list of resource of this schedule
- getSolver() → KSolver *¶
Return the solver object used to optimize the schedule
- getStartDatesArray() → KIntVarArray *¶
Return a pointer to the start dates array of all the tasks in this schedule
- getTask(nbTask: int) → KTask *¶
Return a pointer to the task number ‘nbTask” in the input order
- getTaskArray() → KTaskArray *¶
Return a pointer to the list of tasks of this schedule
- getTimeMax() → int¶
Return the maximal time horizon of this schedule
- getTimeMin() → int¶
Return the minimal time horizon of this schedule
- isClosed() → bool¶
Return true if the schedule is closed
- localOptimization() → int¶
Find suboptimal solutions for this schedule using a local search algorithm.
Return Inconsistent if this schedule has no solution. Return Suboptimal if the heuristic solution is suboptimal.
- optimize() → int¶
Launch the optimization phase
- printRessourcesGantt(sol: KSolution, factor: int) → void¶
Pretty printing of the solution of this schedule
- setDblAttrib(attribute: KSolver::DblAttrib, value: double) → void¶
Set the value of a double attribute
- Parameters
attribute (int) – the double attribute to set
value (float) – value of the attribute
See also: DblAttrib
- setDblControl(control: KSolver::DblControl, value: double) → void¶
Set the value of a double control
- Parameters
control (int) – the double control to set
value (float) – value of the control
See also: DblControl
- setFunctionPointers(asyncfunc: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, sol: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, nodes: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, goup: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, godown: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, param: void *) → void¶
Set the callback functions to call when the schedule is optimized
- Parameters
asyncfunc (int) – the callback to call to stop the optimization process
sol (int) – the callback to call when a solution has been found
nodes (int) – the callback to call when a node is created
goup (int) – the callback to call when a branch has been fully explored
godown (int) – the callback to call when a branch is explored
- setIntAttrib(attribute: KSolver::IntAttrib, value: int) → void¶
Set the value of an int attribute of the solver
- Parameters
attribute (int) – the int attribute to set
value (int) – the value of the attribute
See also: IntAttrib
- setIntControl(control: KSolver::IntControl, value: int) → void¶
Set the value of an int control of the solver
- Parameters
control (int) – the int control to set
value (int) – the value of the control
See also: IntControl
- setObjective(*args) → void¶
Overload 1:
Set the objective variable for this schedule as a KFloatVar
- Parameters
obj (
KFloatVar) – the objective variable for this schedule as a KFloatVar
Overload 2:
Set the objective variable for this schedule as a KIntVar
- Parameters
the – objective variable for this schedule as a KIntVar
- setTimeMax(timemax: int) → void¶
Setting the maxiaml horizon timestep
- setTimeMin(timemin: int) → void¶
Setting the minimal horizon timestep
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSession(*args)¶
Bases:
objectNothing can be done in Artelys Kalis outside a KSession object. All the problems stated and solved must be held by such an object : for this reason the creation of a KSession object is the first thing to do at the beginning of the program.
- The KSession class has one main functionality :
license checking : when created, the KSession object will look for a valid license of the software
The syntax for the creation of a KSession object is the following :
KSession mySession(false);
This statement creates a KSession object variable named mySession with no printing of the banner. We could have created our KSession using this syntax :
KSession mySession;
In this case, the banner would have been printed.
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return current version of library
- getVersion() → float¶
Return current version of library
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSettleDisjunction(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeKSettleDisjunction branching scheme
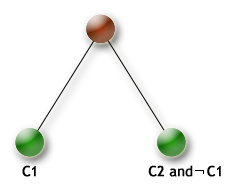
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSettleDisjunction();
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestDomDegRatio(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the smallest ratio domain size / degree in the constraint graph.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomDegRatio(),KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the smallest domain.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KSmallestDomain(),KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestEarliestCompletionTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorSmallest Earliest Completion time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestEarliestStartTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorSmallest Earliest Start time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)Return a copy of this task selector
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestLatestCompletionTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorSmallest Latest Completion time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestLatestStartTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorSmallest Latest Start time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestMax(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects first the variable with the smallest upperbound.
Example:
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KSmallestMax(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestMin(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the smallest value in its domain.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KAssignVar(KSmallestMin(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSmallestTargetStartTime(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorSmallest Target Start time task selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSolution(*args)¶
Bases:
objectThis class represents a solution of a KProblem.
Example :
KProblem p(...); KSolver solver(p); solver.solve(); KSolution sol = p.getSolution();
See also: KProblem
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return the objective value of the solution if applicable
getValue(*args)Overload 1: Return the instantiation of a variable in the solution
- getObjectiveValue() → double¶
Return the objective value of the solution if applicable
- getValue(*args) → double¶
Overload 1: Return the instantiation of a variable in the solution
Overload 2: Return the instantiation of a variable in the solution
Overload 3: Return the instantiation of the variable in the solution
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSolutionArray(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.solutionlistAn array of KSolution objects
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSolutionContainer(*args)¶
Bases:
objectThis class represent a pool of solution of a KProblem. Example:
KProblem p(...); KSolver solver(p); solver.optimize(); KSolution sol = p.getSolutionContainer().getBestSolution();
See also: KProblem Since: 2016.1
Methods:
add(solution)Add a new solution of the solution container
clear()Remove all solutions from the solution container
Return the best solution found (if applicable)
Return the last solution found
Return the number of solutions found
getSolution(index)Return solution by index
Return true if the problem as at least one solution
- clear() → void¶
Remove all solutions from the solution container
- getBestSolution() → KSolution &¶
Return the best solution found (if applicable)
- getLastSolution() → KSolution &¶
Return the last solution found
- getNumberOfSolutions() → int¶
Return the number of solutions found
- getSolution(index: int const) → KSolution &¶
Return solution by index
- problemIsSolved() → bool¶
Return true if the problem as at least one solution
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSolver(*args)¶
Bases:
objectKSolver is the main class for solving problems defined in a KProblem instance.
Once the problem has been fully built, we can begin to look for solutions. For this, the main class to be used is KSolver, which allows us to :
look for one solution
look for all solutions
look for another solution when we already know some of them
look for the optimal solution according to the problem objective
A KSolver object must be associated to a specific problem. Here is how we can declare and create a KSolver which will be associated to our problem :
KSolver mySolver(myProblem);
When performing its solving functionalities, our object mySolver will store all solutions in the myProblem object. Retrieving these solutions and working on them is the subject of the next section.
In order to find only one solution to our problem, we would write:
mySolver.solve();
The solve() method looks for any valid solution and stores it in the associated KProblem object.
In order to fine all solutions to the problem, we would write :
mySolver.findAllSolutions();
The findAllSolutions() method searches for all solutions of the problem and stores them in the associated KProblem object.
When the problem is too large, it can be very time consuming to search for all solutions. If one needs to obtain more than one unique solution, then he should use the KSolver findNextSolution() method. For example :
for (int solutionIndex = 0; solutionIndex < 5; ++solutionIndex) mySolver.findNextSolution(); mySolver.endLookingForSolution();
The findNextSolution() method searches for the next solution and stop in a restartable state. To go back to the state before search, it is necessary to call the endLookingForSolution() method after the successive calls to findNextSolution().
In order to find the optimal solution to the problem, we would write:
mySolver.optimize();
The optimize() method searches for the optimal solutions according to the problem objective and stores it in the associated KProblem object.
In order to fine tune the search, one may set integer or double control parameters using the setIntControl() and setDblControl() methods.
Statistics on the search can be obtained using the getIntAttrib() and getDblAttrib() methods.
Multi-threaded search is automatically activated provided that the KProblem object holds multiple problem instances and that the KSolver::NumberOfThreads control parameter is greater than 1.
See also: KProblem
Version: 2016.1
Methods:
addRelaxationSolver(solver[, …])Add a relaxation solver
Stop looking for solutions and restore the state before search
Search for all solutions to the problem
Start looking for a solution to the problem or look for a new one
Return a pointer to the current branching object
Return the current branching scheme
Return the current value selector
Return the current variable selector
getDblAttrib(attrib)Return a double attribute of the solver.
getDblControl(control)Return the value of a double control
Return the default branching scheme array
getIntAttrib(attrib)Return a integer attribute of the solver.
getIntControl(control)Return the value of an int control
Get the KProblem instance
Return the shaving activation flag
Do a local optimization
optimize([optimizeWithRestart, dichotomicSearch])Search for an optimal solution to the problem.
setBranchFunctionPtr(ptr1, ptr2, param)Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
setBranchingSchemeArray(branchingSchemeArray)Sets the branching scheme array
setBranchingSchemeFunctionPtr(ptr1, param)Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
setDblControl(control, value)Set the value of a double control
setIntControl(control, value)Set the value of an int control
setNodeFunctionPtr(ptr, param)Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
setSolutionFunctionPtr(ptr, param)Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
setSolverEventListener(listener)Set the solver event listener for tracking and controlling the search
setUseReducedCostFixing(flag)Use reducing cost fixing
solve()Search for a solution to the problem
useShaving(use)Set shaving activation flag
- Backtracks = 4¶
Number of backtracks.
- BestBound = 1¶
Best bound on the optimal solution.
- CallBackTime = 2¶
Time spent in callbacks
- CheckSolutionStatus = 5¶
Check each solution for validity.
- ClearExistingSolutions = 10¶
Control to clear or not the existing solutions before an optimization: 1 for yes (default), 0 for no
- ComputationTime = 0¶
Total computation time.
- Depth = 1¶
Depth of the search tree.
- LastCallPropagationIter = 8¶
Fix point iterations during last propagation.
- LastCallPropagationTime = 6¶
Time elapsed during last propagation.
- MaxComputationTime = 0¶
Maximum computation time.
- MaxDepth = 2¶
Maximum depth of the search tree.
- MaxNumberOfBackTracks = 3¶
Maximum number of backtracks during search.
- MaxNumberOfNodes = 0¶
Maximum number of nodes to explore.
- MaxNumberOfNodesBetweenSolutions = 6¶
Maximum number of nodes between two succesive solutions.
- MaxNumberOfSolutions = 1¶
Maximum number of solutions to find.
- MaxReachedDepth = 9¶
Maximum depth reached during search.
- NumberOfNodes = 0¶
Number of nodes explored.
- NumberOfSolutionBetweenRestarts = 9¶
Number of solutions between search restarts : less or equal to 0 (default) for no restarts.
- NumberOfThreads = 7¶
Number of threads to be used during search. This control parameter is automatically limited by the number of instances in the KProblem object.
- OptimalityRelativeTolerance = 2¶
Relative optimality tolerance (default value: 0.000001 for continuous objective, 0 for integer objective).
- OptimalityRelativeToleranceReached = 2¶
Optimality relative tolerance has been reached. See also: OptimalityRelativeTolerance
- OptimalityTolerance = 1¶
Absolute optimality tolerance (default value: 0.000001 for continuous objective, 1 for integer objective).
- OptimalityToleranceReached = 1¶
Optimality absolute tolerance has been reached. See also: OptimalityTolerance
- OptimizationAlgorithm = 8¶
Algorithm used for optimization: less or equal to 0 (default) for branch and bound, 1 for binary search on objective interval, 2 for n-ary search on objective interval (available for multi-threaded optimization only).
- SearchLimitReached = 2¶
Limit reached during resolution. See also: SearchLimitAttrib
- SearchLimitUnreached = 0¶
Search has not been limited
- SearchLimitedByBacktracks = 5¶
Search has been limited by maximum number of backtracks. See also: MaxNumberOfBackTracks
- SearchLimitedByDepth = 3¶
Search has been limited by maximal tree search depth. See also: MaxDepth
- SearchLimitedByNodes = 1¶
Search has been limited by maximum number of nodes explored. See also: MaxNumberOfNodes
- SearchLimitedByNodesBetweenSolutions = 6¶
Search has been limited by maximum nodes between two solutions. See also: MaxNumberOfNodesBetweenSolutions
- SearchLimitedBySolutions = 2¶
Search has been limited by maximum number of solutions found. See also: MaxNumberOfSolutions
- SearchLimitedByTime = 4¶
Search has been limited by time. See also: MaxComputationTime
- SearchLimitedByUser = 7¶
Search has been limited by user.
- StatsPrinting = 4¶
Print search statistics each KSolver::StatsPrinting seconds (at max).
- ToleranceLimitReached = 3¶
Tolerance limit reached during resolution. See also: ToleranceLimitAttrib
- ToleranceLimitUnreached = 0¶
Tolerance limit has not been reached.
- TotalPropagationIter = 7¶
Total fix point iterations for propagation.
- TotalPropagationTime = 5¶
Total time elapsed during propagation.
- addRelaxationSolver(solver: KLinearRelaxationSolver, initDefaultBranchingScheme: bool = False) → void¶
Add a relaxation solver
- endLookingForSolution() → int¶
Stop looking for solutions and restore the state before search
- findAllSolutions() → int¶
Search for all solutions to the problem
- Return type
int
- Returns
number of solutions found
See also: IntControls DblControls
- findNextSolution() → int¶
Start looking for a solution to the problem or look for a new one
- Return type
int
- Returns
0 if no solution was found
See also: IntControls DblControls
- getCurrentBranchingObject() → void *¶
Return a pointer to the current branching object
- getCurrentBranchingScheme() → kalis.KBranchingScheme¶
Return the current branching scheme
- getCurrentValueSelector() → kalis.KValueSelector¶
Return the current value selector
- getCurrentVariableSelector() → kalis.KVariableSelector¶
Return the current variable selector
- getDblAttrib(attrib: KSolver::DblAttrib) → double¶
Return a double attribute of the solver.
- Parameters
attrib (int) – the double attribute to retrieve
See also: DblAttrib
- getDblControl(control: KSolver::DblControl) → double¶
Return the value of a double control
- Parameters
control (int) – double control to retrieve
See also: DblControl
- getDefaultBranchingSchemeArray() → KBranchingSchemeArray *¶
Return the default branching scheme array
- getIntAttrib(attrib: KSolver::IntAttrib) → int¶
Return a integer attribute of the solver.
- Parameters
attrib (int) – the integer attribute to retrieve
See also: IntAttrib
- getIntControl(control: KSolver::IntControl) → int¶
Return the value of an int control
- Parameters
control (int) – integer control to retrieve
See also: IntControl
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
Get the KProblem instance
- getUseShaving() → bool¶
Return the shaving activation flag
- localOptimization() → bool¶
Do a local optimization
- optimize(optimizeWithRestart: bool const = False, dichotomicSearch: bool const = False) → int¶
Search for an optimal solution to the problem.
- Parameters
optimizeWithRestart (boolean, optional) – boolean indicating if the search has to be restarted after finding a solution (See also: NumberOfSolutionBetweenRestarts)
dichotomicSearch (boolean, optional) – boolean indicating the type of search (linear or dichotomic) to optimize the objective variable (See also: OptimizationAlgorithm)
- Return type
int
- Returns
0 if no solution was found
See also: IntControls DblControls
- setBranchFunctionPtr(ptr1: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, ptr2: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, param: void *) → void¶
Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
Set the branch explored function ptr (called each time a branch is explored)
- Parameters
ptr – function pointer
param (void) – user parameter passed to the function when called
- setBranchingSchemeArray(branchingSchemeArray: KBranchingSchemeArray, solverInstance: int = - 1) → void¶
Sets the branching scheme array
- setBranchingSchemeFunctionPtr(ptr1: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, param: void *) → void¶
Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
Set the Branching scheme switch function ptr
- Parameters
ptr – function pointer
param (void) – user parameter passed to the function when called
- setDblControl(control: KSolver::DblControl, value: double) → void¶
Set the value of a double control
- Parameters
control (int) – tjhe double control to set
value (float) – value of the control
See also: DblControl
- setIntControl(control: KSolver::IntControl, value: int) → void¶
Set the value of an int control
- Parameters
control (int) – the int control to set
value (int) – the value of the control
See also: IntControl
- setNodeFunctionPtr(ptr: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, param: void *) → void¶
Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
Set the node explored function ptr
- Parameters
ptr (int) – function pointer
param (void) – user parameter passed to the function when called
- setSolutionFunctionPtr(ptr: KalisCallBackFunctionPtr, param: void *) → void¶
Deprecated: See also: setSolverEventListener
Set the solution function ptr (called each time a solution is found)
- Parameters
ptr (int) – function pointer
param (void) – user parameter passed to the function when called
- setSolverEventListener(listener: KSolverEventListener) → void¶
Set the solver event listener for tracking and controlling the search
See also: KSolverEventListener
- setUseReducedCostFixing(flag: bool) → void¶
Use reducing cost fixing
- solve() → int¶
Search for a solution to the problem
- Return type
int
- Returns
0 if no solution was found, 1 otherwise
See also: IntControl DblControl
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- useShaving(use: bool) → void¶
Set shaving activation flag
- class kalis.KSolverEventListener(*args)¶
Bases:
objectCallbacks for a KSolver events.
Methods:
branchGoDown(thread)Called after each branchGoDown event
branchGoUp(thread)Called after each branchGoUp event
Called after each bracnhing scheme switch
nodeExplored(thread)Called after constraint propagation in each node
Ask user for termination at each node
- branchGoDown(thread: int) → void¶
Called after each branchGoDown event
- branchGoUp(thread: int) → void¶
Called after each branchGoUp event
- branchingScheme() → void¶
Called after each bracnhing scheme switch
- nodeExplored(thread: int) → void¶
Called after constraint propagation in each node
- stopComputations() → bool¶
Ask user for termination at each node
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSplitDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeSplitDomain Branching scheme
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSplitDomain(KSmallestDomain(),KMaxToMin());
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KSplitNumDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeSplitDomain Branching scheme

Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray; myBranchingSchemeArray += KSplitNumDomain(KSmallestDomain(),KMaxToMin());
See also: KBranchingScheme KAssignVar KAssignAndForbid KSettleDisjunction KProbe KSplitNumDomain
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTask(*args)¶
Bases:
object- Tasks (processing operations, activities) are represented by the class KTask. This object contains three variables :
a start variable representing the starting time of the task
an end variable representing the ending time of the task
a duration variable representing the duration of the task
These three structural variables are linked by Artelys-Kalis with the following constraint :
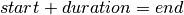
- The starting time variable represents two specific parameters of the task:
the Earliest Starting Time (EST represented by the start variable lower bound)
and its Latest Starting Time (LST represented by the start variable upper bound)
- The end variable represents two specific parameters of the task:
the Earliest Completion Time (ECT represented by the end variable lower bound)
and its Latest Completion Time (LCT represented by the end variable upper bound)
- The duration variable represents two specific parameters of the task:
the minimum task duration (Dmin represented by the duration variable lower bound)
the maximum task duration (Dmax represented by the duration variable upper bound)
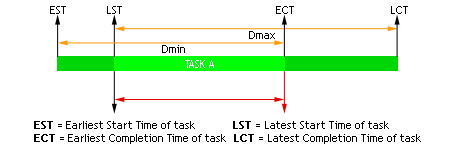
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
consumes(*args)Overload 1:
display(*args)Overload 1:
endsBefore(task[, delay])State that this task ends delay time unit before the completion of the given task
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource requirement of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource consumtion of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
Return the constant duration of this task or the lowerbound if duration is not constant
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the duration of this task
Return the earliest completion time of this task
Return the earliest starting time of this task
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the ending date of this task
getIndex()Return the id of this task
Return the latest completion time of this task
Return the latest starting time of this task
getMaximalProduction(resource, tslot)Return the maximal resource production for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
getMaximalProvision(resource, tslot)Return the maximal resource provision for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
Return the maximum duration of this task
getMinimalConsumption(resource, tslot)Return the minimal resource consumption for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
getMinimalRequirement(resource, tslot)Return the minimal resource requirement for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
Return the minimum duration of this task
getName()Return the name of this task
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource production of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource provision of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource requirement of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
Pretty printing of the task to stdout
getSetupTime(task)Return the setup time between the current task and the one passed in parameter
getSizeVar(r)Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the product requirement * duration
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the starting date of this task
isFixed()Return true IFF this task is fixed (Start,End,Duration, and resource utilizations variables are instantiated)
postEndToEndMaxC(task[, Max])State that the distance between the completion of this task and the completion of task task cannot exceed Max time units
postEndToStartMaxC(task[, Max])State that the distance between the completion of this task and the start of task task cannot exceed Max time units
postEndToStartMinC(task[, Min])State that the distance between the completion of this task and the start of task task must exceed Min time units
postStartToStartMinC(task[, Min])State that the distance between the start of this task and the start of task task must exceed Min time units
produces(*args)Overload 1:
provides(*args)Overload 1:
requires(*args)Overload 1:
setDuration(duration)Set the duration of this task to duration
Set the earliest completion time of this task
setEarliestStartTime(time)Set the earliest starting time of this task
setEndTime(endTime)Set the ending time of this task to endTime
setLatestCompletionTime(time)Set the latest completion time of this task
setLatestStartTime(time)Set the latest starting time of this task
setMaximumDuration(durationmax)Set the maximum duration of this task
setMinimumDuration(durationmin)Set the minimum duration of this task
setName(name)Set the name of this task
setSetupTime(task, before, after)Set the sequence dependent setup time between the current task,and the one passed in parameters to before/after
setStartTime(startTime)Set the starting time of this task to startTime
startsAfter(task[, delay])State that this task starts delay time unit after the completion of the given task
- consumes(*args) → int¶
- Overload 1:
Add a resource usage consumption for this task
Overload 2:
Add optional resources usages consumptions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 3:
Add optional resources usages consumptions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 4:
Add optional resources usages consumptions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 5:
State that this ressource consumes ( non-renewable ) consumption unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the involved resourceconsumption (int) – the resource consumption
Overload 6:
State that this ressource consumes ( non-renewable ) between consumptionmin and consumptionmax unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourceconsumptionmin (int) – the minimal resource consumption
consumptionmax (int) – the maximal resource consumption
Overload 7:
State that this ressource consumes ( non-renewable ) one unit of resource resource
- display(*args) → void¶
- Overload 1:
Pretty printing the task
Overload 2:
Pretty printing of the task with a PrintFunctionPtr
- endsBefore(task: KTask, delay: int = 0) → void¶
State that this task ends delay time unit before the completion of the given task
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – the task before the current taskdelay (int, optional) – the time distance between the two tasks
- getAssignmentVar(r: KResource) → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource requirement of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
- getConsumesVar(r: KResource) → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource consumtion of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
- getDurationValue() → int¶
Return the constant duration of this task or the lowerbound if duration is not constant
- getDurationVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the duration of this task
- getEarliestCompletionTime() → int¶
Return the earliest completion time of this task
- getEarliestStartTime() → int¶
Return the earliest starting time of this task
- getEndDateVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the ending date of this task
- getIndex() → int¶
Return the id of this task
- getLatestCompletionTime() → int¶
Return the latest completion time of this task
- getLatestStartTime() → int¶
Return the latest starting time of this task
- getMaximalProduction(resource: kalis.KResource, tslot: int) → int¶
Return the maximal resource production for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
- getMaximalProvision(resource: kalis.KResource, tslot: int) → int¶
Return the maximal resource provision for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
- getMaximumDuration() → int¶
Return the maximum duration of this task
- getMinimalConsumption(resource: kalis.KResource, tslot: int) → int¶
Return the minimal resource consumption for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
- getMinimalRequirement(resource: kalis.KResource, tslot: int) → int¶
Return the minimal resource requirement for this task and the resource in parameters at time step tslot
- getMinimumDuration() → int¶
Return the minimum duration of this task
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task
- getProducesVar(r: KResource) → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource production of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
- getProvidesVar(r: KResource) → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource provision of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
- getRequiresVar(r: KResource) → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the resource requirement of this task for resource r if any or nullptr
- getSchedule() → KSchedule *¶
Pretty printing of the task to stdout
- getSetupTime(task: kalis.KTask) → int¶
Return the setup time between the current task and the one passed in parameter
- getSizeVar(r: KResource) → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the product requirement * duration
- getStartDateVar() → KIntVar *¶
Return a pointer to the KIntVar representing the starting date of this task
- isFixed() → bool¶
Return true IFF this task is fixed (Start,End,Duration, and resource utilizations variables are instantiated)
- postEndToEndMaxC(task: KTask, Max: int = 0) → void¶
State that the distance between the completion of this task and the completion of task task cannot exceed Max time units
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – the taskMax (int, optional) – the distance between the completion of this task and the completion of task task
- postEndToStartMaxC(task: KTask, Max: int = 0) → void¶
State that the distance between the completion of this task and the start of task task cannot exceed Max time units
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – the taskMax (int, optional) – the distance between the completion of this task and the start of task task
- postEndToStartMinC(task: KTask, Min: int = 0) → void¶
State that the distance between the completion of this task and the start of task task must exceed Min time units
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – the taskMin (int, optional) – the distance between the completion of this task and the start of task task
- postStartToStartMinC(task: KTask, Min: int = 0) → void¶
State that the distance between the start of this task and the start of task task must exceed Min time units
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – the taskMin (int, optional) – the distance between the start of this task and the start of task task
- produces(*args) → int¶
- Overload 1:
Add a resource usage production for this task
Overload 2:
Add optional resources usages productions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 3:
Add optional resources usages productions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 4:
Add optional resources usages productions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 5:
State that this ressource produces ( non-renewable ) production unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourceproduction (int) – the resource production
Overload 6:
State that this ressource produces ( non-renewable ) between productionmin and productionmax unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourceproductionmin (int) – the minimal resource production
productionmax (int) – the maximal resource production
Overload 7:
State that this ressource produces ( non-renewable ) one unit of resource resource
- provides(*args) → int¶
- Overload 1:
Add a resource usage provision for this task
Overload 2:
Add optional resources usages provisions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 3:
Add optional resources usages provisions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 4:
Add optional resources usages provisions for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 5:
State that this ressource provides ( renewable ) provision unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourceprovision (int) – the resource provision
Overload 6:
State that this ressource provides ( renewable ) between provisionmin and ‘provisionmax unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourceprovisionmin (int) – the minimal resource provision
provisionmax (int) – the maximal resource provision
Overload 7:
State that this ressource provides ( renewable ) one unit of resource resource
- requires(*args) → int¶
- Overload 1:
Add a resource usage requirement for this task
Overload 2:
Add optional resources usages requirements for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 3:
Add optional resources usages requirements for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 4:
Add optional resources usages requirements for this task and ensure that between [min..max] of theses requirements are satisfied
Overload 5:
State that this ressource requires ( renewable ) requirement unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourcerequirement (int) – the resource requirement
Overload 6:
State that this ressource requires ( renewable ) between requirementmin and ‘requirementmax unit of resource resource
- Parameters
resource (
KResource) – the resourcerequirementmin (int) – the minimal resource requirement
requirementmax (int) – the maximal resource requirement
Overload 7:
State that this ressource requires ( renewable ) one unit of resource resource
- setDuration(duration: int) → void¶
Set the duration of this task to duration
- setEarliestCompletionTime(time: int) → void¶
Set the earliest completion time of this task
- setEarliestStartTime(time: int) → void¶
Set the earliest starting time of this task
- setEndTime(endTime: int) → void¶
Set the ending time of this task to endTime
- setLatestCompletionTime(time: int) → void¶
Set the latest completion time of this task
- setLatestStartTime(time: int) → void¶
Set the latest starting time of this task
- setMaximumDuration(durationmax: int) → void¶
Set the maximum duration of this task
- setMinimumDuration(durationmin: int) → void¶
Set the minimum duration of this task
- setName(name: char const *) → void¶
Set the name of this task
- setSetupTime(task: KTask, before: int, after: int) → void¶
Set the sequence dependent setup time between the current task,and the one passed in parameters to before/after
- setStartTime(startTime: int) → void¶
Set the starting time of this task to startTime
- startsAfter(task: KTask, delay: int = 0) → void¶
State that this task starts delay time unit after the completion of the given task
- Parameters
task (
KTask) – the task before the current taskdelay (int, optional) – the time distance between the two tasks
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTaskArray(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.tasklistThis class implements an array of KTask
Example :
KSchedule s(...); // T is an array of KTask T0 T1 T2 T3 T4 KTaskArray T(s,5,0,10,"T");
See also: KIntVar
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTaskInputOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorTasks input order selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTaskRandomOrder(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTaskSelectorTasks random order selection heuristic
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTaskSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract interface class for task selection heuristic A custom scheduling optimization strategy can be specified by using the KTaskSerializer branching scheme to select the task to be scheduled and value choice heuristics for its start and duration variables.
- See also: KSmallestEarliestStartTime KSmallestEarliestCompletionTime
KLargestEarliestStartTime KLargestEarliestCompletionTime KSmallestLatestStartTime KSmallestLatestCompletionTime KLargestLatestStartTime KLargestLatestCompletionTime
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return a copy of this task selector
getName()Return the name of this task selector
Pretty printing
selectNextTask(taskArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- getCopyPtr() → KTaskSelector *¶
Return a copy of this task selector
- Return type
- Returns
a copy of this task selector
- getName() → char const *¶
Return the name of this task selector
- printName() → void¶
Pretty printing
- selectNextTask(taskArray: KTaskArray) → KTask *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own task selection heuristics
- Parameters
intVarArray – Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTaskSerializer(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KBranchingSchemeTask-based branching strategy
A custom scheduling optimization strategy can be specified by using the KTaskSerializer branching scheme to select the task to be scheduled and value choice heuristics for its start, duration and assignments variables.

- See also: KSmallestEarliestStartTime KSmallestEarliestCompletionTime
KLargestEarliestStartTime KLargestEarliestCompletionTime KSmallestLatestStartTime KSmallestLatestCompletionTime KLargestLatestStartTime KLargestLatestCompletionTime
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Get a copy pointer
- AFF_DUR_START = 0¶
Variable branching order: * affectations * duration * start time
- AFF_START_DUR = 1¶
Variable branching order: * affectations * start time * duration
- DUR_AFF_START = 3¶
Variable branching order: * duration * affectations * start time
- DUR_START_AFF = 2¶
Variable branching order: * duration * start time * affectations
- START_AFF_DUR = 5¶
Variable branching order: * start time * affectations * duration
- START_DUR_AFF = 4¶
Variable branching order: * start time * duration * affectations
- getCopyPtr() → KBranchingScheme *¶
Get a copy pointer
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTasksRankConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintConstraint linking tasks and rank variables for unary scheduling.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
objectSuperclass of KUnTerm and KBinTerm
Methods:
getCste()Get method
setCste(cste)Set the constant
- getCste() → double¶
Get method
- setCste(cste: double const) → void¶
Set the constant
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTimeTable(*args)¶
Bases:
objectTimetable object for time-dependant resource usage constraint.
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KTupleArray¶
Bases:
objectThis class implements an array of tuples of fixed arity
Example :
KTupleArray tupleArray(3); KIntArray tuple(3, 1, 2, 3); tupleArray += tuple; // tupleArray = { (1,2,3) } tuple[0] = 3; tuple[2] = 2; tuple[3] = 1; // tupleArray = { (1,2,3), (3,2,1) }
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KUnTerm(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KTerm- This class represent an expression of the form X + cste where X is a variable
and cste , an integer constant
See also: KBinTerm KLinTerm
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
getSign1()return true if the sign of the first variable is positive
getV1()return a pointer to the first variable
- getSign1() → bool¶
return true if the sign of the first variable is positive
- getV1() → KNumVar *¶
return a pointer to the first variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KUnaryResource(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KResourceUnary Resource
Unary resources can process only one task at a time.
The following schema shows an example with three tasks A,B and C executing on a disjunctive resource and on a cumulative resource with resource usage 3 for task A, 1 for task B and 1 for task C :

- Tasks may require, provide, consume and produce resources :
A task requires a resource if some amount of the resource capacity must be made available for the execution of the activity. The capacity is renewable which means that the required capacity is available after the end of the task.
A task provides a resource if some amount of the resource capacity is made available through the execution of the task. The capacity is renewable which means that the provided capacity is available only during the execution of the task.
A task consumes a resource if some amount of the resource capacity must be made available for the execution of the task and the capacity is non-renewable which means that the consumed capacity if no longer available at the end of the task.
A task produces a resource if some amount of the resource capacity is made available through the execution of the task and the capacity is non-renewable which means that the produced capacity is definitively available after the starting of the task.
- Disjunctions = 4¶
Disjunction propagation scheme
- TasksIntervals = 2¶
Tasks Intervals propagation scheme
- TimeTabling = 1¶
TimeTabling propagation scheme
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KUnaryResourceConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis constraint states that some tasks are not overlapping chronologically.
- Resources (machines, raw material etc) can be of two different types :
Disjunctive when the resource can process only one task at a time (represented by the class KUnaryResource).
Cumulative when the resource can process several tasks at the same time (represented by the class KDiscreteResource).
Traditional examples of disjunctive resources are Jobshop problems, cumulative resources are heavily used for the Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP). Note that a disjunctive resource is semantically equivalent to a cumulative resource with maximal capacity one and unit resource usage for each task using this resource but this equivalence does not hold in terms of constraint propagation.
The following schema shows an example with three tasks A,B and C executing on a disjunctive resource and on a cumulative resource with resource usage 3 for task A, 1 for task B and 1 for task C :

Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KUserConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintAbstract interface class for definition of user constraints
To create your own constraints in Artelys Kalis, you must create a specific class that inherits from the KUserConstraint class. Then, you need to implement the pruning scheme corresponding to the semantic of your constraint by overloading the propagate method or awakeOnXXX methods for incremental propagation of the constraint
the awake method is launched one time upon initialization of the constraint
the awakeOnInf method is launched when the lowerbound of a variable increase
the awakeOnSup method is launched when the upperbound of a variable decrease
the awakeOnRem method is lanched when a specific value has been removed from the domain of a variable
the awakeOnInst method is launched when a variable has been instantiated to a value
the awakeOnVar method is launched when the domain of one specific variable has changed
the propagate method is launched when one or more variables have seen their domain modified
- askIfEntailed method is called when the constraints is used within a boolean connector (KGuard, KEquiv, KDisjunction, KConjunction).
It should return :
CTRUE whenever the constraint is definitively verified
CFALSE whenever the constraint is definitively violated
CUNKNOWN otherwhise
The awake, propagate and print methods <u>must<u> be overloaded (pure virtual functions). The default behavior of the awakeOnInf, awakeOnSup, awakeOnInst, awakeOnVar and awakeOnRem is to call the propagate method.
Additionally, it is necessary to implement the getInstanceCopyPtr(const KProblem& problem) that returns a copy pointer of the user constraint by calling the KProblem::getCopyPtr() on each modelling object used in the constraint.
Here is an example of user defined constraint definition : V1 == V2 % modulo
// ModuloConstraint class inherits from KUserConstraint class class ModuloConstraint : public KUserConstraint { private: // Modulo constant int _modulo; // Variables V1 and V2 KIntVar* _v1; KIntVar* _v2; public: // Primary constructor of the constraint V1 == V2 % modulo ModuloConstraint(KIntVar &v1, KIntVar &v2, const int modulo); // Destructor virtual ~ModuloConstraint(); // Virtual copy method virtual KConstraint* getInstanceCopyPtr(const KProblem& problem) const; ///////////////////////// // Propagation methods ///////////////////////// virtual void awake(void); virtual void propagate(void); virtual void awakeOnInst(KIntVar & var); virtual void print(); /////////////////////////////////////// // For use within boolean connectors /////////////////////////////////////// virtual int askIfEntailed(void); }; // Main constructor ModuloConstraint::ModuloConstraint(KIntVar &v1, KIntVar &v2, const int modulo) : KUserConstraint(v1,v2) { _modulo = modulo; _v1 = &v1; _v2 = &v2; } // Destructor ModuloConstraint::~ModuloConstraint() { } // Virtual copy method KConstraint * ModuloConstraintXYC::getInstanceCopyPtr(const KProblem& problem) const { return new ModuloConstraintXYC(*problem.getInstanceOf(_v1), *problem.getInstanceOf(_v2), _modulo); } /////////////////////////////////////////// // initial propagation of the constraint /////////////////////////////////////////// void ModuloConstraint::awake() { propagate(); } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Some variables of the constraints have seen their domain reduced... must propagate the changes /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void ModuloConstraint::propagate() { int v0, v1; std::cout << "ModuloConstraint#Propagate()" << std::endl; // V1 is trivialy bounded by 0 <= V1 <= modulo - 1 _v1.setInf(0); _v1.setSup(_modulo-1); ////////////////////////////// // Arc consistent filtering ////////////////////////////// ///////////////////////// // First from V1 to V2 ///////////////////////// for ( v1 = _v2.getInf();v1<=_v2.getSup();v1 ++) { bool supporte = false; for ( v0 = _v1.getInf();v0<=_v1.getSup();v0 ++) { // check if v0 == v1 % _modulo hold if ( v0 == v1 % _modulo) { // value v0 is a support for value v1 of variable V2 supporte = true; break; } } if ( !supporte) { // no support was found for value v1 of variable V2 so we can safely remove it from its domain _v2.remVal(v1); } } //////////////////////// // Then from V2 to V1 //////////////////////// for ( v0 = _v1.getInf(); v0 <= _v1.getSup(); v0++) { bool supporte = false; for ( v1 = _v2.getInf(); v1 <= _v2.getSup(); v1++) { // check if v0 == v1 % _modulo hold if ( v0 == v1 % _modulo) { // value v1 is a support for value v0 of variable V1 supporte = true; break; } } if ( !supporte) { // no support was found for value v0 of variable V1 so we can safely remove it from its domain _v1.remVal(v0); } } } int ModuloConstraint::askIfEntailed() { if (_v1.getIsInstantiated() && _v2.getIsInstantiated() ) { if ( _v1.getValue() == _v2.getValue() % _modulo ) { // The constraint is definitly verified return CTRUE; } else { // The constraint is definitly violated return CFALSE; } } else { // Don't know yet if the constraint is definitly violated or verified return CUNKNOWN; } } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // The variable "var" has been instantiated to var.getValue() //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void ModuloConstraint::awakeOnInst(KIntVar & var) { int v; std::cout << "ModuloConstraint#awakeOnInst" << std::endl; if ( var.isEqualTo(_v1) ) { // V1 was instantiated for ( v = _v2.getInf();v<=_v2.getSup();v ++) { if (_v1.getValue() != v % _modulo) _v2.remVal(v); } } else if ( var.isEqualTo(_v2) ) { // V2 was instantiated for ( v = _v1.getInf();v<=_v1.getSup();v ++) { if ( v != _v2.getValue() % _modulo) _v1.remVal(v); } } } ////////////////////////////////// // For pretty printing purposes ////////////////////////////////// void ModuloConstraint::print() { std::cout << "ModuloConstraint"; }
KProblem problem(...); KIntVar A(problem, "A", 0, 20); KIntVar B(problem, "B", 0, 10); // Now creating the constraint A == B % 7 ModuloConstraint modCst(A, B, 7); // Now posting the constraint to the problem problem.post(modCst); // ...
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Virtual method for use within boolean connectors
awake()Virtual method called upon initialization of the constraint
awakeOnInf(var)Virtual method called when the lower bound of var has been raised
awakeOnInst(var)Virtual method called when the variable var has been instantiated
awakeOnRem(var, removedValue)Virtual method called when the value removedValue has been removed from the domain of var
awakeOnSup(var)Virtual method called when the upper bound of var has been lowered
awakeOnVar(var)Virtual method called when the domain of variable var has changed
Virtual copy method.
getInstanceCopyPtr(problem)Virtual instance copy method.
getLinearRelaxation(strategy)Linear Relaxation
Virtual method called when the domain of some or several variables has changed
- CFALSE = 1¶
Constraint is proven false
- CTRUE = 2¶
Constraint is proven true
- CUNKNOWN = 0¶
Unkown status of constraint
- askIfEntailed() → int¶
Virtual method for use within boolean connectors
- Return type
int
- Returns
CTRUE whenever the constraint is definitively satisfied
- Return type
int
- Returns
CFALSE whenever the constraint is definitively violated
- Return type
int
- Returns
CUNKNOWN otherwhise
- awake() → void¶
Virtual method called upon initialization of the constraint
- awakeOnInst(var: KIntVar) → void¶
Virtual method called when the variable var has been instantiated
- Parameters
var (
KIntVar) – the variable with modified domain
- awakeOnRem(var: KIntVar, removedValue: int) → void¶
Virtual method called when the value removedValue has been removed from the domain of var
- Parameters
var (
KIntVar) – the variable with modified domainremovedValue (int) – the value that has been removed from the domain of var
- awakeOnSup(var: KIntVar) → void¶
Virtual method called when the upper bound of var has been lowered
- Parameters
var (
KIntVar) – the variable with modified domain
- awakeOnVar(var: KIntVar) → void¶
Virtual method called when the domain of variable var has changed
- Parameters
var (
KIntVar) – the variable with modified domain
- getCopyPtr() → KConstraint *¶
Virtual copy method. Must be implemented by the user.
- getInstanceCopyPtr(problem: KProblem) → KConstraint *¶
Virtual instance copy method. Each modeling elements stored (and used) in the user constraint must be copied using the KProblem::getInstanceOf() methods. Must be implemented by the user when solving problems in parallel.
- getLinearRelaxation(strategy: int) → KLinearRelaxation *¶
Linear Relaxation
- propagate() → void¶
Virtual method called when the domain of some or several variables has changed
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KUserNumConstraint(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThe KUserNumConstraint is the generic counterpart to the KUserConstraint for implementing user constraints when using numeric variables.
Methods:
Virtual method for use within boolean connectors
awake()Virtual method called upon initialization of the constraint
awakeOnInf(var)Virtual method called when the lower bound of var has been raised
awakeOnInst(var)Virtual method called when the variable var has been instantiated
awakeOnRem(var, removedValue)Virtual method called when the value removedValue has been removed from the domain of var
awakeOnSup(var)Virtual method called when the upper bound of var has been lowered
awakeOnVar(var)Virtual method called when the domain of variable var has changed
Virtual copy method.
getInstanceCopyPtr(problem)Virtual instance copy method.
Virtual method called when the domain of some or several variables has changed
- askIfEntailed() → int¶
Virtual method for use within boolean connectors
- Return type
int
- Returns
CTRUE whenever the constraint is definitively satisfied
- Return type
int
- Returns
CFALSE whenever the constraint is definitively violated
- Return type
int
- Returns
CUNKNOWN otherwhise
- awake() → void¶
Virtual method called upon initialization of the constraint
- awakeOnInst(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Virtual method called when the variable var has been instantiated
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the variable with modified domain
- awakeOnRem(var: KIntVar, removedValue: int) → void¶
Virtual method called when the value removedValue has been removed from the domain of var
- Parameters
var (
KIntVar) – the variable with modified domainremovedValue (int) – the value that has been removed from the domain of var
- awakeOnSup(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Virtual method called when the upper bound of var has been lowered
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the variable with modified domain
- awakeOnVar(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Virtual method called when the domain of variable var has changed
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the variable with modified domain
- getCopyPtr() → KConstraint *¶
Virtual copy method. Must be implemented by the user.
- getInstanceCopyPtr(problem: KProblem) → KConstraint *¶
Virtual instance copy method. Each modeling elements stored (and used) in the user constraint must be copied using the KProblem::getCopyPtr() method. Must be implemented by the user when solving problems in parallel.
- propagate() → void¶
Virtual method called when the domain of some or several variables has changed
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KValueSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract interface class for value selection heuristic
See also: KMaxToMin KMinToMax KMiddle KRandomValue KNearestValue
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
Return the current problem
selectNextValue(intVar)Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- getProblem() → KProblem *¶
Return the current problem
- selectNextValue(intVar: kalis.KIntVar) → int¶
Virtual method to overload with your own value selection heuristic.
- Parameters
intVar (
KIntVar) – the variable to selects a value for
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KVariableSelector(*args)¶
Bases:
objectAbstract interface class for variable selection heuristic
- See also: KSmallestDomain KMaxDegree KSmallestMin KSmallestMax KLargestMin
KLargestMax KRandomVariable KSmallestDomDegRatio KMaxRegretOnLowerBound KMaxRegretOnUpperBound
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextVariable(intVarArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics
- selectNextVariable(intVarArray: KIntVarArray) → KIntVar *¶
- virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics
- type intVarArray
- param intVarArray
Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KWidestDomain(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KNumVariableSelectorThis class implements a variable selector that selects the first uninstantiated variable with the widest domain.
Example :
KBranchingSchemeArray bsa; bsa += KSplitNumDomain(KWidestDomain(), KMaxToMin();
See also: KNumVariableSelector
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
selectNextVariable(numVarArray)virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- selectNextVariable(numVarArray: KNumVarArray) → KNumVar *¶
virtual interface method to overload for definition of your own variable selection heuristics :param intVarArray: Array of variable from wich selecting a variable
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KXEqualYMinusZ(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KConstraintThis class creates a X == Y - Z constraint
Example :
KIntVar X(...); KIntVar Y(...); KIntVar Z(...); // ... problem.post(X == Y - Z); // or problem.post(KXEqualYMinusZ(X,Y,Z));
See also: KConstraint
Since: 2016.1
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- class kalis.KXPRSLinearRelaxationSolver(*args)¶
Bases:
kalis.KLinearRelaxationSolverThis linear relaxation solver relies on XPress Optimizer to solve the LP/MIP problem.
Example:
// ... KProblem myProblem(mySession,""); // ... KLinearRelaxation * relax = myProblem.getLinearRelaxation(); KXPRSLinearRelaxationSolver mySolver(*relax, objectiveVar, KProblem::Minimize);
You must have XPress Optimizer installed to use this.
Since: 2016.1
Methods:
display()Print the internal state of the solver.
generateCuts(relaxation)Generate cuts.
Get the best bound in a branch and bound tree.
getBound()Get the bound computed by the solver (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver).
getLPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
getMIPSolution(*args)Overload 1:
Get the number of global variables.
getReducedCost(*args)Overload 1:
Get a pointer to the solution contained in the solver.
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
printSolution(MIPflag)Print the current solution.
Print variables name and their rank.
setMipRelStop(arg2)Set MIPRELSTOP double control.
setObjective(var)Set objective variable.
setPresolve(arg2)Activate or deactivate presolve.
solve()Call (XPress-Optimizer) and return an error code (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver for its meaning).
updateSolution(MIPflag)Update the KHybridSolution object with the current MIP (MIPflag=true) or LP (MIPflag=false) solution.
writeLP(filename)Write the current problem to a file in lp format.
- display() → void¶
Print the internal state of the solver. Use is discouraged, use method writeLP to output the content of the solver.
- generateCuts(relaxation: KLinearRelaxation) → void¶
Generate cuts.
If possible, cuts are added to the matrix of constraints to make the relaxation tighter and improve the bound.
- getBestBound() → double¶
Get the best bound in a branch and bound tree.
Useful if search terminated before optimality.
- getBound() → double¶
Get the bound computed by the solver (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver).
- getLPSolution(*args) → double¶
- Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a KNumVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – variable whose value is checked
Overload 2:
Get the current LP solution for a KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose value is checked
- getMIPSolution(*args) → double¶
- Overload 1:
Get the current MIP solution for a KNumVar variable.
- type var
- param var
variable whose value is checked
Overload 2:
Get the current MIP solution for a KAuxVar variable.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – variable whose value is checked
- getNumberGlobals() → int¶
Get the number of global variables.
- Return type
int
- Returns
number of global variables
- getReducedCost(*args) → double¶
Overload 1:
Get reduced costs. Note that LP solve is must be complete.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the variable whose reduced cost in the current LP solution is retrieved- Return type
float
- Returns
reduced cost value
Overload 2:
Get reduced costs. Note that LP solve must be complete.
- Parameters
var (
KAuxVar) – the variable whose reduced cost in the current LP solution is retrieved- Return type
float
- Returns
reduced cost value
- getSolutionPtr() → KHybridSolution *¶
Get a pointer to the solution contained in the solver. Method updateSolution must be used before the call.
- instantiateNumVarToCurrentSol(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Instantiate a variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- instantiateNumVarsToCurrentSol() → void¶
Instantiate variables to current solution obtained by linear relaxation solver
- printSolution(MIPflag: bool) → void¶
Print the current solution.
- Parameters
MIPflag (boolean) – to choose whether to print the current MIP solution or the current LP solution
- printVariables() → void¶
Print variables name and their rank. This is useful to recover the meaning of the columns in the LP file produced by writeLP().
- setMipRelStop(arg2: double) → void¶
Set MIPRELSTOP double control.
- setObjective(var: KNumVar) → void¶
Set objective variable.
- Parameters
var (
KNumVar) – the new objective variable
- setPresolve(arg2: bool) → void¶
Activate or deactivate presolve.
- solve() → int¶
Call (XPress-Optimizer) and return an error code (see class KLinearRelaxationSolver for its meaning).
- property thisown¶
The membership flag
- updateSolution(MIPflag: bool) → void¶
Update the KHybridSolution object with the current MIP (MIPflag=true) or LP (MIPflag=false) solution.
- Parameters
MIPflag (boolean) – true to get the current MIP solution, false for LP.
- writeLP(filename: char const *) → int¶
Write the current problem to a file in lp format.
- kalis.krand() → int¶
return a random integer between 0 and RAND_MAX (excluded)
- kalis.ksrand(seed: unsigned int) → void¶
set the random seed to ‘seed’