Location of income tax offices¶
The example description in the following section is taken from Section 15.5 Location of income tax offices of the book Applications of optimization with Xpress-MP. The income tax administration is planning to restructure the network of income tax offices in a region. The number of inhabitants of every city and the distances between each pair of cities are known (see table below). The income tax administration has determined that offices should be established in three cities to provide sufficient coverage. Where should these offices be located to minimize the average distance per inhabitant to the closest income tax office ?
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
|
1 |
0 |
15 |
37 |
55 |
24 |
60 |
18 |
33 |
48 |
40 |
58 |
67 |
2 |
15 |
0 |
22 |
40 |
38 |
52 |
33 |
48 |
42 |
55 |
61 |
61 |
3 |
37 |
22 |
0 |
18 |
16 |
30 |
43 |
28 |
20 |
58 |
39 |
39 |
4 |
55 |
40 |
18 |
0 |
34 |
12 |
61 |
46 |
24 |
62 |
43 |
34 |
5 |
24 |
38 |
16 |
34 |
0 |
36 |
27 |
12 |
24 |
49 |
37 |
43 |
6 |
60 |
52 |
30 |
12 |
36 |
0 |
57 |
42 |
12 |
50 |
31 |
22 |
7 |
18 |
33 |
43 |
61 |
27 |
57 |
0 |
15 |
45 |
22 |
40 |
61 |
8 |
33 |
48 |
28 |
46 |
12 |
42 |
15 |
0 |
30 |
37 |
25 |
46 |
9 |
48 |
42 |
20 |
24 |
24 |
12 |
45 |
30 |
0 |
38 |
19 |
19 |
10 |
40 |
55 |
58 |
62 |
49 |
50 |
22 |
37 |
38 |
0 |
19 |
40 |
11 |
58 |
61 |
39 |
43 |
37 |
31 |
40 |
25 |
19 |
19 |
0 |
21 |
12 |
67 |
61 |
39 |
34 |
43 |
22 |
61 |
46 |
19 |
40 |
21 |
0 |
Pop. (in 1000) |
15 |
10 |
12 |
18 |
5 |
24 |
11 |
16 |
13 |
22 |
19 |
20 |
Model formulation¶
Let  be the set of cities. For the formulation of the problem, two groups of decision variables are necessary: a variable
be the set of cities. For the formulation of the problem, two groups of decision variables are necessary: a variable  that is one if and only if a tax office is established in city
that is one if and only if a tax office is established in city  , and a variable
, and a variable  that takes the number of the office on which city
that takes the number of the office on which city  depends. For the formulation of the constraints, we further introduce two sets of auxiliary variables:
depends. For the formulation of the constraints, we further introduce two sets of auxiliary variables:  , the distance from city
, the distance from city  to the office indicated by
to the office indicated by  , and
, and  , the number of cities depending on an office location.
, the number of cities depending on an office location.
The following relations are required to link the  with the
with the  variables:
variables:
 counts the number of occurrences of office location
counts the number of occurrences of office location  among the variables dependc;
among the variables dependc;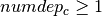 if and only if the office in
if and only if the office in  is built (as a consequence, if the office in
is built (as a consequence, if the office in  is not built, then we must have
is not built, then we must have  );
);

Since the number of offices built is limited by the given bound  , i.e.
, i.e.  , it would actually be sufficient to formulate the second relation between the
, it would actually be sufficient to formulate the second relation between the  and
and  variables as the implication If
variables as the implication If 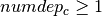 then the office in
then the office in  must be built, and inversely, if the office in
must be built, and inversely, if the office in  is not built, then we must have
is not built, then we must have  .
.
The objective function to be minimized is the total distance weighted by the number of inhabitants of the cities. We need to divide the resulting value by the total population of the region to obtain the average distance per inhabitant to the closest income tax office. The distance  from city
from city  to the closest tax office location is obtained by a discrete function, namely the row
to the closest tax office location is obtained by a discrete function, namely the row  of the distance matrix
of the distance matrix  indexed by the value of
indexed by the value of  :
:

Implementation¶
To solve this problem, we define a branching strategy with two parts, one for the  variables and a second strategy for the
variables and a second strategy for the  variables. The latter are enumerated using the
variables. The latter are enumerated using the KSplitDomain branching scheme that divides the domain of the branching variable into several disjoint subsets (instead of assigning a value to the variable). We now pass an array of type KBranchingSchemeArray as the argument to the constructor of KSolver. The different strategies will be applied in their order in this array. Since our enumeration strategy does not explicitly include all decision variables of the problem, Artelys Kalis will enumerate these using the default strategy if any unassigned variables remain after the application of our search strategy.
// Number of cities
int NC = 12;
// Distance matrix
int DIST[12][12];
// Population of cities
int POP[12] = {15, 10, 12 ,18 ,5 ,24, 11, 16, 13, 22, 19 ,20};
// Desired number of tax offices
int NUMLOC = 3;
// 1 if office in city, 0 otherwise
KIntVarArray build;
// Office on which city depends
KIntVarArray depend;
// Distance to tax office
KIntVarArray depdist;
// Number of depending cities per off.
KIntVarArray numdep;
// Objective function variable
KIntVar * totDist;
// Creation of the problem in this session
KProblem problem(session,"J-5 Tax office location");
// index variables
int b,c,d;
// Calculate the distance matrix
// Initialize all distance labels with a sufficiently large value
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
for (d=0;d<NC;d++) {
DIST[c][d] = MAX_INT;
}
}
// Set values on the diagonal to 0
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
DIST[c][c] = 0;
}
// Length of existing road connections
DIST[0][1] = 15;DIST[0][4] = 24;DIST[0][6] = 18;DIST[1][2] = 22;
DIST[2][3] = 18;DIST[2][4] = 16;DIST[2][8] = 20;DIST[3][5] = 12;
DIST[4][7] = 12;DIST[4][8] = 24;DIST[5][8] = 12;DIST[5][11] = 22;
DIST[6][7] = 15;DIST[6][9] = 22;DIST[7][8] = 30;DIST[7][10] = 25;
DIST[8][10] = 19;DIST[8][11] = 19;DIST[9][10] = 19;DIST[10][11] = 21;
// distances are symetric
for (b=0;b<NC;b++) {
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
if (DIST[b][c] != MAX_INT) {
DIST[c][b] = DIST[b][c];
}
}
}
// Update shortest distance for every node triple
for (b=0;b<NC;b++) {
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
for (d=0;d<NC;d++) {
if (c<d) {
if (DIST[c][d] > DIST[c][b]+DIST[b][d]) {
DIST[c][d] = DIST[c][b]+DIST[b][d];
DIST[d][c] = DIST[c][b]+DIST[b][d];
}
}
}
}
}
// total popuplation
int sumPop=0;
char name[80];
// building variables
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
sprintf(name,"build(%i)",c);
build += (* new KIntVar(problem,name,0,1) );
sprintf(name,"depend(%i)",c);
depend += (* new KIntVar(problem,name,0,NC-1) );
int dmin=DIST[c][0];
int dmax=DIST[c][0];
int d;
for (d=1;d<NC;d++) {
if (DIST[d][c] < dmin) {
dmin = DIST[c][d];
}
if (DIST[c][d] > dmax) {
dmax = DIST[c][d];
}
}
sprintf(name,"depdist(%i)",c);
depdist += (* new KIntVar(problem,name,dmin,dmax) );
sprintf(name,"numdep(%i)",c);
numdep += (* new KIntVar(problem,name,0,NC) );
// compute total popuplation for solution printing routines
sumPop += POP[c];
}
// Distance from cities to tax offices
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
// Auxiliary array used in constr. def.
KIntArray D;
for (d=0;d<NC;d++) {
D += DIST[d][c];
}
KEltTerm kelt(D,depend[c]);
problem.post(kelt == depdist[c]);
}
// Number of cities depending on every office
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
KOccurTerm koc(c,depend);
problem.post(koc == numdep[c]);
}
// Relations between dependencies and offices built
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
problem.post(KEquiv(build[c] == 1, numdep[c] >= 1));
}
// Limit total number of offices
KLinTerm sbuild;
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
sbuild = sbuild + build[c];
}
problem.post(sbuild <= NUMLOC);
// Objective: weighted total distance
totDist = new KIntVar(problem,"totdDist",0,10000);
KLinTerm popDistTerm;
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
popDistTerm = popDistTerm + POP[c] * depdist[c];
}
problem.post(popDistTerm == *totDist);
// propagating problem
if (problem.propagate()) {
printf("Problem is infeasible\n");
exit(1);
}
problem.setObjective(*totDist);
problem.setSense(KProblem::Minimize);
// Search strategy
KBranchingSchemeArray myBa;
myBa += KAssignAndForbid(KMaxDegree(),KMaxToMin(),build);
myBa += KSplitDomain(KSmallestDomain(),KMinToMax(),depdist,true,5);
// creation of the solver
KSolver solver(problem,myBa);
// Solve the problem
if (solver.optimize()) {
KSolution * sol = &problem.getSolution();
// do something with optimal solution
}
int totalDist = problem.getSolution().getValue(*totDist);
// Solution printing
printf("Total weighted distance: %d (average per inhabitant: %f\n", totalDist,totalDist / (float)sumPop);
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
if (problem.getSolution().getValue(build[c]) > 0) {
printf("Office in %i: ",c);
for (d=0;d<NC;d++) {
if (problem.getSolution().getValue(depend[d]) == c) {
printf(" %i",d);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
from kalis import *
### Data
# Number of cities
nb_cities = 12
# Distance matrix
distances = [[float('inf') if c != b else 0 for c in range(nb_cities)] for b in range(nb_cities)]
# Existing roads:
distances[0][1] = 15;distances[0][4] = 24;distances[0][6] = 18;distances[1][2] = 22
distances[2][3] = 18;distances[2][4] = 16;distances[2][8] = 20;distances[3][5] = 12
distances[4][7] = 12;distances[4][8] = 24;distances[5][8] = 12;distances[5][11] = 22
distances[6][7] = 15;distances[6][9] = 22;distances[7][8] = 30;distances[7][10] = 25
distances[8][10] = 19;distances[8][11] = 19;distances[9][10] = 19;distances[10][11] = 21
# Distances are symmetric
for i in range(nb_cities):
for j in range(nb_cities):
if distances[i][j] != float('inf'):
distances[j][i] = distances[i][j]
# Update shortest distance for every node triple
for b in range(nb_cities):
for c in range(nb_cities):
for d in range(c + 1, nb_cities):
if distances[c][d] > distances[c][b] + distances[b][d]:
distances[c][d] = distances[c][b] + distances[b][d]
distances[d][c] = distances[c][b] + distances[b][d]
# Population of cities
populations = [15, 10, 12, 18, 5, 24, 11, 16, 13, 22, 19, 20]
total_population = sum(populations)
# Desired number of tax offices
nb_offices = 3
### Variables creation
# Creation of the Kalis session and of the optimization problem
session = KSession()
problem = KProblem(session, "J-5 Tax office location")
# Building variables: 1 if office in city, 0 otherwise
build = KIntVarArray()
for c in range(nb_cities):
build += KIntVar(problem, "build(%d)" % c, 0, 1)
# Office on which city depends
depend = KIntVarArray()
for c in range(nb_cities):
depend += KIntVar(problem, "depend(%d)" % c, 0, nb_cities - 1)
# Distance to tax office
dep_dist = KIntVarArray()
for c in range(nb_cities):
min_dist = min(distances[c])
max_dist = max(distances[c])
dep_dist += KIntVar(problem, "depdist(%d)" % c, min_dist, max_dist)
# Number of depending cities per off
num_dep = KIntVarArray()
for c in range(nb_cities):
num_dep += KIntVar(problem, "numdep(%d)" % c, 0, nb_cities)
### Constraints creation
# Set distances variables to their corresponding data
for c in range(nb_cities):
# auxiliary array used to set up the constraint
K_dist = KIntArray()
for d in range(nb_cities):
res = K_dist.add(distances[c][d])
# set KElement constraint: "dep_dist[c] == distances[depend[c]]"
kelt = KEltTerm(K_dist, depend[c])
problem.post(kelt == dep_dist[c])
# Set the number of cities depending for each office
for c in range(nb_cities):
koc = KOccurTerm(c, depend)
problem.post(koc == num_dep[c])
# Relations between dependencies and offices built
for c in range(nb_cities):
problem.post(KEquiv(build[c] == 1, num_dep[c] >= 1))
# Limit total number of offices
build_sum = 0
for c in range(nb_cities):
build_sum += build[c]
problem.post(build_sum <= nb_offices)
# Set objective
total_distance = KIntVar(problem, "totDist", 0, 10000)
populations_distance_product = 0
for c in range(nb_cities):
populations_distance_product += populations[c] * dep_dist[c]
problem.post(populations_distance_product == total_distance)
### Solve the problem
# First propagation to check inconsistency
if problem.propagate():
print("Problem is infeasible")
sys.exit(1)
# Setting objective and sense of optimization
problem.setSense(KProblem.Minimize)
problem.setObjective(total_distance)
# Set the branching strategy
myBranchingArray = KBranchingSchemeArray()
# KAssignAndForbid for the "build" variables
myBranchingArray += KAssignAndForbid(KMaxDegree(), KMaxToMin(), build)
# KSplit domain for the "dep_dist" variables ('True' stand for exploring the lower part first,
# '5' stand for the minimum domain size where the domain is not split anymore)
myBranchingArray += KSplitDomain(KSmallestDomain(), KMinToMax(), dep_dist, True, 5)
# Set the solver
solver = KSolver(problem, myBranchingArray)
# Run optimization
result = solver.optimize()
# Solution printing
if result:
solution = problem.getSolution()
solution.printResume()
total_distance_found = solution.getValue(total_distance)
print("Total weighted distance: %f (average per inhabitant: %f)" % (total_distance_found,
total_distance_found / float(total_population)))
for c in range(nb_cities):
if solution.getValue(build[c]) > 0:
print("Office in %d: " % c)
for d in range(nb_cities):
if solution.getValue(depend[d]) == c:
print(d, end=" ")
print("")
// *** Creation of the session
KSession session = new KSession();
// Number of cities
int NC = 12;
// Distance matrix
int DIST[][];
// Population of cities
int POP[] = {15, 10, 12 ,18 ,5 ,24, 11, 16, 13, 22, 19 ,20};
// Desired number of tax offices
int NUMLOC = 3;
// 1 if office in city, 0 otherwise
KIntVarArray build = new KIntVarArray();
// Office on which city depends
KIntVarArray depend = new KIntVarArray();
// Distance to tax office
KIntVarArray depdist = new KIntVarArray();
// Number of depending cities per off.
KIntVarArray numdep = new KIntVarArray();
// Objective function variable
KIntVar totDist = new KIntVar();
// Creation of the problem in this session
KProblem problem = new KProblem(session,"J-5 Tax office location");
// index variables
int b,c,d;
// Calculate the distance matrix
// Initialize all distance labels with a sufficiently large value
DIST = new int[NC][NC];
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
for (d=0;d<NC;d++)
{
DIST[c][d] = 10000000;
}
}
// Set values on the diagonal to 0
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
DIST[c][c] = 0;
}
// Length of existing road connections
DIST[0][1] = 15;
DIST[0][4] = 24;
DIST[0][6] = 18;
DIST[1][2] = 22;
DIST[2][3] = 18;
DIST[2][4] = 16;
DIST[2][8] = 20;
DIST[3][5] = 12;
DIST[4][7] = 12;
DIST[4][8] = 24;
DIST[5][8] = 12;
DIST[5][11] = 22;
DIST[6][7] = 15;
DIST[6][9] = 22;
DIST[7][8] = 30;
DIST[7][10] = 25;
DIST[8][10] = 19;
DIST[8][11] = 19;
DIST[9][10] = 19;
DIST[10][11] = 21;
// distances are symetric
for (b=0;b<NC;b++)
{
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
if (DIST[b][c] != Integer.MAX_VALUE)
{
DIST[c][b] = DIST[b][c];
}
}
}
// Update shortest distance for every node triple
for (b=0;b<NC;b++)
{
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
for (d=0;d<NC;d++)
{
if (c<d)
{
if (DIST[c][d] > DIST[c][b]+DIST[b][d])
{
DIST[c][d] = DIST[c][b]+DIST[b][d];
DIST[d][c] = DIST[c][b]+DIST[b][d];
}
}
}
}
}
// total popuplation
int sumPop=0;
// building variables
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
build.add( new KIntVar(problem,"build("+c+")",0,1) );
depend.add( new KIntVar(problem,"depend("+c+")",0,NC-1) );
int dmin=DIST[c][0];
int dmax=DIST[c][0];
for (d=1;d<NC;d++)
{
if (DIST[d][c] < dmin)
{
dmin = DIST[c][d];
}
if (DIST[c][d] > dmax)
{
dmax = DIST[c][d];
}
//System.out.println("dmin="+dmin);
//System.out.println("dmax="+dmax);
}
depdist.add(new KIntVar(problem,"depdist("+c+")",dmin,dmax) );
numdep.add(new KIntVar(problem,"numdep("+c+")",0,NC) );
// compute total popuplation for solution printing routines
sumPop += POP[c];
}
// Distance from cities to tax offices
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
// Auxiliary array used in constr. def.
KIntArray D = new KIntArray();
for (d=0;d<NC;d++)
{
D.add(DIST[d][c]);
}
KEltTerm kelt = new KEltTerm(D,depend.getElt(c));
//problem.post(kelt == depdist.getElt(c));
problem.post(new KElement(kelt,depdist.getElt(c)));
}
// Number of cities depending on every office
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
KOccurTerm koc = new KOccurTerm(c,depend);
//problem.post(koc == numdep.getElt(c));
problem.post(new KOccurrence(koc,numdep.getElt(c),true,true));
}
// Relations between dependencies and offices built
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
problem.post(new KEquiv(new KEqualXc(build.getElt(c),1), new KGreaterOrEqualXc(numdep.getElt(c),1)));
}
// Limit total number of offices
KLinTerm sbuild = new KLinTerm();
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
sbuild.add(build.getElt(c),1);
}
problem.post(new KNumLinComb("",sbuild.getCoeffs(),sbuild.getLvars(),-NUMLOC,KNumLinComb.LinCombOperator.LessOrEqual));
// Objective: weighted total distance
totDist = new KIntVar(problem,"totdDist",0,10000);
KLinTerm popDistTerm = new KLinTerm();
for (c=0;c<NC;c++)
{
popDistTerm.add( depdist.getElt(c),POP[c]);
}
popDistTerm.add(totDist,-1);
problem.post(new KNumLinComb("",popDistTerm.getCoeffs(),popDistTerm.getLvars(),0,KLinComb.LinCombOperator.Equal));
problem.print();
// propagating problem
if (problem.propagate())
{
System.out.println("Problem is infeasible\n");
System.exit(1);
}
problem.setObjective(totDist);
problem.setSense(KProblem.Sense.Minimize);
// Search strategy
KBranchingSchemeArray myBa = new KBranchingSchemeArray();
myBa.add(new KAssignAndForbid(new KMaxDegree(),new KMaxToMin(),build));
myBa.add(new KSplitDomain(new KSmallestDomain(),new KMinToMax(),depdist,true,5));
// creation of the solver
KSolver solver = new KSolver(problem,myBa);
solver.setSolverEventListener(new MySolverEventListener());
// Solve the problem
if (solver.optimize() != 0) {
KSolution sol = problem.getSolution();
sol.print();
// do something with optimal solution
int totalDist = problem.getSolution().getValue(totDist);
// Solution printing
System.out.println("Total weighted distance: "+totalDist+" (average per inhabitant: "+(totalDist / (float)sumPop));
for (c=0;c<NC;c++) {
if (problem.getSolution().getValue(build.getElt(c)) > 0) {
System.out.print("Office in "+c+" :");
for (d=0;d<NC;d++) {
if (problem.getSolution().getValue(depend.getElt(d)) == c) {
System.out.print(" "+d);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Results¶
The optimal solution to this problem has a total weighted distance of 2438. Since the region has a total of 185,000 inhabitants, the average distance per inhabitant is 2438/185 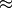 13.178 km. The three offices are established at nodes 1, 6, and 11. The first serves cities 1, 2, 5, 7, the office in node 6 cities 3, 4, 6, 9, and the office in node 11 cities 8, 10, 11, 12.
13.178 km. The three offices are established at nodes 1, 6, and 11. The first serves cities 1, 2, 5, 7, the office in node 6 cities 3, 4, 6, 9, and the office in node 11 cities 8, 10, 11, 12.