Multi-Mode Resource Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (MRCPSP)¶
The Resource Constrained Project Scheduling Problem (RCPSP) consists in determining the start time of each task of a project, these tasks being subject to precedence and resources constraints. The precedence constraints are defined by the impossibility to start processing a task while the processing of at least one of its predecessor is not finished. Each task consumes a certain amount of resources, all of which are renewable. This means that all the consumptions of tasks are restored to the resource once the task’s processing is finished. In the RCPSP, the tasks’ duration is fixed. For the Multi-Mode version (MRCPSP), both the duration and the consumptions of tasks depend on the mode assigned to the task.
Model formulation¶
To express a mathematical model for the MRCPSP suited for Artelys Kalis, we will use Tasks, which are objects that rely on integer variables as their start time, duration time and end time. We note  the number of tasks to schedule and for each task
the number of tasks to schedule and for each task  its start time is an integer variable
its start time is an integer variable  , its duration is an integer variable
, its duration is an integer variable  and its end time is an integer variable
and its end time is an integer variable  .
.
As said, the MRCPSP is different from the RCPSP by the fact that the durations and resource consumptions of tasks depend on their mode. For a task  , its mode is an integer variable
, its mode is an integer variable  , the set of potential durations
, the set of potential durations  and
and  is the set of potential consumption on each resource
is the set of potential consumption on each resource  . For each task
. For each task  and each resource
and each resource  ,
,  is an integer variable representing the consumption of task
is an integer variable representing the consumption of task  on resource
on resource  .
.
For each resource  , its capacity (or availability) is noted
, its capacity (or availability) is noted  , and the number of renewable resources is noted
, and the number of renewable resources is noted 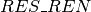 , while the number of non-renewable resources is noted
, while the number of non-renewable resources is noted  .
.
Finally, we note  the set of precedence, with
the set of precedence, with  meaning that task
meaning that task  precedes task
precedes task  .
.
We therefore have the following model for the MRCPSP:
![&\forall (i,j) \in P, e_i \leq s_j\\
&\forall i \in \{1, \dots, N\}, s_i + d_i = e_i\\
&\forall k \in \{1, \dots, RES\_REN\}, \text{cumulative}(\{T_1, \dots, T_N \}, \{h_{1,k}, \dots, h_{N,k} \}, C_k)\\
&\forall k \in \{1, \dots, RES\_NON\}, \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{N} h_{i,k} \leq C_{k}\\
&\forall i \in \{1, \dots, N\}, d_i = D_i[ \,m_i] \,\\
&\forall i \in \{1, \dots, N\}, \forall k \in \{1, \dots, RES\}, h_{i,k} = H_{i,k}[ \,m_i] \,\\](../_images/math/2fe5ef53139a543c18c689de2df818fc0edb1e25.png)
Let note that the last two sets of constraints of our model are implemented using element constraints.
Implementation¶
In this section, we will see how to implement the mathematical model formulated above using the different interfaces of Artelys Kalis. Most especially, we will benefit from the API dedicated to scheduling problems.
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
// Including "kalis.h" to access the library
#include "Kalis.h"
// ********************************************************************
// * Main Program *
// ********************************************************************
int min(int a[], int size) {
int min = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if(min > a[i]) {
min = a[i];
}
}
return min;
}
int max(int a[], int size) {
int max = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
if(max < a[i]) {
max = a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
template <size_t x, size_t y, size_t z>
int * retrieveConsumptions(int nbModes[], int (&consumptions)[x][y][z], int task, int res) {
int *c = new int[nbModes[task]];
for(int i = 0; i < nbModes[task]; i++) {
c[i] = consumptions[task][i][res];
}
return c;
}
int main(void) {
// *** Description of datas
// *** Number of tasks in the project
int const nbTasks = 10;
// *** Number of resources
int const nbResources = 4;
// *** Number of renewable resources
int const nbResRen = 2;
// *** Horizon
int const horizon = 61;
// *** Number of modes of each task
int nbModes[10] = {3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3};
// *** Set of successors of eack task
int nbSuccessors[10] = {2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0};
int successors[][nbTasks] = {
{2, 3},
{3, 4},
{5},
{5, 6},
{6, 7},
{8, 9},
{9},
{9},
{},
{}
};
// *** Duration of eack task depending on their mode
int durations[nbTasks][3] = {
{3, 5, 7},
{1, 4, 8},
{2, 3, 4},
{4, 5, 5},
{3},
{2, 4, 8},
{4, 5, 9},
{2, 3, 5},
{2, 4, 5},
{1, 4, 7}
};
// *** Consumption of resources by tasks depending on their mode: consumptions[idTask][idMode][idResource]
int consumptions[nbTasks][3][nbResources] = {
{{4, 2, 4, 5}, {2, 2, 3, 4}, {2, 1, 2, 1}},
{{5, 4, 4, 5}, {3, 3, 0, 3}, {2, 2, 0, 0}},
{{3, 3, 2, 0}, {2, 3, 2, 0}, {2, 2, 1, 0}},
{{3, 3, 4, 5}, {3, 3, 2, 0}, {3, 3, 0, 2}},
{{5, 5, 0, 0}},
{{4, 4, 4, 7}, {3, 3, 2, 5}, {2, 2, 0, 4}},
{{3, 2, 7, 3}, {3, 2, 3, 5}, {3, 2, 0, 0}},
{{2, 2, 5, 6}, {2, 4, 3, 3}, {2, 2, 0, 1}},
{{3, 3, 6, 4}, {4, 3, 4, 4}, {2, 2, 2, 2}},
{{4, 4, 6, 9}, {3, 3, 3, 5}, {4, 3, 2, 4}}
};
// *** Resource capacities
int resourceAvailabilities[nbResources] = {8, 7, 20, 25};
try {
// *** Creation of the Session
KSession session;
// *** Modeling of the problem
// *** Creation of the problem "MRCPSP" in this Session
KProblem problem(session, const_cast<char *>("MRCPSP"));
// Creation of the schedule
KSchedule schedule(problem, "Schedule", 0, horizon);
// Create tasks
KTask *tasks = new KTask[nbTasks];
for(int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i++) {
std::stringstream sout("");
sout << "task(" << i << ")";
tasks[i] = KTask(schedule, sout.str().c_str(), 0, horizon, min(durations[i], nbModes[i]), max(durations[i], nbModes[i]));
}
// Precedence
for(int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < nbSuccessors[i]; j++) {
tasks[successors[i][j]].startsAfter(tasks[i]);
}
}
// Resources
KIntVar *resourceConsumptions = new KIntVar[nbTasks*nbResources];
// renewable resources
KResource *resources = new KResource[nbResources];
for(int j = 0; j < nbResources; j++) {
std::stringstream sout("");
sout << "res(" << j << ")";
resources[j] = KDiscreteResource(schedule, sout.str().c_str(), resourceAvailabilities[j]);
for(int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i++) {
int *c = retrieveConsumptions(nbModes, consumptions, i, j);
if(j < nbResRen) {
tasks[i].requires(resources[j], min(c, nbModes[i]), max(c, nbModes[i]));
resourceConsumptions[i*nbResources + j] = * tasks[i].getRequiresVar(&resources[j]);
} else {
tasks[i].consumes(resources[j], min(c, nbModes[i]), max(c, nbModes[i]));
resourceConsumptions[i*nbResources + j] = * tasks[i].getConsumesVar(&resources[j]);
}
delete [] c;
}
}
// Manage modes
KIntVarArray modes;
for(int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i++) {
std::stringstream sout("");
sout << "mode(" << i << ")";
modes += KIntVar(problem, sout.str().c_str(), 0, nbModes[i] - 1);
KIntArray durationsValues;
for(int k = 0; k < nbModes[i]; k++) {
durationsValues += durations[i][k];
}
KEltTerm kelt(durationsValues, *(modes.getElt(i)));
problem.post(new KElement(kelt, *(tasks[i].getDurationVar())));
for(int j = 0; j < nbResources; j++) {
KIntArray consumptionsValues;
for(int k = 0; k < nbModes[i]; k++) {
consumptionsValues += consumptions[i][k][j];
}
KEltTerm keltConsumptions(consumptionsValues, *(modes.getElt(i)));
problem.post(new KElement(keltConsumptions, resourceConsumptions[i*nbResources + j]));
}
}
schedule.close();
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray;
KIntVarArray intvarArray;
for(int i = 0; i < nbTasks; i++) {
intvarArray += *(tasks[i].getStartDateVar());
intvarArray += *(modes.getElt(i));
}
myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KInputOrder(),KMinToMax(), intvarArray);
// problem.print();
// propagating problem
if (problem.propagate()) {
std::cout << "Problem is infeasible" << std::endl;
exit(1);
}
// *** Creation of the solver using our tree search controls for this problem
KSolver solver(problem, myBranchingSchemeArray);
solver.optimize();
// *** Get the last ( therefore the best ) solution and store it in a Solution object
KSolution solution = problem.getSolution();
// *** Print variables values for this solution
std::cout << "Best solution :" << std::endl;
solution.print();
// *** Print the objective value
std::cout << "Objective Value = " << solution.getObjectiveValue() << std::endl;
delete [] tasks;
delete [] resourceConsumptions;
delete [] resources;
} catch (ArtelysException &artelysException) {
// *** An error occured
std::cout << "Exception " << artelysException.getCode() << " raised : " << artelysException.getMessage() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
from kalis import *
### Data
nb_activities = 10
nb_resources = 4
nb_resources_renewable = 2
nb_resources_non = 2
horizon = 61
nb_modes = [3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3]
successors = [[2, 3],
[3, 4],
[5],
[5, 6],
[6, 7],
[8, 9],
[9],
[9],
[],
[]
]
durations_by_modes = [[3, 5, 7],
[1, 4, 8],
[2, 3, 4],
[4, 5, 5],
[3],
[2, 4, 8],
[4, 5, 9],
[2, 3, 5],
[2, 4, 5],
[1, 4, 7]
]
resources_usages = [[[4, 2, 4, 5], [2, 2, 3, 4], [2, 1, 2, 1]],
[[5, 4, 4, 5], [3, 3, 0, 3], [2, 2, 0, 0]],
[[3, 3, 2, 0], [2, 3, 2, 0], [2, 2, 1, 0]],
[[3, 3, 4, 5], [3, 3, 2, 0], [3, 3, 0, 2]],
[[5, 5, 0, 0]],
[[4, 4, 4, 7], [3, 3, 2, 5], [2, 2, 0, 4]],
[[3, 2, 7, 3], [3, 2, 3, 5], [3, 2, 0, 0]],
[[2, 2, 5, 6], [2, 4, 3, 3], [2, 2, 0, 1]],
[[3, 3, 6, 4], [4, 3, 4, 4], [2, 2, 2, 2]],
[[4, 4, 6, 9], [3, 3, 3, 5], [4, 3, 2, 4]]
]
resources_availabilities = [8, 7, 20, 25]
def get_consumption_domain_modes(activity, res):
consumption_domain_modes = []
for i_mode in range(nb_modes[activity]):
consumption_domain_modes.append(resources_usages[activity][i_mode][res])
return consumption_domain_modes
### Model
tasks = {}
modes = {}
resources = {}
consumptions = {}
session = KSession()
problem = KProblem(session, "PSP problem")
schedule = KSchedule(problem, "PSP schedule", 0, horizon)
### Variables creation
# Tasks to be planned
for act in range(nb_activities):
d = durations_by_modes[act]
tasks[act] = KTask(schedule, "task(" + str(act) + ")", 0, horizon, min(d), max(d))
consumptions[act] = dict()
# Declare resources
for j in range(nb_resources):
resources[j] = KDiscreteResource(schedule, "res(" + str(j) + ")",
resources_availabilities[j],
KDiscreteResource.TimeTabling)
# Declare consumption variables
for act in range(nb_activities):
for j in range(nb_resources):
c = get_consumption_domain_modes(act, j)
if j < nb_resources_renewable:
tasks[act].requires(resources[j], min(c), max(c))
consumptions[act][j] = tasks[act].getRequiresVar(resources[j])
else:
tasks[act].consumes(resources[j], min(c), max(c))
consumptions[act][j] = tasks[act].getConsumesVar(resources[j])
### Constraints
# Setting the successors of each task
for i1 in range(nb_activities):
for i2 in successors[i1]:
tasks[i2].startsAfter(tasks[i1])
for act in range(nb_activities):
modes[act] = KIntVar(problem, "mode(" + str(act) + ")", 0, nb_modes[act] - 1)
# Durations of tasks depend of their mode
durations = KIntArray()
for im in range(nb_modes[act]):
durations.add(durations_by_modes[act][im])
problem.post(KElement(durations, modes[act], tasks[act].getDurationVar()))
# Tasks' consumption on resources depend of their mode
for act in range(nb_activities):
for j in range(nb_resources):
consumption_by_modes = KIntArray()
for im in range(nb_modes[act]):
consumption_by_modes.add(resources_usages[act][im][j])
problem.post(KElement(consumption_by_modes, modes[act], consumptions[act][j]))
schedule.close()
myBranchingSchemeArray = KBranchingSchemeArray()
intvarArray = KIntVarArray()
for i in range(nb_activities):
intvarArray += tasks[i].getStartDateVar()
intvarArray += modes.get(i)
myBranchingSchemeArray += KAssignVar(KInputOrder(), KMinToMax(), intvarArray)
### Solve the problem
# First propagation to check inconsistency
if problem.propagate():
print("Problem is infeasible")
sys.exit(1)
# Set the solver
solver = KSolver(problem, myBranchingSchemeArray)
# Run optimization
result = solver.optimize()
# Solution printing
if result:
solution = problem.getSolution()
solution.printResume()
makespan_value = solution.getValue(schedule.getObjective())
print("makespan_value=", makespan_value)
import com.artelys.kalis.*;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class MRCPSP {
public static final int NB_ACTIVITIES = 10;
public static final int NB_RESOURCES = 4;
public static final int RES_REN = 2;
public static final int HORIZON = 61;
public static final int[] NB_MODES = new int[]{
3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3
};
public static final int[][] SUCCESSORS = new int[][]{
{2, 3},
{3, 4},
{5},
{5, 6},
{6, 7},
{8, 9},
{9},
{9},
{},
{}
};
public static final int[][] DURATIONS = new int[][]{
{3, 5, 7},
{1, 4, 8},
{2, 3, 4},
{4, 5, 5},
{3},
{2, 4, 8},
{4, 5, 9},
{2, 3, 5},
{2, 4, 5},
{1, 4, 7}
};
public static final int[][][] CONSUMPTIONS = new int[][][] {
{{4, 2, 4, 5}, {2, 2, 3, 4}, {2, 1, 2, 1}},
{{5, 4, 4, 5}, {3, 3, 0, 3}, {2, 2, 0, 0}},
{{3, 3, 2, 0}, {2, 3, 2, 0}, {2, 2, 1, 0}},
{{3, 3, 4, 5}, {3, 3, 2, 0}, {3, 3, 0, 2}},
{{5, 5, 0, 0}},
{{4, 4, 4, 7}, {3, 3, 2, 5}, {2, 2, 0, 4}},
{{3, 2, 7, 3}, {3, 2, 3, 5}, {3, 2, 0, 0}},
{{2, 2, 5, 6}, {2, 4, 3, 3}, {2, 2, 0, 1}},
{{3, 3, 6, 4}, {4, 3, 4, 4}, {2, 2, 2, 2}},
{{4, 4, 6, 9}, {3, 3, 3, 5}, {4, 3, 2, 4}}
};
public static final int[] RESOURCE_AVAILABILITIES = new int[]{
8, 7, 20, 25
};
public static int[] retrieveConsumptions(int activity, int res) {
return IntStream.range(0, NB_MODES[activity]).map(k -> CONSUMPTIONS[activity][k][res]).toArray();
}
public static int min(int[] a) {
int min = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if(min > a[i]) {
min = a[i];
}
}
return min;
}
public static int max(int[] a) {
int max = a[0];
for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if(max < a[i]) {
max = a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.loadLibrary("Kalis"); // uses java option -Djava.library.path=path to find Kalis.dll
System.loadLibrary("KalisJava"); // uses java option -Djava.library.path=path to find KalisJava.dll
// Creation of the session
KSession session = new KSession();
// Creation of the problem
KProblem problem = new KProblem(session,"RCPSP multi-mode");
// Creation of the schedule
KSchedule schedule = new KSchedule(problem, "Schedule", 0, HORIZON);
// Create tasks
KTask[] tasks = new KTask[NB_ACTIVITIES];
for(int i = 0; i < NB_ACTIVITIES; i++) {
int[] d = DURATIONS[i];
tasks[i] = new KTask(schedule, "task(" + i + ")", 0, HORIZON, min(d), max(d));
}
// Precedence
for(int i = 0; i < NB_ACTIVITIES; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < SUCCESSORS[i].length; j++) {
tasks[SUCCESSORS[i][j]].startsAfter(tasks[i]);
}
}
// Resources
KIntVar[][] resourceConsumptions = new KIntVar[NB_ACTIVITIES][NB_RESOURCES];
// renewable resources
KDiscreteResource[] resources = new KDiscreteResource[NB_RESOURCES];
for(int j = 0; j < resources.length; j++) {
resources[j] = new KDiscreteResource(schedule, "res(" + j + ")", RESOURCE_AVAILABILITIES[j]);
for(int i = 0; i < NB_ACTIVITIES; i++) {
int[] c = retrieveConsumptions(i, j);
if(j < RES_REN) {
tasks[i].requires(resources[j], min(c), max(c));
resourceConsumptions[i][j] = tasks[i].getRequiresVar(resources[j]);
} else {
tasks[i].consumes(resources[j], min(c), max(c));
resourceConsumptions[i][j] = tasks[i].getConsumesVar(resources[j]);
}
}
}
// Manage modes
KIntVarArray modes = new KIntVarArray();
for(int i = 0; i < NB_ACTIVITIES; i++) {
modes.add(new KIntVar(problem, "mode(" + i + ")", 0, NB_MODES[i] - 1));
KIntArray durations = new KIntArray();
for(int k = 0; k < NB_MODES[i]; k++) {
durations.add(DURATIONS[i][k]);
}
problem.post(new KElement(durations, modes.getElt(i), tasks[i].getDurationVar(), 0));
for(int j = 0; j < NB_RESOURCES; j++) {
KIntArray consumptions = new KIntArray();
for(int k = 0; k < NB_MODES[i]; k++) {
consumptions.add(CONSUMPTIONS[i][k][j]);
}
problem.post(new KElement(consumptions, modes.getElt(i), resourceConsumptions[i][j], 0));
}
}
schedule.close();
KBranchingSchemeArray myBranchingSchemeArray = new KBranchingSchemeArray();
KIntVarArray intvarArray = new KIntVarArray();
for(int i = 0; i < tasks.length; i++) {
intvarArray.add(tasks[i].getStartDateVar());
intvarArray.add(modes.getElt(i));
}
myBranchingSchemeArray.add(new KAssignVar(new KInputOrder(), new KMinToMax(), intvarArray));
// Propagating the constraints
if (problem.propagate()) {
System.out.println("Problem is infeasible");
System.exit(1);
}
// Minimize the makespan
KSolver solver = new KSolver(problem, myBranchingSchemeArray);
int result = solver.optimize();
if (result == 0) {
System.out.println("No solution found");
System.exit(1);
}
// Printing solution
problem.getSolution().print();
double makespanValue = problem.getSolution().getValue(schedule.getObjective());
System.out.println("makespan_value= "+makespanValue);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Results¶
The minimum makespan of the schedule is 20, with the following start times and modes for the tasks:
Task |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
Start Time |
0 |
0 |
7 |
7 |
4 |
12 |
12 |
9 |
16 |
16 |
Mode |
2 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |