Artificial intelligence applied to the valorization of parking control data from Paris City Council
The Paris City Council, thanks to a collaboration with Artelys, now benefits from a solution to further exploit the data collected by its parking control agents and vehicles. The objective is threefold: estimate the number of parking spaces actually occupied on a neighborhood-by-neighborhood basis, measure the frequency with which enforcement officers pass through neighborhoods and compare it to the contractual one, and update the city’s parking spaces mapping.
Parking enforcement in Paris
In order to control parking in Paris, officers on foot circulate through different neighborhoods to check that parked vehicles are in compliance with the applicable parking regimen. The introduction of parking receipts linked to vehicle license plates allows for more effective control by officers. In addition, vehicles equipped with automatic license plate readers (ALPR vehicles) also travel throughout the city and scan the license plates of all parked vehicles they encounter. During these control missions, the ALPR vehicles and the agents transmit the information of their GPS position at the time of the control. This data can then be used for other purposes than regularity control.
The valorization of the collected data
Beyond parking control, the Paris City Council wanted to leverage the GPS data collected by the agents/vehicles to study the actual use of the parking offer in the city (occupancy rate, zonal availability, etc.).
- Study of the actual occupation of parking spaces over time
- Reconstruction of the routes taken by enforcement officers and validation of contractual parking enforcement requirements by street/neighborhood
- Update the parking space reference map after finding discrepancies between the reference and the field data
However, the GPS data collected during enforcement operations is often noisy and is not usable as is (wrong location of the agent in an adjacent street, on the opposite sidewalk, in a building, etc.). Before any use, it is necessary to increase the reliability of collected GPS datasets in order to link the scan position with the location where the vehicle is actually parked.
To achieve this, Artelys has implemented an automatic method called map-matching to assign GPS readings to actual locations, taking into account the consistency of the paths followed by the control officers. Based on the computation of a scan emission probability (matching position and location) and a transition probability (moving from one location to another, taking into account, for example, the fact that an agent rarely crosses the road), Artelys has developed an algorithm that determines the most probable sequence of controlled parking locations (Viterbi algorithm).
The calculation of the different variables is subject to three parameters that have been visually calibrated separately for pedestrians and vehicles:
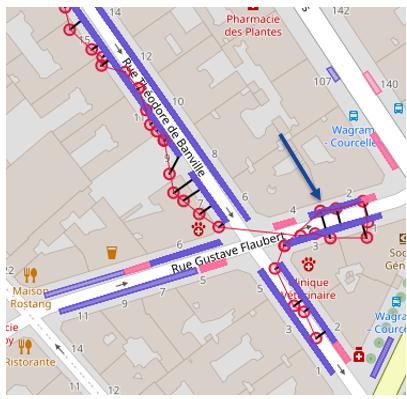

Sequence of the most probable estimated readings (black lines) compared to the real measurements (red dots) for one set of the algorithm’s parameters
To learn more about the city’s digital and smart city’s projects from the first deputy mayor’s point of view, see here (French only).
If you want to know more about our services, you can contact us or visit our dedicated web page.

Artelys Knitro 15.1: Solve your toughest pooling applications!
Artelys releases Knitro 15.1, bringing a new wave of performance upgrades and usability improvements to help you solve large-scale optimization problems faster than ever.

Artelys contributes to SNCF Voyageurs’ OPTIPLACE project
Artelys is contributing to the development and industrialisation of the OPTIPLACE project, which aims to improve passenger seating arrangements on Ouigo trains by developing the optimisation module used for seat assignment.

Swissgrid selects Artelys Crystal Super Grid
Artelys is pleased to announce that Swissgrid, the Swiss electricity Transmission System Operator (TSO), has selected Artelys Crystal Super Grid, our multi-energy simulation solution, to support their strategic planning and system analysis activities.

Artelys led the Assessment of Policy Options for Securing Inertia for the European Commission
The European Commission’s Directorate-General for Energy (DG ENER) selected Artelys (leader), Trinomics, and Tractebel ENGIE to study solutions for ensuring the future frequency stability of the European power system. The study report was published in August 2025 by...
subscribe to our newsletters
© ARTELYS • All rights reserved • Legal mentions