Knitro 10.x and Earlier Callable Library API¶
All functions offered by the Knitro callable library are listed here.
Creating and destroying solver objects¶
- KTR_new()¶
KTR_context_ptr KNITRO_API KTR_new (void);
This function must be called first. It returns a pointer to an object
(the Knitro “context pointer”) that is used in all other calls.
If you enable Knitro with the floating network license handler,
then this call also checks out a license and reserves it until
KTR_free() is called with the context pointer, or the program ends.
The contents of the context pointer should never be modified by a calling
program. Returns NULL on error.
- KTR_new_puts()¶
KTR_context_ptr KNITRO_API KTR_new_puts (KTR_puts * const fnPtr,
void * const userParams);
This function is similar to KTR_new(), but
also takes an argument that sets a “put string” callback
function to handle output generated by the Knitro solver, and a pointer
for passing user-defined data. See KTR_set_puts_callback()
for more information. Returns NULL on error.
Call KTR_new() or KTR_new_puts() first.
Either returns a pointer to the
solver object that is used in all other Knitro API calls.
A new Knitro license is acquired and held until KTR_free()
has been called, or until the calling program ends.
- KTR_free()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_free (KTR_context_ptr * kc_handle);
This function should be called last and will free the context pointer. The address of the context pointer is passed so that Knitro can set it to NULL after freeing all memory. This prevents the application from mistakenly calling Knitro functions after the context pointer has been freed. Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
Changing and reading solver parameters¶
Parameters cannot be set after Knitro begins solving; ie, after
the KTR_solve() function is called. They may be set
again after calling KTR_restart().
Note
The gradopt and hessopt user options must be
set before calling KTR_init_problem() or KTR_lsq_init_problem() or
KTR_mip_init_problem(), and cannnot be changed after
calling these functions.
All methods return 0 if OK, nonzero if there was an error.
In most cases, parameter values are not validated until
KTR_init_problem() or KTR_solve() is called.
- KTR_reset_params_to_defaults()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_reset_params_to_defaults (KTR_context_ptr kc);
Reset all parameters to default values.
- KTR_load_param_file()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_load_param_file
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const filename);
Set all parameters specified in the given file.
- KTR_save_param_file()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_save_param_file
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const filename);
Write all current parameter values to a file.
- KTR_set_int_param_by_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_int_param_by_name
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const name, const int value);
Set an integer valued parameter using its string name.
- KTR_set_char_param_by_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_char_param_by_name
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const name, const char * const value);
Set a character valued parameter using its string name.
- KTR_set_double_param_by_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_double_param_by_name
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const name, const double value);
Set a double valued parameter using its string name.
- KTR_set_param_by_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_param_by_name
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const name, const double value);
Set an integer or double valued parameter using its string name.
- KTR_set_int_param()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_int_param
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const int param_id, const int value);
Set an integer valued parameter using its integer identifier (see Knitro user options).
- KTR_set_char_param()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_char_param
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const int param_id, const char * const value);
Set a character valued parameter using its integer identifier (see Knitro user options).
- KTR_set_double_param()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_double_param
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const int param_id, const double value);
Set a double valued parameter using its integer identifier (see Knitro user options).
- KTR_get_int_param_by_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_int_param_by_name
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const name, int * const value);
Get an integer valued parameter using its string name.
- KTR_get_double_param_by_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_double_param_by_name
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const name, double * const value);
Get a double valued parameter using its string name.
- KTR_get_int_param()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_int_param
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const int param_id, int * const value);
Get an integer valued parameter using its integer identifier (see Knitro user options).
- KTR_get_double_param()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_double_param
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const int param_id, double * const value);
Get a double valued parameter using its integer identifier (see Knitro user options).
- KTR_get_param_name()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_param_name
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int param_id,
char * const param_name,
const size_t output_size);
Sets the string param_name to the name of parameter indexed by integer
identifier param_id (see Knitro user options) and returns 0. Returns an error if
param_id does not correspond to any parameter, or if the parameter output_size
(the size of char array param_name) is less than the size of the parameter’s
description.
- KTR_get_param_doc()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_param_doc
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int param_id,
char * const description,
const size_t output_size);
Sets the string description to the description of the parameter indexed by
integer identifier param_id (see Knitro user options) and its possible values and
returns 0. Returns an error if param_id does not correspond to any parameter, or
if the parameter output_size (the size of char array description) is less than
the size of the parameter’s description.
- KTR_get_param_type()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_param_type
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int param_id,
int * const param_type);
Sets the int * param_type to the type of the parameter indexed by
integer identifier param_id (see Knitro user options). Possible values are
KTR_PARAMTYPE_INT, KTR_PARAMTYPE_FLOAT, KTR_PARAMTYPE_STRING. Returns an error
if param_id does not correspond to any parameter.
- KTR_get_num_param_values()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_num_param_values
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int param_id,
int * const num_param_values);
Set the int * num_param_values to the number of possible parameter values for
the parameter indexed by integer identifier param_id and returns 0. If there is not
a finite number of possible values, num_param_values will be zero. Returns an
error if param_id does not correspond to any parameter.
- KTR_get_param_value_doc()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_param_value_doc
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int param_id,
const int value_id,
char * const param_value_string,
const size_t output_size);
Set string param_value_string to the description of the parameter value indexed by
[param_id][value_id]. Returns an error if param_id does not correspond to any
parameter, or if value_id is greater than the number of possible parameter
values, or if there are not a finite number of possible parameter values, or if
the parameter output_size (the size of char array param_value_string) is less
than the size of the parameter’s description.
- KTR_get_param_id()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_param_id
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const char * const name,
int * const param_id);
Gets the integer value corresponding to the parameter name input and copies it
into param_id input. Returns zero if successful and an error code otherwise.
- KTR_get_release()¶
void KNITRO_API KTR_get_release(const int length, char * const release);
Copy the Knitro release name into release. This variable must be
preallocated to have length elements, including the string termination
character. For compatibility with future releases, please allocate at
least 15 characters.
- KTR_load_tuner_file()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_load_tuner_file
(KTR_context_ptr kc, const char * const filename);
Similar to KTR_load_param_file() but specifically allows user to
specify a file of options (and option values) to explore for
the Knitro-Tuner (see The Knitro-Tuner).
- KTR_set_feastols()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_feastols
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double * const cFeasTols,
const double * const xFeasTols,
const double * const ccFeasTols);
Set an array of absolute feasibility tolerances (one for each
constraint and variable) to use for the termination tests.
The user options KTR_PARAM_FEASTOL / KTR_PARAM_FEASTOLABS
define a single tolerance that is applied equally to every constraint
and variable. This API function allows the user to specify
separate feasibility termination tolerances for each constraint
and variable. Values specified through this function will override
the value determined by KTR_PARAM_FEASTOL / KTR_PARAM_FEASTOLABS.
The tolerances should be positive values. If a non-positive value is
specified, that constraint or variable will use the standard tolerances
based on KTR_PARAM_FEASTOL / KTR_PARAM_FEASTOLABS.
Array cFeasTols has length m, array xFeasTols has length n, and
array ccFeasTols has length ncc, where ncc is the number of
complementarity constraints added through KTR_set_compcons().
The regular constraints are considered to be satisfied when:
c[i] - cUpBnds[i] <= cFeasTols[i] for all i=1..m, and
cLoBnds[i] - c[i] <= cFeasTols[i] for all i=1..m.
The variables are considered to be satisfied when:
x[i] - xUpBnds[i] <= xFeasTols[i] for all i=1..n, and
xLoBnds[i] - x[i] <= xFeasTols[i] for all i=1..n.
The complementarity constraints are considered to be satisfied when:
min(x1_i, x2_i) <= ccFeasTols[i] for all i=1..ncc,
where x1 and x2 are the arrays of complementary pairs.
If there are no regular (or complementarity) constraints set
cFeasTols=NULL (or ccFeasTols=NULL). If
cFeasTols/xFeasTols/ccFeasTols=NULL, then the standard tolerances will
be used. Knitro makes a local copy of all inputs, so the application
may free memory after the call.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and after any calls to KTR_set_compcons().
It must be called before calling KTR_solve() / KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_set_var_scalings()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_var_scalings
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double * const xScaleFactors,
const double * const xScaleCenters);
Set an array of variable scaling and centering values (one for each variable) to perform a linear scaling:
x[i] = xScaleFactors[i] * xScaled[i] + xScaleCenters[i]
for each variable. These scaling factors should try to
represent the “typical” values of the x variables so that the
scaled variables (xScaled) used internally by Knitro are close
to one. The values for xScaleFactors should be positive.
If a non-positive value is specified, that variable will not
be scaled.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and before calling KTR_solve() /
KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_set_con_scalings()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_con_scalings
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double * const cScaleFactors,
const double * const ccScaleFactors);
Set an array of constraint scaling values (one for each constraint) to perform a scaling:
cScaled[i] = cScaleFactors[i] * c[i]
for each constraint. These scaling factors should try to
represent the “typical” values of the inverse of the constraint
values c so that the scaled constraints (cScaled) used
internally by Knitro are close to one. Scaling factors for
standard constraints can be provided with cScaleFactors, while
scalings for complementarity constraints can be specified with
ccScaleFactors. The values for cScaleFactors / ccScaleFactors
should be positive. If a non-positive value is specified, that
constraint will use either the standard Knitro scaling
(KTR_SCALE_USER_INTERNAL), or no scaling (KTR_SCALE_USER_NONE).
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and before calling KTR_solve() /
KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_set_obj_scaling()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_obj_scaling
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double objScaleFactor);
Set a scaling value for the objective function:
objScaled = objScaleFactor * obj
This scaling factor should try to represent the “typical”
value of the inverse of the objective function value obj so
that the scaled objective (objScaled) used internally by
Knitro is close to one. The value for objScaleFactor
should be positive. If a non-positive value is specified, then
the objective will use either the standard Knitro scaling
(KTR_SCALE_USER_INTERNAL), or no scaling (KTR_SCALE_USER_NONE).
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and before calling KTR_solve() /
KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_set_names()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_names
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const char * const objName,
char * const varNames[],
char * const conNames[]);
Set names for model components passed in by the user/modeling
language so that Knitro can internally print out these names.
Knitro makes a local copy of all inputs, so the application may
free memory after the call.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and before calling
KTR_solve() / KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_set_linearvars()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_linearvars
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int * const linearVars);
This API function can be used to identify which variables only
appear linearly in the model (KTR_LINEARVAR_YES). This information
can be used by Knitro to perform more extensive preprocessing. If a
variable appears nonlinearly in any constraint or the objective (or
if the user does not know) then it should be marked as
KTR_LINEARVAR_NO. Knitro makes a local copy of all inputs, so the
application may free memory after the call.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and before calling
KTR_solve() / KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_set_honorbnds()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_honorbnds
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int * const honorBnds);
This API function can be used to identify which variables
should satisfy their variable bounds throughout the optimization
process (KTR_HONORBNDS_ALWAYS). The user option KTR_PARAM_HONORBNDS
can be used to set ALL variables to honor their bounds. This
routine takes precedence over the setting of KTR_PARAM_HONORBNDS
and is used to customize the settings for individual variables.
Knitro makes a local copy of all inputs, so the application may
free memory after the call.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_init_problem() /
KTR_lsq_init_problem() / KTR_mip_init_problem() and before calling KTR_solve() /
KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
Problem modification¶
- KTR_set_compcons()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_compcons (KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int numCompConstraints,
const int * const indexList1,
const int * const indexList2);
This function adds complementarity constraints to the problem.
It must be called after KTR_init_problem() and before
KTR_solve().
The two lists are of equal length, and contain matching pairs of
variable indices. Each pair defines a complementarity constraint
between the two variables. The function can only be called once to
set all the complementarity constraints in the model at one time.
Returns 0 if OK, or a negative value on error.
- KTR_chgvarbnds()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_chgvarbnds ( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double * const xLoBnds,
const double * const xUpBnds);
This function prepares Knitro to re-optimize the current problem after
modifying the variable bounds from a previous solve. The arrays xLoBnds
and xUpBnds have the same meaning as in KTR_init_problem()
and must be specified completely.
This function must be called after KTR_init_problem() and precedes a call
to KTR_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
Solving¶
Problem structure is passed to Knitro using KTR_init_problem().
Functions KTR_solve() and KTR_mip_solve() have the same
parameter list. Function KTR_solve() should be used for models where all
the variables are continuous, while KTR_mip_solve() should be used
for models with one or more binary or integer variables.
Applications must provide a means of evaluating the nonlinear objective, constraints,
first derivatives, and (optionally) second derivatives. (First
derivatives are also optional, but highly recommended.)
A single call to KTR_solve()
The typical calling sequence is:
KTR_new
KTR_set_xxx_callback (set all the necessary callbacks)
KTR_init_problem
KTR_set_xxx_param (set any number of parameters)
KTR_solve
KTR_free
Calling sequence if the same problem is to be solved again, with different parameters, a different start point, or a change to the bounds on the variables:
KTR_new
KTR_set_xxx_callback (set all the necessary callbacks)
KTR_init_problem
KTR_set_xxx_param (set any number of parameters)
KTR_solve
KTR_restart (if changing the initial point or some user parameters)
KTR_chgvarbnds (if modifying variable bounds)
KTR_set_xxx_param (set any number of parameters)
KTR_solve
KTR_free
Note
KTR_set_xxx_param() may also be called before
KTR_init_problem() (and gradopt and hessopt
must be set before KTR_init_problem() and remain constant).
API
- KTR_init_problem()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_init_problem (KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int n,
const int objGoal,
const int objType,
const double * const xLoBnds,
const double * const xUpBnds,
const int m,
const int * const cType,
const double * const cLoBnds,
const double * const cUpBnds,
const int nnzJ,
const int * const jacIndexVars,
const int * const jacIndexCons,
const int nnzH,
const int * const hessIndexRows,
const int * const hessIndexCols,
const double * const xInitial,
const double * const lambdaInitial);
These functions pass the optimization problem definition to Knitro,
where it is copied and stored internally until KTR_free() is called.
Once initialized, the problem may be solved any number of times with
different user options or initial points (see the KTR_restart() call
below). Array arguments passed to KTR_init_problem(), KTR_lsq_init_problem() or
KTR_mip_init_problem() are not
referenced again and may be freed or reused if desired.
In the description below, some programming macros are mentioned as alternatives
to fixed numeric constants; e.g., KTR_OBJGOAL_MINIMIZE. These macros
are defined in knitro.h.
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
Arguments:
kc is the Knitro context pointer. Do not modify its contents.
n is a scalar specifying the number of variables in the problem; i.e., the length of x.
objGoal is the optimization goal (see
KTR_OBJGOAL_MINIMIZE,KTR_OBJGOAL_MAXIMIZE).objType is a scalar that describes the type of objective function f(x) (see
KTR_OBJTYPE_GENERAL,KTR_OBJTYPE_LINEAR,KTR_OBJTYPE_QUADRATIC,KTR_OBJTYPE_CONSTANT).xLoBnds is an array of length n specifying the lower bounds on x. xLoBnds[i] must be set to the lower bound of the corresponding i-th variable
 . If the variable has no lower bound,
set xLoBnds[i] to be -
. If the variable has no lower bound,
set xLoBnds[i] to be -KTR_INFBOUND. For binary variables, set xLoBnds[i]=0.xUpBnds is an array of length n specifying the upper bounds on x. xUpBnds[i] must be set to the upper bound of the corresponding i-th variable. If the variable has no upper bound, set xUpBnds[i] to be
KTR_INFBOUND. For binary variables, set xUpBnds[i]=1.
Note
If xLoBnds or xUpBnds are NULL, then Knitro assumes all variables are unbounded in that direction.
m is a scalar specifying the number of constraints c(x).
cType is an array of length m that describes the types of the constraint functions c(x) (see
KTR_CONTYPE_GENERAL,KTR_CONTYPE_LINEAR,KTR_CONTYPE_QUADRATIC).cLoBnds is an array of length m specifying the lower bounds on the constraints c(x) . cLoBnds[i] must be set to the lower bound of the corresponding i-th constraint. If the constraint has no lower bound, set cLoBnds[i] to be -
KTR_INFBOUND. If the constraint is an equality, then cLoBnds[i] should equal cUpBnds[i].cUpBnds is an array of length m specifying the upper bounds on the constraints c(x) . cUpBnds[i] must be set to the upper bound of the corresponding i-th constraint. If the constraint has no upper bound, set cUpBnds[i] to be
KTR_INFBOUND. If the constraint is an equality, then cLoBnds[i] should equal cUpBnds[i].nnzJ is a scalar specifying the number of nonzero elements in the sparse constraint Jacobian.
jacIndexVars is an array of length nnzJ specifying the variable indices of the constraint Jacobian nonzeros. If jacIndexVars[i]=j, then jac[i] refers to the j-th variable, where jac is the array of constraint Jacobian nonzero elements passed in the call to
KTR_solve().jacIndexCons[i] and jacIndexVars[i] determine the row numbers and the column numbers, respectively, of the nonzero constraint Jacobian element jac[i].
Note
C array numbering starts with index 0. Therefore, the
j-th variable  maps to array element x[j],
and
maps to array element x[j],
and 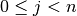 .
.
jacIndexCons is an array of length nnzJ specifying the constraint indices of the constraint Jacobian nonzeros. If jacIndexCons[i]=k, then jac[i] refers to the k-th constraint, where jac is the array of constraint Jacobian nonzero elements passed in the call to
KTR_solve().jacIndexCons[i] and jacIndexVars[i] determine the row numbers and the column numbers, respectively, of the nonzero constraint Jacobian element jac[i].
Note
C array numbering starts with index 0. Therefore, the
k-th constraint 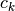 maps to array element c[k],
and
maps to array element c[k],
and 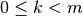 .
.
nnzH is a scalar specifying the number of nonzero elements in the sparse Hessian of the Lagrangian. Only nonzeros in the upper triangle (including diagonal nonzeros) should be counted.
Note
If user option hessopt is not set
to KTR_HESSOPT_EXACT, then Hessian nonzeros will not
be used.
In this case, set nnzH=0, and pass NULL pointers for
hessIndexRows and hessIndexCols.
hessIndexRows is an array of length nnzH specifying the row number indices of the Hessian nonzeros.
hessIndexRows[i] and hessIndexCols[i] determine the row numbers and the column numbers, respectively, of the nonzero Hessian element hess[i], where hess is the array of Hessian elements passed in the call
KTR_solve().
Note
Row numbers are in the range 0 , … , n - 1.
hessIndexCols is an array of length nnzH specifying the column number indices of the Hessian nonzeros.
hessIndexRows[i] and hessIndexCols[i] determine the row numbers and the column numbers, respectively, of the nonzero Hessian element hess[i], where hess is the array of Hessian elements passed in the call to
KTR_solve().
Note
Column numbers are in the range 0 , … , n - 1.
xInitial is an array of length n containing an initial guess of the solution vector x. If the application prefers to let Knitro make an initial guess, then pass a NULL pointer for xInitial.
lambdaInitial is an array of length m+n containing an initial guess of the Lagrange multipliers for the constraints c(x) and bounds on the variables x. The first m components of lambdaInitial are multipliers corresponding to the constraints specified in c(x), while the last n components are multipliers corresponding to the bounds on x. If the application prefers to let Knitro make an initial guess, then pass a NULL pointer for lambdaInitial.
- KTR_solve()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_solve ( KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const x,
double * const lambda,
const int evalStatus,
double * const obj,
const double * const c,
double * const objGrad,
double * const jac,
const double * const hess,
double * const hessVector,
void * const userParams);
Arguments:
kc is the Knitro context pointer. Do not modify its contents.
x is an array of length n output by Knitro. If
KTR_solve()returnsKTR_RC_OPTIMAL_OR_SATISFACTORY, then x contains the solution.Reverse communications mode (deprecated): upon return, x contains the value of unknowns at which Knitro needs more problem information. For continuous problems, if user option
newpointis set toKTR_NEWPOINT_USERandKTR_solve()returnsKTR_RC_NEWPOINT, then x contains a newly accepted iterate, but not the final solution.lambda is an array of length m+n output by Knitro. If
KTR_solve()returns zero, then lambda contains the multiplier values at the solution. The first m components of lambda are multipliers corresponding to the constraints specified in c(x), while the last n components are multipliers corresponding to the bounds on x.Reverse communications mode (deprecated): upon return, lambda contains the value of multipliers at which Knitro needs more problem information.
evalStatus is a scalar input to Knitro used only in reverse communications mode (deprecated). A value of zero means the application successfully computed the problem information requested by Knitro at x and lambda. A nonzero value means the application failed to compute problem information (e.g., if a function is undefined at the requested value x). Set to 0 for callback mode.
obj is a scalar holding the value of f(x) at the current x. If
KTR_solve()returnsKTR_RC_OPTIMAL_OR_SATISFACTORY, then obj contains the value of the objective function f(x) at the solution.c is an array of length m used only in reverse communications mode (deprecated). Set to NULL for callback mode.
objGrad is an array of length n used only in reverse communications mode (deprecated). Set to NULL for callback mode.
jac is an array of length nnzJ used only in reverse communications mode (deprecated). Set to NULL for callback mode.
hess is an array of length nnzH used only in reverse communications mode (deprecated), and only if option
hessoptis set toKTR_HESSOPT_EXACT. Set to NULL for callback mode.hessVector is an array of length n used only in reverse communications mode (deprecated), and only if option
hessoptis set toKTR_HESSOPT_PRODUCT. Set to NULL for callback mode.userParams is a pointer to a structure used in callback functions. The pointer is provided so the application can pass additional parameters needed for its callback routines. If the application needs no additional parameters, then pass a NULL pointer.
The return value of KTR_solve() and KTR_mip_solve()
specifies the final exit code from the optimization process.
A detailed description of the possible return values is given
in Return codes.
- KTR_restart()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_restart (KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double * const xInitial,
const double * const lambdaInitial);
This function can be called to start another
KTR_solve()
sequence after making small modifications.
The problem structure cannot be changed
(e.g., KTR_init_problem()
cannot be called between KTR_solve()
and KTR_restart()). However, user options
(with the exception of gradopt and hessopt)
can be modified, and a new initial value can be passed with
KTR_restart().
Knitro parameter values are not changed by this call.
The sample program examples/C/restartExample.c uses
KTR_restart() to solve the same problem from the same start point,
but each time changing the interior point bar_murule option to
a different value.
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
Note
If output to a file is enabled, this will erase the current file.
- KTR_lsq_init_problem()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_lsq_init_problem(KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int n,
const double * const xLoBnds,
const double * const xUpBnds,
const int m,
const int * const rType,
const int nnzJ,
const int * const jacIndexVars,
const int * const jacIndexRes,
const double * const xInitial,
const double * const lambdaInitial);
KTR_lsq_init_problem() is used to initialize a nonlinear
least squares problem.
This function only varies from KTR_init_problem() by the
use of arguments specific to least squares problems, namely:
m is the number of residuals
rType is an array of length m that describes the types of the residuals (
KTR_RESTYPE_GENERALorKTR_RESTYPE_LINEAR)
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_mip_init_problem()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_mip_init_problem( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int n,
const int objGoal,
const int objType,
const int objFnType,
const int * const xType,
const double * const xLoBnds,
const double * const xUpBnds,
const int m,
const int * const cType,
const int * const cFnType,
const double * const cLoBnds,
const double * const cUpBnds,
const int nnzJ,
const int * const jacIndexVars,
const int * const jacIndexCons,
const int nnzH,
const int * const hessIndexRows,
const int * const hessIndexCols,
const double * const xInitial,
const double * const lambdaInitial);
See KTR_init_problem() above. The only difference is
the addition of the following arguments.
objFnType is a scalar that describes the convexity status of the objective function f(x) (MIP only; see
KTR_FNTYPE_UNCERTAIN,KTR_FNTYPE_CONVEX,KTR_FNTYPE_NONCONVEX).xType is an array of length n that describes the types of variables x (MIP only; see
KTR_VARTYPE_CONTINUOUS,KTR_VARTYPE_INTEGER,KTR_VARTYPE_BINARY).cFnType is an array of length m that describes the convexity status of the constraint functions c(x) (MIP only; see
KTR_FNTYPE_UNCERTAIN,KTR_FNTYPE_CONVEX,KTR_FNTYPE_NONCONVEX).
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_mip_set_branching_priorities()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_mip_set_branching_priorities(KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int * const xPriorities);
This function can be used to set the branching priorities for integer variables
when using the MIP features in Knitro. Priorities must be positive numbers
(variables with non-positive values are ignored). Variables with higher priority
values will be considered for branching before variables with lower priority values.
When priorities for a subset of variables are equal, the branching rule is
applied as a tiebreaker. Array xPriorities has length n, and values for
continuous variables are ignored. Knitro makes a local copy of all inputs,
so the application may free memory after the call.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_mip_init_problem()
and before calling KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_mip_set_intvar_strategy()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_mip_set_intvar_strategy
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int xIndex,
const int xStrategy);
Set strategies for dealing with individual integer variables. Possible strategy values include:
KTR_MIP_INTVAR_STRATEGY_NONE 0
KTR_MIP_INTVAR_STRATEGY_RELAX 1
KTR_MIP_INTVAR_STRATEGY_MPEC 2
The parameter xIndex should be an index value corresponding to an integer variable
(nothing is done if the index value corresponds to a continuous variable),
and xStrategy should correspond to one of the strategy values listed above.
The default strategy is KTR_MIP_INTVAR_STRATEGY_NONE, and the strategy
KTR_MIP_INTVAR_STRATEGY_MPEC can only be applied to binary variables.
This routine must be called after calling KTR_mip_init_problem() and
before calling KTR_mip_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
- KTR_mip_solve()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_mip_solve( KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const x,
double * const lambda,
const int evalStatus,
double * const obj,
double * const c,
double * const objGrad,
double * const jac,
double * const hess,
double * const hessVector,
void * const userParams);
Call Knitro to solve the MIP problem, similar to KTR_solve().
Returns one of the status codes “KTR_RC_*” (see Return codes).
- KTR_set_findiff_relstepsizes()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_findiff_relstepsizes
( KTR_context_ptr kc,
const double * const relStepSizes);
Set an array of relative stepsizes to use for the finite-difference gradient/Jacobian computations when using finite-difference first derivatives. Finite-difference step sizes “delta” in Knitro are computed as:
delta[i] = relStepSizes[i]*max(abs(x[i]),1);
The default relative step sizes for each component of x are sqrt(eps)
for forward finite differences, and eps^(1/3) for central finite
differences. Use this function to overwrite the default values.
Array relStepSizes has length n. Any zero values will use Knitro
default values, while non-zero values will overwrite default values.
If relStepSizes is set to NULL, then default Knitro values will be used.
Knitro makes a local copy of all inputs, so the application may free
memory after the call. This routine must be called after calling
KTR_init_problem() and before calling KTR_solve().
Returns 0 if OK, nonzero if error.
Callbacks¶
To solve a nonlinear optimization problem, Knitro needs
the application to supply information at various trial points.
Knitro specifies a trial point with a new vector of variable values x,
and sometimes a corresponding vector of Lagrange multipliers  .
This information needs to be provided by the application through callback
functions. The application provides C language function pointers
that Knitro may call to evaluate the functions, gradients, and Hessians
at the trial points.
.
This information needs to be provided by the application through callback
functions. The application provides C language function pointers
that Knitro may call to evaluate the functions, gradients, and Hessians
at the trial points.
For simplicity, the callback functions
KTR_set_func_callback
KTR_set_grad_callback
KTR_set_hess_callback
KTR_set_ms_process_callback
KTR_set_mip_node_callback
(described in detail below) all use the same
KTR_callback() function prototype defined here.
typedef int KTR_callback (const int evalRequestCode,
const int n,
const int m,
const int nnzJ,
const int nnzH,
const double * const x,
const double * const lambda,
double * const obj,
double * const c,
double * const objGrad,
double * const jac,
double * const hessian,
double * const hessVector,
void * userParams);
At a trial point, Knitro may ask the application to:
evaluate
 and
and  at x (
at x (KTR_RC_EVALFC).evaluate
 and
and 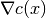 at x
(
at x
(KTR_RC_EVALGA).evaluate the Hessian matrix of the problem at x and
 normally (
normally (KTR_RC_EVALH), or without the objective component included (KTR_RC_EVALH_NO_F).evaluate the Hessian matrix times a vector v at x and
 normally (
normally (KTR_RC_EVALHV), or without the objective component included (KTR_RC_EVALHV_NO_F).
The constants KTR_RC_* are return codes defined in knitro.h
and listed in Return codes.
The argument lambda is not defined when requesting KTR_RC_EVALFC or KTR_RC_EVALGA.
Usually, applications define three callback functions, one for
KTR_RC_EVALFC, one for KTR_RC_EVALGA, and
one for KTR_RC_EVALH / KTR_RC_EVALHV.
It is possible to combine KTR_RC_EVALFC and
KTR_RC_EVALGA into a single function,
because x changes only for an KTR_RC_EVALFC request.
This is advantageous if the application evaluates functions and their
derivatives at the same time. Pass the same callback function
in KTR_set_func_callback() and KTR_set_grad_callback(),
have it populate obj, c, objGrad, and jac for an
KTR_RC_EVALFC request, and do nothing for an KTR_RC_EVALGA request.
Do not combine KTR_RC_EVALFC and KTR_RC_EVALGA if
hessopt = KTR_HESSOPT_PRODUCT_FINDIFF, because the finite difference
Hessian changes x and calls KTR_RC_EVALGA without calling
KTR_RC_EVALFC first.
It is not possible to combine KTR_RC_EVALH / KTR_RC_EVALHV
because lambda changes after the KTR_RC_EVALFC call.
The userParams argument is an arbitrary pointer passed from the Knitro
KTR_solve() call to the callback. It should be used to pass parameters
defined and controlled by the application, or left null if not used.
Knitro does not modify or dereference the userParams pointer.
Callbacks should return 0 if successful, a negative error code if not.
Possible unsuccessful (negative) error codes for the “func”, “grad”,
and “hess” callback functions include KTR_RC_CALLBACK_ERR
(for generic callback errors), and KTR_RC_EVAL_ERR
(for evaluation errors, e.g log(-1)).
In addition, for the “func”, “newpoint”, “ms_process” and “mip_node”
callbacks, the user may set the KTR_RC_USER_TERMINATION
return code to force Knitro
to terminate based on some user-defined condition.
- KTR_set_func_callback()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_func_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_callback * const fnPtr);
Set the callback function that evaluates obj and c at x.
It may also evaluate objGrad and jac if KTR_RC_EVALFC
and KTR_RC_EVALGA are combined into a single call.
Do not modify hessian or hessVector.
- KTR_set_grad_callback()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_grad_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_callback * const fnPtr);
Set the callback function that evaluates objGrad and jac at x.
It may do nothing if KTR_RC_EVALFC and KTR_RC_EVALGA
are combined into a single call.
Do not modify hessian or hessVector.
- KTR_set_hess_callback()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_hess_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_callback * const fnPtr);
Set the callback function that evaluates second derivatives at (x, lambda).
If evalRequestCode equals KTR_RC_EVALH, then the function must
return nonzeros in hessian. If it equals KTR_RC_EVALHV, then the
function multiplies second derivatives by hessVector and returns the
product in hessVector.
Do not modify obj, c, objGrad, or jac.
- KTR_set_newpt_callback()¶
typedef int KTR_newpt_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
const int n,
const int m,
const int nnzJ,
const double * const x,
const double * const lambda,
const double obj,
const double * const c,
const double * const objGrad,
const double * const jac,
void * userParams);
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_newpt_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_newpt_callback * const fnPtr);
Set the callback function that is invoked after Knitro computes a
new estimate of the solution point (i.e., after every major iteration).
The function should not modify any Knitro arguments.
Argument kc is the context pointer for the current problem being
solved inside Knitro (either the main single-solve problem, or a
subproblem when using multi-start, Tuner, etc.). This can then be
used to call Knitro functions to get problem information from
within the callback.
Arguments x and lambda contain the new point and values.
Arguments obj and c contain objective and constraint values at x,
and objGrad and jac contain the objective gradient and constraint
Jacobian at x.
The user may use KTR_RC_USER_TERMINATION as a return value to stop
the execution (for example, if the new point matches a criteria calculated in
KTR_newpt_callback). In this case the Knitro final return code will be
KTR_RC_USER_TERMINATION (“Knitro has been terminated by the user”).
- KTR_set_ms_process_callback()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_ms_process_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_callback * const fnPtr);
This callback function is for multi-start (MS) problems only. Set the callback function that is invoked after Knitro finishes processing a multi-start solve. The function should not modify any Knitro arguments. Arguments x and lambda contain the solution from the last solve. Arguments obj and c contain objective and constraint values at x. First and second derivative arguments are not currently defined and should not be examined.
- KTR_set_mip_node_callback()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_mip_node_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_callback * const fnPtr);
This callback function is for mixed integer (MIP) problems only. Set the callback function that is invoked after Knitro finishes processing a node on the branch-and-bound tree (i.e., after a relaxed subproblem solve in the branch-and-bound procedure). The function should not modify any Knitro arguments. Arguments x and lambda contain the solution from the node solve. Arguments obj and c contain objective and constraint values at x. First and second derivative arguments are not currently defined and should not be examined.
- KTR_set_ms_initpt_callback()¶
typedef int KTR_ms_initpt_callback (const int nSolveNumber,
const int n,
const int m,
const double * const xLoBnds,
const double * const xUpBnds,
double * const x,
double * const lambda,
void * const userParams);
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_ms_initpt_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_ms_initpt_callback * const fnPtr);
This callback allows applications to define a routine that specifies an initial point before each local solve in the multi-start procedure. On input, arguments x and lambda are the randomly generated initial points determined by Knitro, which can be overwritten by the user. The argument nSolveNumber is the number of the multi-start solve. Return 0 if successful, a negative error code if not. Use KTR_set_ms_initpt_callback to set this callback function.
- KTR_set_puts_callback()¶
typedef int KTR_puts (const char * const str,
void * const userParams);
int KNITRO_API KTR_set_puts_callback (KTR_context_ptr kc,
KTR_puts * const fnPtr);
Applications can set a “put string” callback function to handle output
generated by the Knitro solver. By default Knitro prints to stdout
or a file named knitro.log, as determined by KTR_PARAM_OUTMODE.
The KTR_puts() function takes a userParams argument which is a
pointer passed directly from KTR_solve(). Note that userParams will
be a NULL pointer until defined by an application call to KTR_new_puts()
or KTR_solve().
The KTR_puts() function should return the number of characters that were printed.
Reading solution properties¶
- KTR_get_number_FC_evals()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_number_FC_evals (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of function evaluations requested by KTR_solve().
A single request evaluates the objective and all constraint functions.
Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_number_GA_evals()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_number_GA_evals (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of gradient evaluations requested by KTR_solve().
A single request evaluates first derivatives of the objective and
all constraint functions.
Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_number_H_evals()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_number_H_evals (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of Hessian evaluations requested by KTR_solve().
A single request evaluates second derivatives of the objective and
all constraint functions.
Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_number_HV_evals()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_number_HV_evals (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of Hessian-vector products requested by KTR_solve().
A single request evaluates the product of the Hessian of the
Lagrangian with a vector submitted by Knitro.
Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_number_iters()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_number_iters (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of iterations made by KTR_solve().
Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_number_cg_iters()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_number_cg_iters (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of conjugate gradients (CG) iterations made by KTR_solve().
Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_abs_feas_error()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_abs_feas_error (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the absolute feasibility error at the solution. Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc. For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_rel_feas_error()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_rel_feas_error (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the relative feasibility error at the solution. Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc. For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_abs_opt_error()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_abs_opt_error (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the absolute optimality error at the solution. Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc. For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_rel_opt_error()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_rel_opt_error (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the relative optimality error at the solution. Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc. For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_solution()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_solution (const KTR_context_ptr kc,
int * const status,
double * const obj,
double * const x,
double * const lambda);
Return the solution status, objective, primal and dual variables. The status and objective value scalars are returned as pointers that need to be de-referenced to get their values. The arrays x and lambda must be allocated by the user. Returns 0 if call is successful; <0 if there is an error.
- KTR_get_constraint_values()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_constraint_values (const KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const c);
Return the values of the constraint vector in c. The array c must be allocated by the user. Returns 0 if call is successful; <0 if there is an error.
- KTR_get_objgrad_values()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_objgrad_values (const KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const objGrad);
Return the values of the objective gradient vector in objGrad. The array objGrad must be allocated by the user. It is a dense array of dimension “n” (where “n” is the number of variables in the problem). Returns 0 if call is successful; <0 if there is an error. For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_jacobian_values()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_jacobian_values (const KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const jac);
Return the values of the constraint Jacobian in jac.
The Jacobian values returned correspond to the non-zero sparse
Jacobian indices provided by the user in KTR_init_problem().
The array jac must be allocated by the user.
Returns 0 if call is successful; <0 if there is an error.
For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_hessian_values()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_hessian_values (const KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const hess);
Return the values of the Hessian (or possibly Hessian approximation) in hess. This routine is currently only valid if 1 of the 2 following cases holds:
KTR_HESSOPT_EXACT(presolver on or off), or;KTR_HESSOPT_BFGSorKTR_HESSOPT_SR1, but only with the Knitro presolver off (i.e.KTR_PRESOLVE_NONE).
In all other cases, either Knitro does not have an internal representation of the Hessian (or Hessian approximation), or the internal Hessian approximation corresponds only to the presolved problem form and may not be valid for the original problem form. In these cases hess is left unmodified, and the routine has return code 1.
Note that in case 2 above (KTR_HESSOPT_BFGS or KTR_HESSOPT_SR1)
the values returned in hess are the upper triangular values
of the dense quasi-Newton Hessian approximation stored row-wise.
There are ((n*n - n)/2 + n) such values (where “n” is the number
of variables in the problem. These values may be quite different
from the values of the exact Hessian.
When KTR_HESSOPT_EXACT (case 1 above) the Hessian values
returned correspond to the non-zero sparse Hessian indices
provided by the user in KTR_init_problem().
The array hess must be allocated by the user. Returns 0 if call is successful; 1 if hess was not set because Knitro does not have a valid Hessian for the model stored; <0 if there is an error. For continuous problems only.
- KTR_get_mip_num_nodes()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_num_nodes (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of nodes processed in the MIP solve. Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_num_solves()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_num_solves (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the number of continuous subproblems processed in the MIP solve. Returns a negative number if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_abs_gap()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_abs_gap (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the final absolute integrality gap in the MIP solve.
Returns KTR_INFBOUND if no incumbent (i.e., integer
feasible) point found.
Returns KTR_RC_BAD_KCPTR if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_rel_gap()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_rel_gap (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the final absolute integrality gap in the MIP solve.
Returns KTR_INFBOUND if no incumbent (i.e., integer
feasible) point found.
Returns KTR_RC_BAD_KCPTR if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_incumbent_obj()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_incumbent_obj (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the objective value of the MIP incumbent solution.
Returns KTR_INFBOUND if no incumbent (i.e., integer
feasible) point found.
Returns KTR_RC_BAD_KCPTR if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_relaxation_bnd()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_relaxation_bnd (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the value of the current MIP relaxation bound.
Returns KTR_RC_BAD_KCPTR if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_lastnode_obj()¶
double KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_lastnode_obj (const KTR_context_ptr kc);
Return the objective value of the most recently solved MIP
node subproblem.
Returns KTR_RC_BAD_KCPTR if there is a problem with kc.
- KTR_get_mip_incumbent_x()¶
int KNITRO_API KTR_get_mip_incumbent_x (const KTR_context_ptr kc,
double * const x);
Return the MIP incumbent solution in x if one exists. Returns 1 if incumbent solution exists and call is successful; 0 if no incumbent (i.e., integer feasible) exists and leaves x unmodified; <0 if there is an error.
Problem definition defines¶
-
type KTR_OBJGOAL¶
#define KTR_OBJGOAL_MINIMIZE 0
#define KTR_OBJGOAL_MAXIMIZE 1
Possible objective goals for the solver (objGoal in KTR_init_problem()).
-
type KTR_OBJTYPE¶
#define KTR_OBJTYPE_CONSTANT -1
#define KTR_OBJTYPE_GENERAL 0
#define KTR_OBJTYPE_LINEAR 1
#define KTR_OBJTYPE_QUADRATIC 2
Possible values for the objective type (objType in KTR_init_problem()).
-
type KTR_CONTYPE¶
#define KTR_CONTYPE_GENERAL 0
#define KTR_CONTYPE_LINEAR 1
#define KTR_CONTYPE_QUADRATIC 2
Possible values for the constraint type (cType in KTR_init_problem()).
-
type KTR_VARTYPE¶
#define KTR_VARTYPE_CONTINUOUS 0
#define KTR_VARTYPE_INTEGER 1
#define KTR_VARTYPE_BINARY 2
Possible values for the variable type (xType in KTR_mip_init_problem()).
-
type KTR_FNTYPE¶
#define KTR_FNTYPE_UNCERTAIN 0
#define KTR_FNTYPE_CONVEX 1
#define KTR_FNTYPE_NONCONVEX 2
Possible values for the objective and constraint functions (fnType
in KTR_mip_init_problem()).
-
type KTR_LINEARVAR¶
#define KTR_LINEARVAR_NO 0
#define KTR_LINEARVAR_YES 1
Possible values to indicate whether a variable appears only in linear
terms in the problem. Used by KTR_set_linearvars() function.