Analysis of the environmental impact of renewable energies
Agence France Trésor commissioned Artelys to study the environmental impact of subsidised renewable energies (RES). This study resulted in the 6th impact assessment report on green OATs.
A study assessing the environmental impact of subsidised renewable energy in France
The European Union and France have set themselves the goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 to combat climate change. Agence France Trésor has issued a number of sovereign green bonds, the Green OATs, to finance government budget expenditure that helps meet environmental challenges.
An assessment report is produced annually to analyse the environmental impact of the expenditure backed by green OATs. These studies are supervised by the Green OATs Evaluation Council, a panel of independent experts, with the support of French ministries of Ecological Transition and Territorial Cohesion and that of Economy, Finance, and Industrial and digital sovereignty.
A quantitative and qualitative study covering numerous impacts of renewables
The study provided qualitative and quantitative indicators of the main environmental impacts of public support spendings on renewable energy in France. The scope of the analyses includes both mainland France (and therefore the impacts on the European electricity system), and non-interconnected zones (NIZ, i.e. Corsica and most of the French overseas territories). The analysis covered both the historical impact (since 2000) and the future impact of renewables (based in particular on ADEME’s energy mix transition scenarios).
The RES whose impact has been studied are photovoltaic solar energy, onshore and offshore wind, small-scale hydroelectricity and biomethane for mainland France. In insular systems, the impact of all renewable energies has been analysed.
The main impacts (in particular greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, but also emissions of atmospheric pollutants, the use of raw materials and land use) have been quantified on the basis of modelling work carried out using Artelys Crystal Super Grid. This quantitative analysis is supplemented by qualitative elements from a literature review covering all the other environmental impacts of renewables (biodiversity, water and soil pollution, adaptation to climate change, etc.).
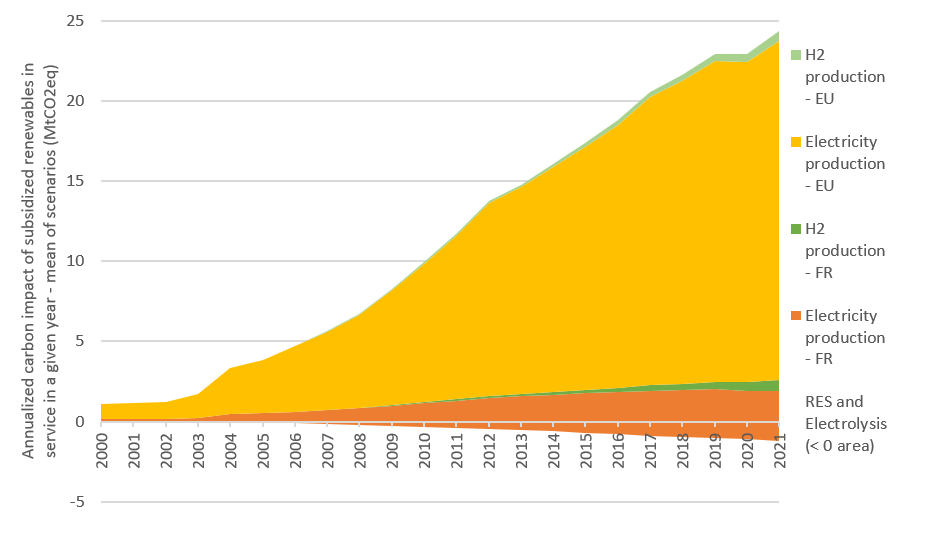
Renewables reduce Europe’s greenhouse gas emissions
The study shows that in recent years, the renewable electricity produced in mainland France has almost exclusively replaced thermal generation, the vast majority of it in neighbouring countries (between 75% and 86%).
In 2021, emissions of almost 28 MtCO2eq (million tonnes of CO2 equivalent) were avoided thanks to subsidised renewables, based on life-cycle analysis. This volume of avoided emissions is equivalent to the GHG emissions of the electricity mix in mainland France, which were around 27 MtCO2eq in 2021 on a life-cycle analysis basis (in the NIZ, emissions in 2021 were around 6 MtCO2eq).
The emissions avoided by subsidised renewables represent around 4.5% of France’s carbon footprint. On average, €180 in subsidies has been spent for each tonne of CO2eq avoided for renewable electricity generation in mainland France since 2014.
Green OATs evaluation council’s testimony
“The Evaluation Council welcomes the results of the renewable energies impact, as it provides a robust and transparent methodology on climate change mitigation, as well as a thorough literature review on other environmental objectives. The Council wishes to underscore the soundness of the evaluation process. […] The Council is confident that this fifth impact evaluation will be useful to other green bond issuers and contribute to the advancement of evaluation best practices on the market.”

Artelys provides support to the French energy regulatory authority (CRE) in assessing the adequate incentive levels to foster distribution networks performance for TURPE 7
Artelys has conducted a quantitative assessment to inform target levels proposals for TURPE 7, examining past performance and the impact of integrating smart meter data (Linky) into indicators measuring the quality of energy supply.

The MARI project is growing
In recent months, several new European TSOs have successfully joined MARI, the pan-European mFRR activation platform whose market clearing engine was developed by Artelys.

Knitro 14.2 solve your toughest nonlinear non-convex models in seconds
— We are pleased to announce that Artelys Knitro 14.0 is now available! This new version enables compagnies to solve complex non-linear optimization problems with unprecedented efficency and precision.

Artelys Powers the Launch of CorNet’s Common Grid Model (CGM) Service
Artelys has been selected to develop computation engine modules for the Common European Merging Function (EMF) used in the core of the CorNet program’s RCC Service Platform, enabling pan-European operational power grid coordination and security analysis.
subscribe to our newsletters
© ARTELYS • All rights reserved • Legal mentions